Uniphore, a Conversational Service Automation (CSA) provider in the contact centre space announced two new services – U-Trust portfolio and U-Assist Assurance solution to support call centre agents and operations. The U-Trust portfolio includes U-Trust Agent to authenticate agents using unique voiceprints and U-Trust Environment to protect sensitive data. The other offering, U-Assist Assurance integrates RPA along with conversations AI and machine learning to track and deliver commitments made by agents in real-time during the call, to align with customer expectations and manages fulfilment post calls.
Security and Automation Driving Investments in Contact Centres
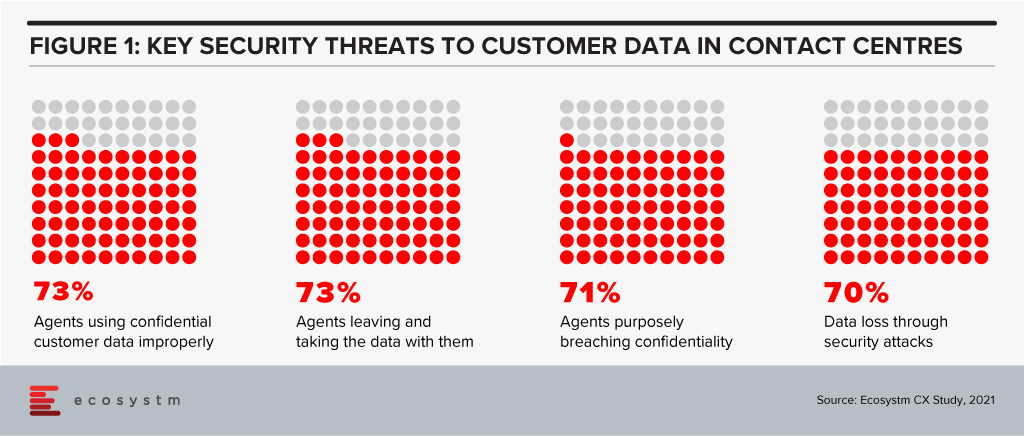
With agents working from both their home and the office, security is a bigger issue today than ever before. In 2021, contact centres will be under pressure to ensure all security requirements are met. For example: agents taking screenshots and photos of confidential information; family members having access to customer conversations and data; how agents access customer data. These are pertinent concerns that must be addressed and mechanisms around securing customer data will be of utmost priority. Any form of misuse of customer’s private information can have negative implications on the brand of a company.
With security efforts high on the agenda for contact centres, Uniphore is addressing critical issues faced by contact centres. The U-Trust portfolio aims to leverage biometrics for voice authentication and ensure safety in customer data handling. Uniphore is clearly listening to the market and have identified “problematic areas” that must be addressed. Ramping up security efforts especially with the work from anywhere model will be high on the agenda for every contact centre.
What is sometimes not talked about often enough in contact centres, is the integration to the back office. There are often follow ups required after the customer interaction – for example when a product needs to be ordered or serviced, the back office has an integral part to play in delivering customer experience. As contact centres realise that back office integration is critical there will be greater Investments in workplace collaboration, robotic process automation (RPA) and other automation technologies.
Uniphore is carving out a name in Conversational Service Automation. They are investing heavily in building an end-to-end automation solution for contact centres across Conversational AI, RPA and security capabilities. Cost pressures are rising and the need to automate will be greater than ever in 2021.
Uniphore focused on Growing AI/Automation Capabilities through Acquisitions & Partnerships
The last 12 months have been impressive for the company in terms of partnerships and acquisitions. For example, last October they partnered with NTT Data and will license NTT’s RPA technology for contact centres. The company issued a press release saying based on internal projections and the opportunities currently underway, this partnership could generate more than USD 50 million in revenue over the next five years. They also announced a partnership with Sitel. Through the partnership, Sitel will deploy Uniphore’s solution to its customer base. These are global partnerships that will help Uniphore scale its presence with outsourcers and in-house contact centres and help them with their customer experience transformation efforts.
Last month saw Uniphore collaborating with Idiap Research Institute, and joined World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Global Innovators Community. Uniphore and Idiap will work on the development of speech recognition algorithms, spoken language and signals for detection of emotions and semantic and pragmatic applications to generate insights and enhance customer experience. As a member of WEF, Uniphore will focus on co-designing and developing policy frameworks, standards for protecting children, creating an AI regulator for the 21st century and addressing concerns of facial recognition technology.
They also acquired Spanish video and emotion AI start-up Emotion Research Lab. Through this acquisition, Uniphore is looking to create advanced AI-based voice and video products for innovations in conversations service automation services and to expand its footprints in the European market. Moreover, combining voice and video AI with automation and machine learning will open up new use cases, including customer experience, sales, marketing, HR and other critical areas of business.
The comprehensive portfolio solution aims to strengthen overall contact centre interactions between customers and agents, optimise the connection through RPA and improve the contact centre security aspects through agent verification and data security.
2021 will see contact centres, dealing with new ways of working by employing various AI and Automation capabilities. See how you can empower your teams and agents to deliver exceptional customer experience in 2021. We outline the contact centre trends for 2021 in our Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Contact Centre Trends for 2021 report.

Last week saw 8×8 and Verint announce a partnership that aims to deliver integrated cloud-based contact centre services and workforce management applications to medium and large enterprises worldwide. The integrated solution will leverage 8×8’s expertise in unified communications as a service (UCaaS) and contact centre as a service (CCaaS) with Verint’s workforce management solutions.
The Need for Better Workforce Optimisation Solutions
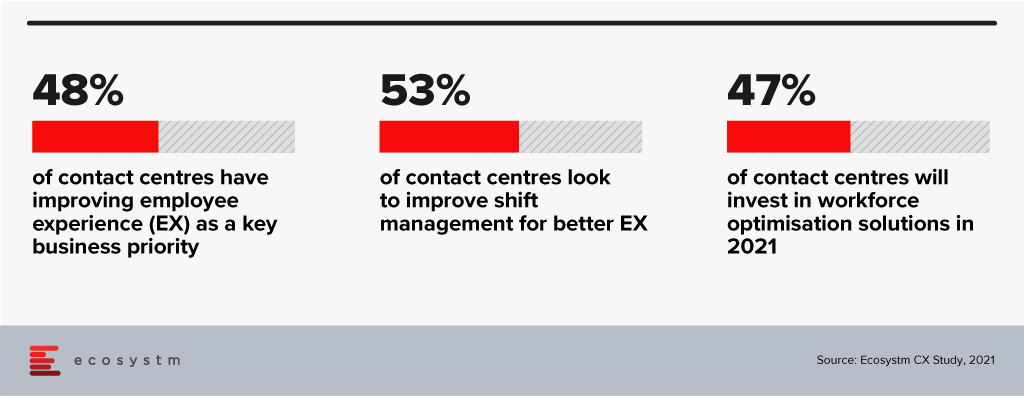
Talking about the need for integrated solutions such as this in the Contact Centre space, Ecosystm Principal Advisor for Enterprise Communications and Contact Centres, Audrey William, says, “With agents working from both their homes and the office, contact centres will be challenged with managing staffing requirements and scheduling. The key to delivering exceptional customer experience will be to have the right agent working on the right assignments, across the right channels. On top of that, contact centres have to manage shifts, flexible work hours and part-time agents working across multiple locations. This does not make workforce optmisation an easy task!”
“Driving better employee experience is a top priority for contact centres – and this will include investments in solutions that can alleviate stress for the agent. The industry continues to be challenged by agent attrition – the most common causes being work overload and stress. To provide a consistently good customer experience, contact centres have to listen better to their agents, understand their workloads better, show empathy, and monitor their emotional well-being A workforce optimisation solution will ensure that inbound enquiries are not impacted, and agents’ times are better utilised, through forecasting and better scheduling.”
Synergy between 8×8 and Verint
The single-vendor integrated communications and contact centre solution is anticipated to create better customer engagement and smoother remote operations by empowering employees and agents to plan, forecast and schedule contact centre activities and manage workloads through omnichannel routing.
William says, “8×8 has been establishing its presence in the unified communications and contact centre solutions space in Asia Pacific, particularly in small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Partnering with a market leader in workforce management such as Verint is a positive step. Verint’s strengths in gap analysis from historical data patterns and predicting will help 8×8’s customers to drive optimisation and accuracy in planning in the contact centre. This will have an impact on reducing overstaffing and overtime. Additionally, it will give agents greater control over their schedules and the flexibility to plan their shifts around their desired hours of work.”
“While 8×8 has its own workforce engagement solution, this partnership demonstrates how 8×8 is elevating its game and wants to offer its customers a more robust workforce management solution through Verint Monet and Verint Enterprise. This solution is also out of the box for 8×8’s customers without the need for professional services. That is a plus!”, says William.

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Audrey William
There is a lot of hope on AI and automation to create intellectual wealth, efficiency, and support for some level of process stability. After all, can’t we just ask Siri or Alexa and get answers so we can make a decision and carry on?
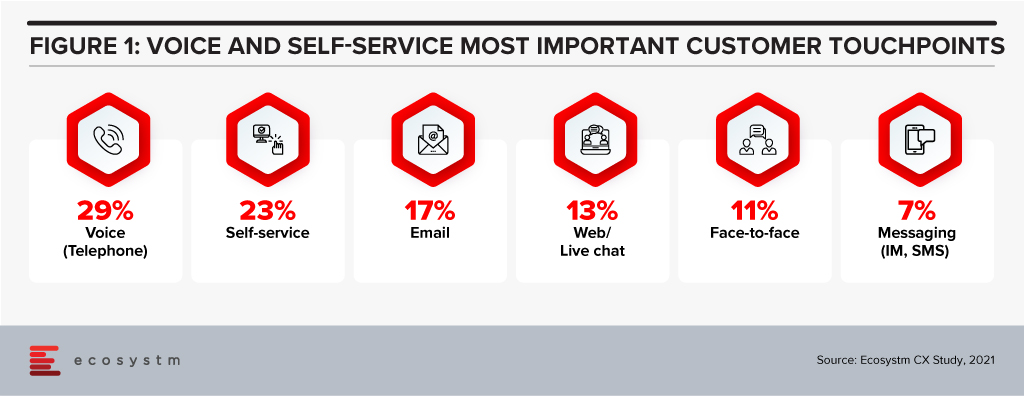
Automation has been touted as the wonder formula for workplace process optimisation. In reality it’s not the quick fix that many business leaders desire. But we keep raising the bar on expectations from automation. Investments in voice technologies, intelligent assistants, augmented reality and touchscreens are changing customer experience (Figure 1). Chatbots are ubiquitous, and everything has the potential to be personalised. But will they solve our problems?
100 percent automation is not effective
Let’s first consider using automation to replace face-to-face interactions. There was a time when people were raving about the check-in experience at some of the hotels in Japan where robots and automated systems would take care of the check-in, in-stay and check-out processes. Sounds simple and good? Till 2019, if you checked into the Henn-na Hotel in Japan, you would be served and taken care of by 243 robots. It was viewed by many as a template for what a fully automated hotel could look like in the future.
The hotel had an in-room voice assistant called Churi. It could cope with basic commands, such as turning the lights on and off, but it was found to be deficient when guests started asking questions about places to visit or other more sophisticated queries. It was not surprising that the hotel decided to retire their robots. In the end it created more work for the hotel staff on-site.
People love the personal touch when they are in a hotel; and talking to someone at the front desk, requesting assistance from hotel staff, or even just a short chat over breakfast are some of the small nuances of why the emotional connection matters. Many quarantine hotels today use robots for food delivery, but the hotel staff is still widely available for questions. That automation is good, but you need the human intervention. So, getting the balance right is key.
Empathy plays a big role in delivering great Customer Experience
Similarly, there was a time when many industry observers and technology providers said that a contact centre will be fully automated, reducing the number of agents. While technologies such as Conversational AI have come along where you can now automate common or repetitive questions and with higher accuracy levels, the human agent still plays a critical role in answering the more complex queries. When the customer has a complicated question or request, then they will WANT to speak to an agent.
When it reaches a point where the conversation with the chatbot starts getting complicated and the customers need more help there should be the option – within the app, website or any other channel – to escalate the call seamlessly to a human agent. Sometimes, a chat is where the good experience happens – the emotional side of the conversation, the laughter, the detailed explanation. This human touch cannot be replaced by machines. Disgruntled customers are happier when an agent shows empathy. Front line staff and human agents act as the face of a company’s brand. Complete automation will not allow the individual to understand the culture of the company. These can be attained through conversations.
Humans as supervisors for AI – The New Workplace
Empathy, intuitiveness, and creativity are all human elements in the intelligence equation. Workers in the future will need to make their niche in a fluid and unpredictable environment; and translating data into action in a non-replicable way is one of the values of human input. The essence of engineering is the capacity to design around human limitations. This requires an understanding of how humans behave and what they want. We call that empathy. It is the difference between the engineer who designs a product, and the engineer who delivers a solution. We don’t teach our computer scientists and engineering students a formula for empathy. But we do try to teach them respect for both the people and the process.
For efficiency, we turn to automation of processes, such as RPA. This is designed to try to eradicate human error and assist us in doing our job better, faster and at a lower cost by automating routine processes. If we design it right, humans take the role of monitoring or supervisory controlling, rather than active participation.
At present, AI is not seen as a replacement for our ingenuity and knowledge, but as a support tool. The value in AI is in understanding and translating human preferences. Humans-in-the-loop AI system building puts humans in the decision loop. They also shift pressure away from building “perfect” algorithms. Having humans involved in the ethical norms of the decision allows the backstop of overly orchestrated algorithms.
That being said, the astute use of AI can deepen insights into what truly makes us human and can humanise experiences by setting a better tone and a more trusted engagement. Using things like sentiment analysis can de-escalate customer service encounters to regain customer loyalty.
The next transformational activity for renovating work is to advance interactions with customers by interpreting what they are asking for and humanising the experience of acquiring it which may include actually dealing with a human contact centre agent – decisions that are supported at the edge by automation, but at the core by a human being.
Implications
Ecosystm research shows that process automation will be a key priority for technology investments in 2021 (Figure 2).
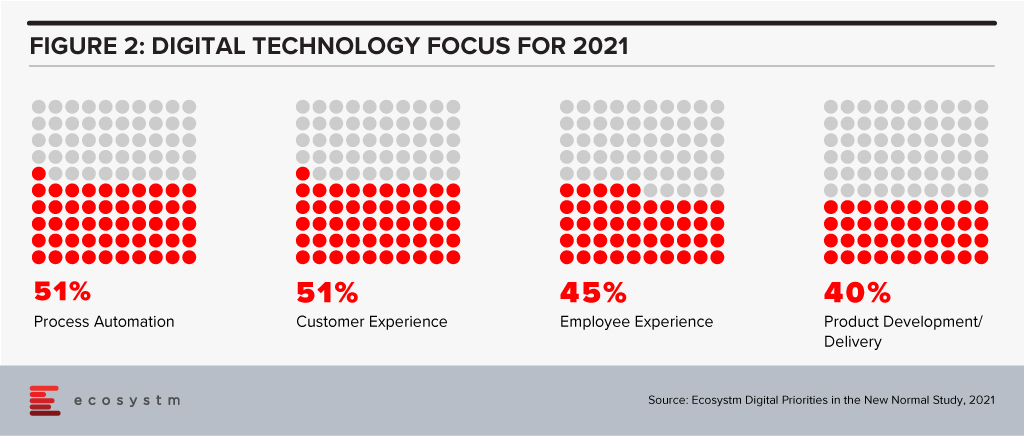
With AI and automation, a priority in 2021, it will be important to keep these considerations in mind:
- Making empathy and the human connection the core of customer experiences will bring success.
- Rigorous, outcome-based testing will be required when process automation solutions are being evaluated. In areas where there are unsatisfactory results, human interactions cannot – and should not – be replaced.
- It may be easy to achieve 90% automation for dealing with common, repetitive questions and processes. But there should always be room for human intervention in the event of an issue – and it should be immediate and not 24 hours later!
- Employees can drive greater value by working alongside the chatbot, robot or machine.
Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Customer Experience Trends for 2021
Download Ecosystm’s complimentary report detailing the top 5 customer experience trends for 2021 that your company should pay attention to along with tips on how to stay ahead of the curve.

Probe Group, a Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) solutions provider and Stellar – a customer experience (CX) management organisation announced a merger to create Australia’s largest and most diverse CX provider group. The partnership will combine the experience and expertise of both companies and will employ 12,600 people to provide outsourcing of business process services for customers across six countries. Probe Group is backed by Quadrant Private Equity and Five V Capital.
Probe Group has been expanding its business presence since being acquired by Five V Capital in early 2018. At the time, Probe acquired Salmat’s Contact business, a broad-based CX operation which helped Probe expand their presence in Australia, New Zealand and the Philippines. Looking out for further opportunities, in December last year Probe Group acquired Australia-based and Philippines-focused Beepo and quickly followed this with an acquisition in January this year of the Philippines outsourcing agency MicroSourcing, a counterpart to Beepo which greatly expanded Probe’s Philippines offering. These acquisitions helped Probe extend their service offering from CX into Shared Services and Knowledge Services.
This is a brilliant move as Stellar is one of the most successful contact centre outsourcing providers in Australia. With successive growth for 22 years and having a strong footprint in both the public and private sectors, the acquisition will give Probe Group entry into some large accounts. Additionally, Probe will gain a large pool of well-trained agents in Australia and other locations across the globe.
The merger comes at an interesting time when we are seeing several organisations re-evaluate their outsourcing strategy. There is also an active interest in enhancing CX through AI/automation. Both the Probe Group and Stellar understand the Australian market and consumer sentiments and the merger is expected to drive better customer outcomes in the Australia market.
Prior to COVID-19, Probe Group employed 8,500 agents. With this acquisition, they will have 12,600 agents and an expected turnover of USD 420 million. That is not only impressive but will help Probe offer a variety of services including both onshore and offshore, to take on their rivals.
Rise of Onshore Activity will see New Shifts in CX Delivery Models
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought about several changes to the outsourcing sector. The disruption caused by services in many key offshore markets led to organisations re-evaluating their contact centre outsourcing strategy and some have started moving contact centre jobs back to Australia. Westpac is the latest organisation to announce that they are moving 1,000 jobs back to Australia. They have stated that while they expect productivity benefits over time, there is clearly a cost to adding 1,000 roles – likely an uplift of around $45 million per annum in its costs by the end of 2021.
The cost element is bound to creep in over time and contact centres will ask outsourcing providers to help drive costs down. Options would include moving some services offshore, while the critical remain onshore. Striking that balance to manage costs will be important and so will be the ability to offer various options for customers. Additionally, we can expect to see an increased demand for self-service technologies. Many organisations are in the midst of re-evaluating the use of AI and automation technologies not only as a way to drive great CX but as a way to also reduce costs (Figure 1).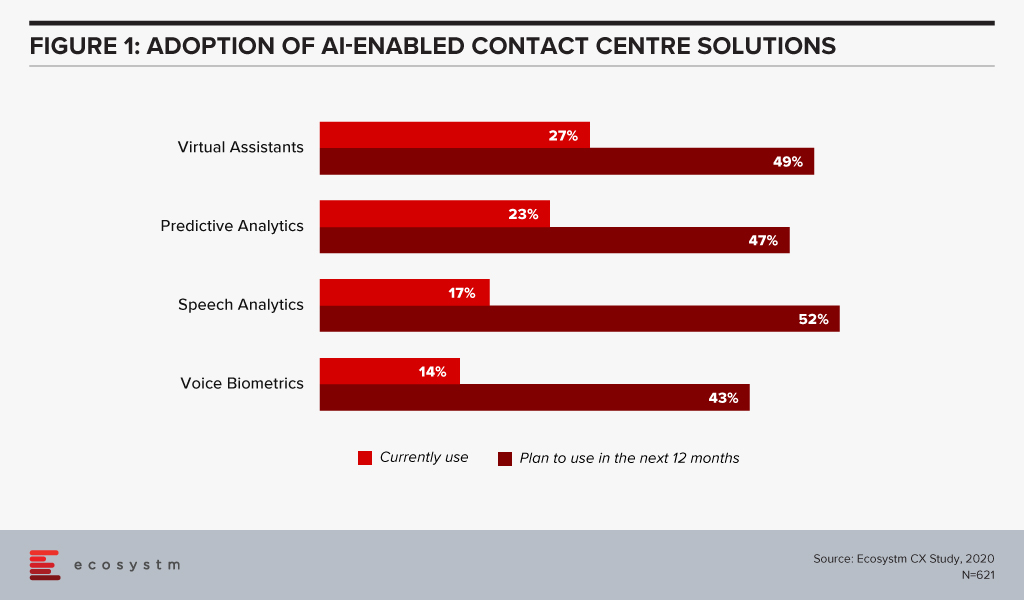
Contact centres are starting to realise that to modernise their contact centre, the ability to lead with machine learning and AI technologies are critical. It will drive the deployment of natural language understanding (NLU) and conversational AI, sentiment analysis, transcription capabilities – and ultimately provide intelligence about the call even prior to the call being fielded. However, it is worth noting that whilst automation is on the rise, the role of the agent is not going away anytime soon and will grow in importance. We will see the rise of the “super-agent’’ and the agent’s role will evolve over time and AI/automation will generate rich insights to help aid the agent and the contact centre team to better predict customer behaviour and patterns.
The Next Generation of Outsourcing Providers must Drive Innovation for their Customers
Companies today are not outsourcing just to save labour costs. While cost remains an important angle, it will not often be the main driver for outsourcing in the future. The next generation of outsourcing providers will have to build rich solution capabilities, customer journey maps and help customers understand how to align all channels. This involves working with many different technology providers to build the right capabilities for their client organisations. Organisations are keen to modernise their contact centre operations to achieve excellence in CX. Outsourcing providers must have the capability to deliver that innovation.
Ecosystm research finds that 63% of organisations that outsource their contact centre functions are challenged with finding the right partner that can drive innovations (Figure 2).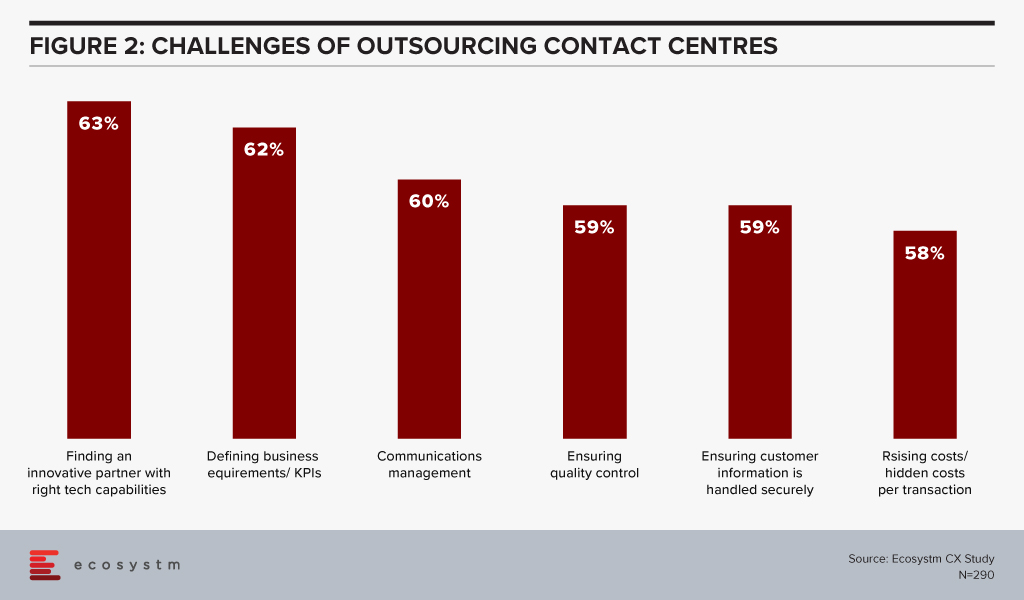
Contact centre outsourcing providers have a role to play in some of the following areas:
- The ability to adapt to change and take on risks together with the client
- Ensuring that all forms of security and governance measures are in place. This includes considering factors such as data security, data handling, and security features enabled across devices, applications, and the network. This is especially true for Government and Financial services contracts. Additionally, with some organisations preferring the work from a home model, there are security issues that must be addressed for the scenario.
- Helping the move from a traditional contact centre to a contact centre that delivers the highest levels of CX for its customers. Applying technologies such as AI and machine learning, NLU, biometrics, speech analytics, customer journey analytics and robotic process automation (RPA) will be key to modernisation.
- Being able to build a business continuity plan (BCP) for their customers in the event of another crisis.
Ecosystm Comment
Probe Group started off as a business specialising in outsourcing services in the credit and collections segment. Their customers in 2016 ranged from organisations across Financial Services, Utilities, and Federal and State Government. At that time, Probe employed about 300 people and their turnover was about USD 25 million. They did not rest on their laurels and realised that organic growth combined with strategic acquisitions would give them a foothold across various geographies and add new capabilities to their portfolio. With the rise in onshore activity, they will now be in a strong position to offer their customers various services and models of engagement to help drive CX excellence. The acquisition of Stellar will help Probe Group propel to greater heights and we see a new CX outsourcing giant being born.

This week, Vodafone New Zealand launched a contact centre solution known as Vodafone Connect that runs on AWS cloud infrastructure. The solution is designed for contact centres and customer service providers to reduce their operating cost and deliver an improved customer experience (CX).
The move comes as many businesses and governments are witnessing a spike in inbound contact centre volumes since the outbreak of the pandemic. The telecom company aims to help the contact centre industry through its on-demand contact centre suite of solutions that can be scaled up or down according to the organisations’ requirements. It can be combined with existing CRM platforms in a single dashboard for better access to data and resolution support.
Vodafone Connect is built on the AWS Connect cloud contact centre solution and uses data analytics and machine learning tools to automate customer interactions across multiple channels – email, messaging and social media – to support the contact centre agents with real-time information.
COVID-19 has accelerated the move to the cloud
The recent pandemic has seen many organisations make a leap almost overnight to cloud contact centre technologies. Many organisations that previously had concerns around data privacy, and securing customer data – and were thus hesitant about deploying cloud contact centre solutions – have moved to the cloud model. The cloud model helped get agents that were forced to work from home up and running in a short duration. The immediate urgency was primarily due to a massive spike in voice calls and non-voice activity such as emails. During the COVID-19 crisis, many organisations used Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections to their legacy on-premises phone system to enable the remote agents. However, there have been challenges reported by many organisations with that approach such as increases to IT budget, difficulty in scaling easily, and the requirement for more IT support that could have been avoided.
Ecosystm research finds that only 30% of organisations have fully migrated their cloud contact centre solutions on the cloud. 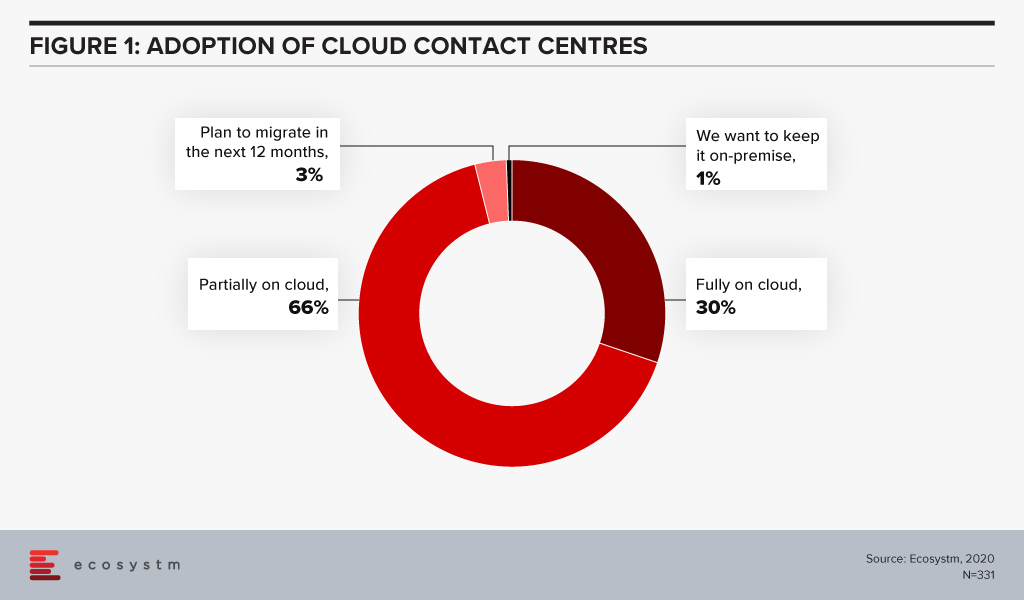
This indicates a market opportunity for vendors in the cloud contact centre space. The COVID-19 pandemic has definitely triggered a strong move towards the cloud model. It has become imperative for vendors and solutions providers to strengthen their cloud capabilities.
Driving an Omni-Channel Experience has become increasingly difficult
Ecosystm research also finds that organisations find siloed organisational data as one of the biggest challenges in driving consistent customer experience.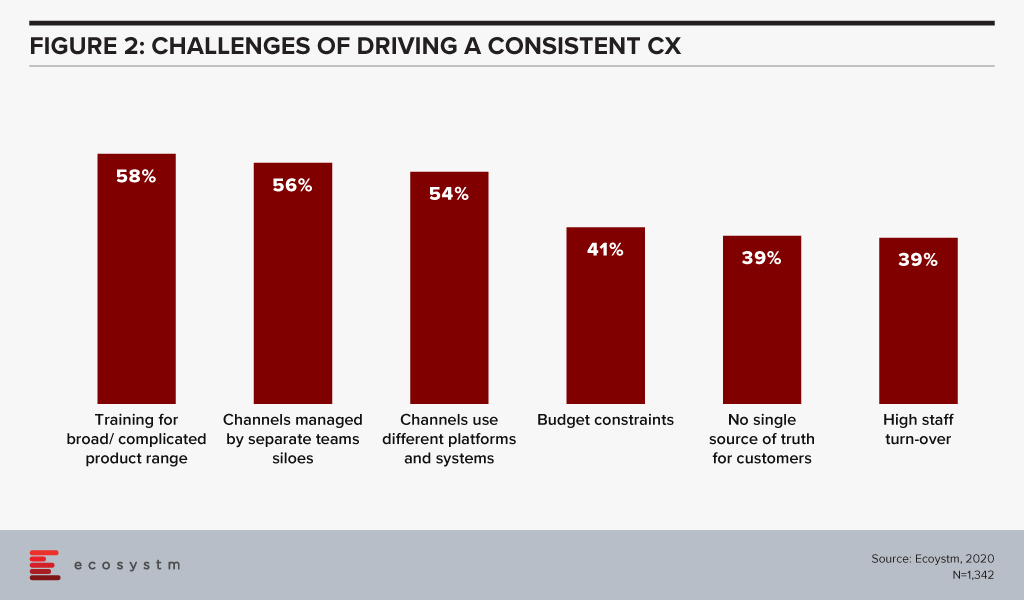
This has been further exacerbated by the high volume of interactions that organisations have been having with their customers, and the need to accommodate work-from-home policies for their customer care agents. At the same time, nearly 60% of organisations want to drive an omni-channel experience to improve CX. This provides a huge opportunity for contact centre vendors and partners to offer consulting services to help organisations bridge the gaps in achieving an omni-channel experience. For many organisations there has been a greater push to integrate CRM, the voice of the customer/surveys, customer journey analytics to the contact centre technologies and this is not an easy task as it involves different stakeholders with different sets of KPIs. Having a single platform that can manage this omni-channel experience will be a huge benefit for many organisations.
New Players in the Competitive Landscape
AWS is a relatively new player in the contact centre market, but it is starting to disrupt the existing players, with a global installed base. However, it is worth noting that Avaya, Cisco and Genesys have a higher installed base and they continue to win new deals. The move to the cloud is witnessing more service providers, telecom providers and other contact centre partners push more cloud-based solutions in the market. Apart from AWS, other important players include NICEinContact, 8×8, Talkdesk, Twillio, Five9, and UJet. The competitive battleground is heating up and there are a lot of options for customers to choose from. It will all come down to working with a vendor that can help them achieve their desired CX outcomes.
There are other important elements in CX that are growing in importance and these include conversational AI, voice biometrics, knowledge management systems, machine learning and CX management solutions. Contact centre solution providers are having discussions around these areas with tech buyers. This will mean that we can expect deeper partnerships and acquisitions in the short to medium term. Security has also emerged as an important issue to be resolved, especially with agents working from home. This is from a compliance perspective and pertaining to how agents are viewing and handling customer data. These new trends indicate that customers will need to work with different vendors to solve the variety of issues they are facing.
The Vodafone Connect solution on AWS Connect is one of the many examples of how more partners of contact centre solutions are gearing up for the rapid move to the cloud. Globally, Vodafone also sells contact centre solutions from Cisco and Genesys. The next 3 years will see a great movement in the market and this will include vendors from North America that will set up operations to push their offerings across Europe and the Asia Pacific.
Click below to access insights from the Ecosystm Contact Centre Study on visibility into organisations’ priorities when running a Contact Centre (both in-house and outsourced models) and the technologies implemented and being evaluated
Contact centres across industries are being challenged by the current crisis because of the high volume of inbound interactions – through voice and non-voice channels. This has been further compounded by the need to move most of their customer care agents to their homes, especially in countries that have implemented strict social distancing and lockdown measures. This is particularly challenging for the public sector because they are having to respond to an influx of citizen queries regarding COVID-19 specifically (including test centres and availability) and other related areas (information on trade and travel, economic stimulus and so on).
Public Sector Focus on Citizen Experience
Ecosystm research reveals that public sector organisations are hugely focused on citizen experience (Figure 1). But other priorities include employee experience and innovation in their service provision.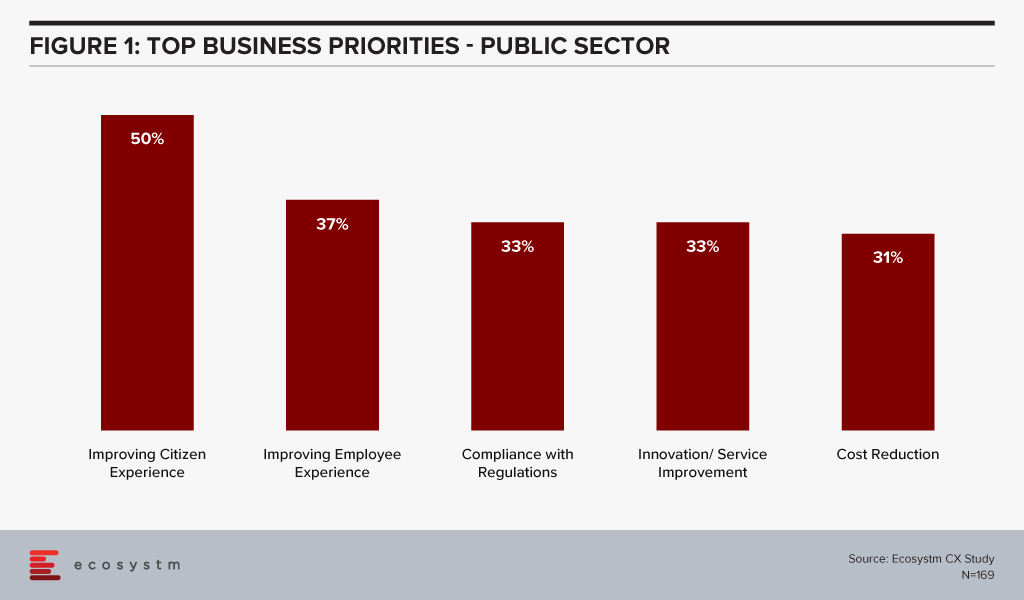
Being able to provide better and innovative service to citizens in a compliant manner is key for every public sector organisation. This has led to governments driving the uptake of cloud solutions, such as the New Zealand Government’s directive to public sector organisations that public cloud services are preferred over traditional IT systems, in order to enhance citizen experiences, streamline operations and create new delivery models. In 2018, the Singapore Government had announced the intention to use commercial cloud services in the public sector. This was fueled as much by the need to overhaul ageing infrastructure, as it was to provide exceptional citizen experience.
Public Sector Adopting Cloud Contact Centres
While the private sector is often quicker in their adoption of digital technologies for better customer experience (CX), the adoption in the public sector can be challenging due to various concerns such as legacy systems, privacy, national security, inter-departmental dependency and more. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “Most cloud contact centre solution providers today have the highest level of security wraps and certifications including country-level certifications. However, verticals such as Government, have remained concerned about security. This has not allowed them to innovate as fast as some of the other sectors on leveraging some of the best-in-class customer experience technologies.”
In the US, MAXIMUS, a government services provider company and Genesys recently announced a partnership to set up the MAXIMUS Genesys Engagement Platform, an integrated, cloud-based omnichannel contact centre solution. This was driven by the government requirement for public sector organisations to provide seamless customer experiences similar to those offered in the private sector. The platform is certified by the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP). FedRAMP promotes the adoption of secure cloud services across the US Federal Government, in partnership with federal agencies, cloud service providers and 3rd party assessment organisations and provides the standards for security and risk assessment.
This is in line with what we see in the Ecosystm data. Government agencies that use contact centres are increasingly evaluating cloud options, with 17% saying that they operate fully on the cloud (Figure 2). While this may be difficult for all public sector organisations, with mandates around data location and security, a majority are partially on the cloud.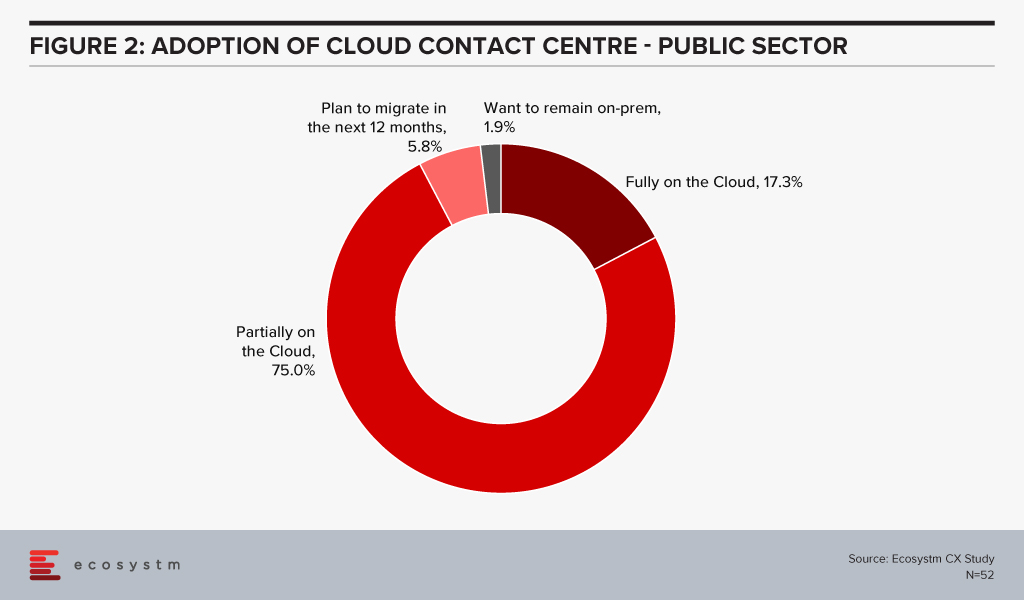
There are several benefits to using the cloud model including the ability to make changes and scale up/down without much customisation or professional services (which can come in handy for a quick re-alignment of the workforce) and manage seasonal spikes. Additionally, cloud solutions allow almost instantaneous access to new features and easy testing of proofs of concept. Public sector organisations are fast realising the value of cloud contact centres.
William sees the FedRAMP certification having immense potential. “FedRamp provides a secured environment for any service that is rolled out as this involves multiple levels of security. Citizens expect a more personalised service through chat, Twitter, mobile, social messaging channels like WhatsApp and many more. However, they also want to feel safe when providing personal information and want to know that the platform that holds their data is secure. When they know that security is at the highest level, they will be more open to providing personal data.”
Managing an Omnichannel Experience
Over half of public sector organisations in the Ecosystm CX study mentioned that they are driving an omnichannel experience for their customers. This has become especially relevant today, as organisations have the need to reduce the call volumes for their contact centres – through non-voice services and customer self-service. The MAXIMUS Genesys Engagement Platform will leverage Genesys Engage, which provides integrated features and functionalities across multiple channels through a single voice and digital user interface. Solutions such as these provide the ability to integrate calls, emails, chats, messages and social comments into one connected platform.
William says, “The cloud platform can help with the highest level of efficiency, scale and speed by integrating multiple channels on a single platform, for more connected customer experience. Government departments will look to leverage capabilities such as Conversational AI, in-app mobile messaging, SMS, email and voice calls within a multi secure environment. Citizens have high expectations from government departments – they expect fast, reliable and efficient service and automation. It would be difficult for governments to provide that level of service without leveraging cloud contact centre technology. That is the only way to move away from inefficient traditional architectures.”
Speaking about the adoption of cloud contact centres in the Asia Pacific region, William says, “Despite initiatives like Australia’s Digital Transformation Agency, the adoption has been relatively low in the public sector. But that has been changing fast with the COVID-19 situation forcing some government departments to move almost immediately to the cloud allowing easier changes to call workflows and other dynamic services that may have to be addressed on a daily basis.”

In 2018, DBS Bank came together with AI start-up impress.ai to implement Jim – Job Intelligence Maestro – a chatbot that helps the bank shortlist candidates for positions in their wealth planning team. This is primarily for screening for entry-level positions. Apart from process efficiency, the introduction of AI in the recruitment process is also aimed at eliminating bias and objectively finding the right candidate for the right job. The DBS chatbot uses cognitive and personality tests to assess candidates, as well as providing them with answers to the candidates’ frequently asked questions. The scores are then passed on to actual recruiters who continue with the rest of the recruitment process. DBS claims that they have curtailed the initial assessment time of each applicant by an average of 22 minutes.
While some organisations have started evaluating the use of AI in their HR function, it has not reached a mass-market yet. In the global Ecosystm AI study, we find that nearly 88% of global organisations do not involve HR in their AI projects. However, the use cases of AI in HR are many and the function should be an active stakeholder in AI investments in customer-focused industries.
Telstra employs AI to vet Applicants
Last month, Australia’s biggest telecommunications provider Telstra announced its plans to hire 1,000 temporary contact centre staff in Australia to meet the surge in demand amidst the global pandemic. In response to the openings, Telstra received overwhelming 19,000 applications to go through and filter, with limited workforce. To make the recruitment process more efficient, the company has been using AI to filter the applications – and has been able to make initial offers two weeks from the screening. The AI software takes the candidates’ inputs and processes them to find the right match for the required skills. The candidates are also presented with cognitive games to measure their assessment scores.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William speaks about the pressure on companies such as Telstra to hire faster for their contact centres. “Several organisations are needing to replace agents in their offshore locations and hire agents onshore. Since this is crucial to the customer experience they deliver, speed is of essence.” However, William warns that the job does not stop with recruiting the right number of agents. “HR teams will need to follow through with a number of processes including setting up home-based employees, training them adequately for the high volume of voice and non-voice interactions and compliance and so on.”
The Future of AI in HR
William sees more companies adopting AI in their HR practices in the Workplace of the Future – and the role of AI will not be restricted to recruitment alone. “A satisfied employee will go the extra mile to deliver better customer experience and it is important to keep evaluating how satisfied your employees are. AI-driven sentiment analysis will replace employee surveys which can be subjective in nature. This will include assessing the spoken words and the emotions of an individual which cannot be captured in a survey.”
In the future, William sees an intelligent conversational AI platform as an HR feedback and engagement platform for staff to engage on what they would like to see, what they are unhappy about, their workplace issues, what they consider their successes and so on. This will be actionable intelligence for HR teams. “But for a conversational AI platform to work well and to encourage users within the organisation to use it, it must be designed well. While it has to be engaging to ensure employee uptake, the design does not stop at user experience. It must include a careful evaluation of the various data sets that should be assessed and how the AI can get easy access to that data.”
AI and Ethics
With the increased use of AI, the elephant in the room is always ethical considerations. While the future may see HR practices using conversational AI platforms, how ethical is it to evaluate your employees constantly and what will be the impact on them? How will the organisation use that data? Will it end up giving employers the right reasons to reduce manpower at will? These and allied issues are areas where stricter government mandates are required.
Going back to AI-assisted recruitment, William warns, “Bias must be assessed from all angles – race, education, gender, voice, accents. Whilst many platforms claim that their solution removes bias, the most important part of getting this right is to make sure that the input data is right from the start. The outcomes desired from the process must be tested – and tested in many different ways – before the organisation can start using AI to eliminate bias. There is also the added angle of the ethical use of the data.”
Agents are the most valuable assets in a contact centre. In the current environment, the biggest threat is agents getting infected, causing the closure of contact centres for weeks or possibly even longer. We are already seeing the impact of that with offices being shut, students not going to school and industry gatherings and events being put on hold or cancelled. So having a business continuity plan (BCP) is critical. The BCP should include ways to continue to engage with customers.
The contact centre manages live interactions. Every second there are voice calls coming in, emails received and self-service tools being accessed. It is important to have multiple backup plans – both from a people and a technology perspective – to keep operations running effectively, without calls being put on hold too long or with other channels going unanswered. Contact centres battle with these challenges every day and the situation will get far more serious with the ongoing changes we are witnessing.
Some important considerations include:
Having a backup plan allowing agents working from home
More contact centres today are gearing up to agents working from home, but the process is not an easy one. To begin with, the initial set up includes having the right connectivity and a reliable network. Ensuring that the agent has the right working environment with minimal distraction is crucial. A good quality headset can help. A poor-quality headset will only create unwanted problems with understanding customer issues and handling them. Other concerns include security, tracking how data is being handled, agent under-performance and safety of the agents from an operational and health perspective. Measures such as listening to call recordings and storing them centrally are growing in importance. Multi-factor authentication and analytics using agent logs are some measures that can be put in place.
While there are lots of tools and technologies to monitor and check on agents, the key for home-based agents will be trust. Some outsourced contact centre providers that have been using home-based agents for years have stated that having trust and not micromanaging the agents, is essential for the model to work. Some contact centres have also deployed a BYOD policy for home-based agents assuming the right security, device management, application management and authentication measures are in place.
Organisations should also consider actively recruiting additional home-based agents. These agents could be retirees, currently unemployed or people with mobility issues who prefer to work from home.
Given the difference in the working environment, the metrics used to measure agent performance needs to be modified to be more realistic and fair to both agents and organisations.
Employing home-based agents will drive employment amidst challenges in the economy. Ecosystm research finds that more than a third of organisations do not have provisions for agents working remotely (Figure 1).
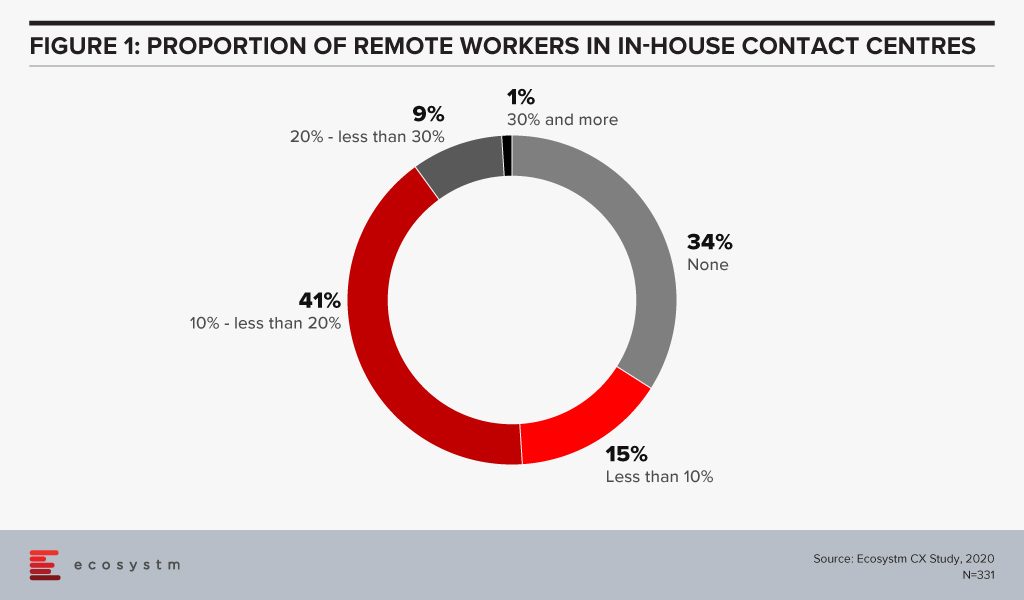
For a long time, the industry has talked about the rise of home-based agents and while it has received positive momentum, it has never really taken off in a big way. This time it will.
Managing spikes in voice and non-voice calls
In industries such as healthcare and airlines, call volumes are exceeding normal volumes. Having the ability to deflect the calls to other non-voice channels will be important. It might need the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) scripts to be changed from time to time to manage the flow of the calls. This is when cloud architecture becomes important. The cloud model can be used to make changes to call workflows easily. The sudden peaks will also require changing the channels easily and without intervention from IT. This is where the agility of cloud comes in as it allows changes and additions – for example when 500 agents need to be added or moved to work on other areas – to be made more easily. Ecosystm research finds that currently, only a third of organisations have their contact centre solutions fully on a cloud, with another 66% with partial cloud solutions. This is set to change with the rise in the number of home-based agents.
There should be thought and planning on how to deflect voice calls to other self-service channels. In the current environment, some organisations deploy a call back option when there is an overflow calls. Similarly looking at deflecting voice calls to self-service channels to ease the load on agents should be evaluated.
Managing back up locations (onshore and offshore)
Contact centre operators are looking at ways to isolate agents and keep them safe. Apart from very strict hygiene measures, organisations are also restricting agents to their specific floor. Some are looking at having agents split into different centres, to contain the risk of mass infection.
Several contact centre operators are building contingency plans to route calls to outside the onshore location in case the situation in a site or a cluster worsens.
For back-end contact centre activities and non-voice calls, taking the load off from the current onshore setup and pushing them offshore, can be an option. The best place to start would be by evaluating each client contract and SLAs especially on security, regulation and privacy issues regarding customer data-handling.
There will be a lot to be considered too should the country go into the full lock-down mode as we are starting to see with a few countries. This makes the case for employing home-based agents stronger.
Using messaging apps, the website and FAQs for daily notifications
Many contact centres are informing citizens and customers about the changes in business operations, services offered, refunds, where to go for help, what do to in an emergency and other essential information through the website, app or the updated FAQ. This will help reduce unnecessary voice and non-voice enquiries to the contact centre. During an emergency, it is normal that phone queries will rise and developing a detailed FAQ is critical to counter that. The more detailed the FAQ giving essential information, the more agents will be able to focus on the more essential day to day activities. Several companies are now sending pop-ups within apps about daily changes to avoid an overflow of inbound enquiries.
Virtual Assistants and Conversational AI can help to ease the load
The more intelligent the virtual assistant and conversational AI platform, the more a customer will be able to get the right response. The challenge has been that many platforms are poorly designed and customers get frustrated because they are unable to get the basic information they need. In times of high inbound activity, if answers to simpler queries can be provided through a chatbot, it can help ease the load on agents. It is good to start planning for this as it will take some time to get the virtual assistant platform up and running and even longer for the algorithms to learn from historical patterns to work well. While it may not be the perfect solution now, planning for a Conversational AI can bring some sort of balance back to the contact centre. Having a solid knowledge management system at the back-end cannot be compromised. Without a good knowledge management system, the virtual assistant solution will force customers to leave the self-service platform and place a call to the contact centre, defeating its very purpose.
The challenging situation we are in is undoubtedly putting pressure on contact centres. It is not uncommon now for customers to be put on hold – for more than two hours and in some extreme cases more than 7 hours! In times like this, understanding data and the patterns around data from each customer touchpoint will help plan the next steps on how best to navigate the situation. Testing and pre-testing the channels and the changes made before they go live must be done rigorously.
Whilst these are very challenging times for the economy, the good news is that contact centres are successfully piloting or have already implemented some or all of the above discussed here. Outsourced contact centre providers are running pilots across various locations and applying technology to deal with the challenges they are witnessing daily. Technology has also come a long way in the contact centre space, and by the application of the right technologies, scale, and business continuity measures, resilience can be achieved.
This blog was created with input from CX leaders across the entire Asia Pacific region. The author wishes to thank everyone for their valuable input.

On December 18, AWS launched Amazon Connect in ASEAN from the Singapore region. I was invited to the ASEAN launch of Connect in Singapore 3 weeks ago where Pasquale DeMaio, GM of Amazon Connect and Robert Killory, ASEAN Solutions Lead presented to analysts.
Pasquale told the audience that the Amazon Connect solution used today has been built over 10 years ago to serve Amazon’s internal needs of servicing millions of customer interactions for their e-commerce transactions. At that time Amazon could not find a solution that was pure cloud-based, cost-effective, scalable and that was easy to use. Since launching Amazon Connect a few years ago, AWS has seen not just small and medium enterprises using Connect – larger organisations have embraced the solution as well.
Amazon Connect has a list of notable clients – Intuit, Rackspace, John Hancock, CapitalOne, GE Appliances, Subway and many others. Intuit, as an example, has had difficulties running experiments in the past and proofs of concept were expensive, complex and time-consuming. With Amazon Connect these run on a test environment allowing their engineers to experiment and if they do not work out, it does not cost Intuit a lot of money to spin up a proof of concept. Philippines telecommunications provider, Globe Telecom wanted to automate and improve their services for their broadband and residential services. It was taking about 2-3 days from payment to the restoration of services. Amazon Connect was deployed to solve this problem by understanding the customer data when calls came through to the contact centre and by using APIs and the Connect suite of applications, there was deep integration with the CRM systems and other platforms that held various pools of data. This produced a faster and scalable way of integrating the payment process and customer service.
The demo of the solution showcased how features such as Amazon Lex can build conversational interfaces for an organisation’s applications powered by the same deep learning technologies like Alexa. With Amazon Lex and Polly, organisations can now build a chatbot without knowing or understanding code.
The Amazon Connect Solution – scaling to become more feature-rich
At ReInvent in Las Vegas in December 2019, Andy Jassy the CEO of AWS unveiled a new offering for their contact centre customers called Contact Lens. The solution is a set of machine learning capabilities integrated into Amazon Connect. The service can be activated through a single click in Connect and can analyse, transcribe calls including previously recorded calls. Jassy also talked about how it allows users to determine the sentiment of the call, pick up on long periods of silence, and times when an agent and customer are talking over the top of each other. These additions can help supervisors understand the challenges faced by agents that can then be addressed during training and coaching sessions. The machine learning models that power Contact Lens for Amazon Connect have been trained specifically to understand the nuances of contact centre conversations including multiple languages and custom vocabularies.
Several other announcements have also been made recently:
- Web and Mobile Chat for customers is a single unified contact centre service for voice and chat. Agents have a single user interface for both voice and chat, reducing the number of screens they have to interact with.
- Amazon Transcribe now supports 31 languages including Indonesian, Malay, Japanese, Korean, and several Indian languages. These are important languages as they expand further across ASEAN and the rest of Asia, given the diversity of languages spoken in the region. Contact centres can convert call recordings into text and analyse the data for actionable intelligence.
Deepening their relationship with Salesforce
At Dreamforce 2019 late last year, Salesforce announced that they will be offering AWS telephony and call transcription services with Amazon Connect as part of their Service Cloud call centre solution. The announcement indicates how the CRM world and the contact centre segments are starting to get closer. CRM vendors are starting to realise that whilst they own the agent at the desktop who have access to the CRM solution, the data from the calls and the actual calls are important. Voice/Telephony is also witnessing greater innovation with vendors in the contact centre space applying machine learning and AI to voice so that intelligence is gathered prior to the call coming to the contact centre and the agent is further empowered through prompts that they can apply when speaking to a customer. As CRM integrates deeper with contact centre solutions, the tight integration between these two solutions cannot be ignored. Salesforce is partnering to innovate in the voice space by applying machine learning at the core of all they do. This is a big announcement given the sheer size of both companies and how both companies are innovating in the contact centre space.
Cloud Contact Centre is high on the agenda in Asia Pacific
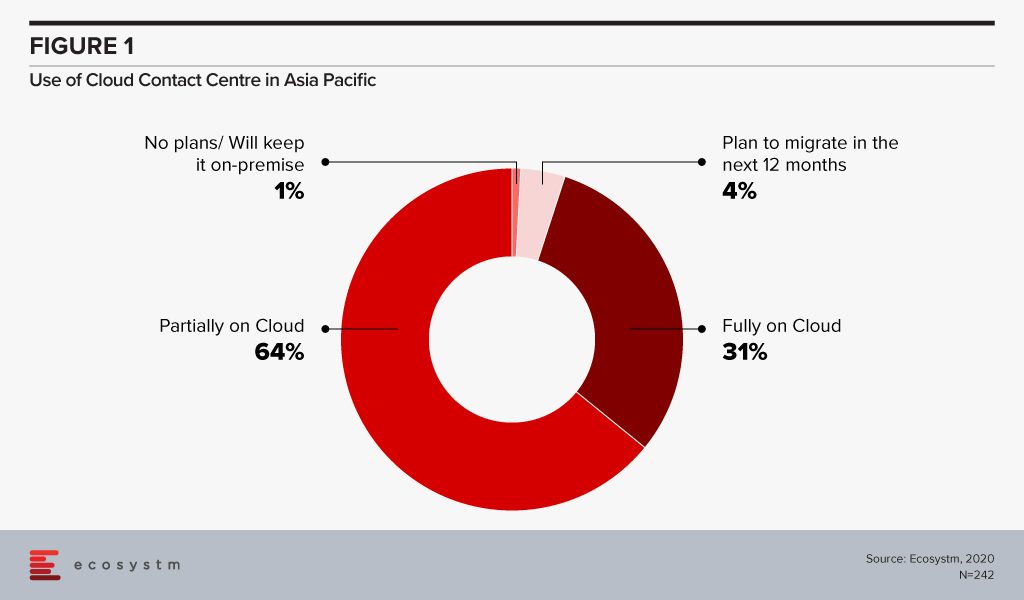
Ecosystm’s CX research finds that most organisations in Asia Pacific are at the inflection point of moving from an on-premise environment to a cloud model. Only 1% of CX decision-makers want to keep their contact centres on-premise – many organisations are evaluating which contact centre vendor they should use to migrate to the cloud. Some countries may see higher adoption than others. Australia and New Zealand have higher cloud contact centre adoption. In ASEAN many organisations are starting to build a wider CX strategy beyond the contact centre including areas such as customer journey analytics and data-driven personalised CX.
Ecosystm comments
In Australia, Amazon Connect has grown its customer base and these include some large enterprises. Big wins in the last 2 years include National Australia Bank and NSW Health. NSW Health shifted its IT service desk and shared services contact centres onto a new cloud-based contact centre platform as part of a broader digital transformation.
AWS has been gearing up for the launch in ASEAN over the last 6 months. The region is very competitive with some long-standing contact centre players having a large share and installed base in the large and medium enterprise accounts. The launch indicates how serious they are about growing their contact centre business in the region. There has been good progress so far in Singapore and the Philippines. Amazon Connect will look to grow its presence in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam in the months to come. The market dynamics in each Asian country is unique and AWS will work with partners such as Accenture, Deloitte, DXC, ECS, NTT and VoiceFoundry to grow their presence in the region. Some of the more traditional partners will need education and upskilling to understand the Amazon Connect value proposition