The telecommunications industry has long been an enabler of Digital Transformation (DX) in other industries. Now it is time for the industry to transform in order to survive a challenging market, newer devices and networking capabilities, and evolving customer requirements. While the telecom industry market dynamics can be very local, we will see a widespread technology disruption in the industry as the world becomes globally connected.
Drivers of Transformation in the Telecom Industry
Remaining Competitive
Nokia Bell Labs expects global telecom operators to fall from 10 to 5 and local operators to fall from 800 to 100, between 2020 and 2025. Simultaneously, there are new players entering the market, many leveraging newer technologies and unconventional business models to gain a share of the pie. While previous DX initiatives happened mostly at the periphery (acquiring new companies, establishing disruptive business units), operators are now focusing on transforming the core – cost reduction, improving CX, capturing new opportunities, and creating new partner ecosystems – in order to remain competitive. There is a steady disaggregation in the retail space, driving consolidation in traditional network business models.
“The telecom industry is looking at gradual decline from traditional services and there has been a concerted effort in reducing costs and introducing new digital services,” says Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah. “Much of the telecom industry is unfortunately still associated with the “dumb pipe” tag as the over-the-top (OTT) players continue to rake in revenues and generate higher margins, using the telecom infrastructure to provide innovative services.”
Bringing Newer Products to Market
Industries and governments have shifted focus to areas such as smart energy, Industry 4.0, autonomous driving, smart buildings, and remote healthcare, to name a few. In the coming days, most initial commercial deployments will centre around network speed and latency. Technologies like GPON, 5G, Wifi 6, WiGig, Edge computing, and software-defined networking are bringing new capabilities and altering costs.
Ecosystm’s telecommunications and mobility predictions for 2020, discusses how 5G will transform the industry in multiple ways. For example, it will give enterprises the opportunity to incorporate fixed network capabilities natively to their mobility solutions, meaning less customisation of enterprise networking. Talking about the opportunity 5G gives to telecom service providers, Amanullah says, “With theoretical speeds of 20 times of 4G, low latency of 1 millisecond and a million connections per square kilometre, the era of mobile Internet of Everything (IoE) is expected to transform industries including Manufacturing, Healthcare and Transportation. Telecom operators can accelerate and realise their DX, as focus shifts to solutions for not just consumers but for enterprises and governments.”
Changing Customer Profile
Amanullah adds, “Telecom operators can no longer offer “basic” services – they must become customer-obsessed and customer experience (CX) must be at the forefront of their DX goals.” But the real challenge is that their traditional customer base has steadily diverged. On the one hand, their existent retail customers expect better CX – at par with other service providers, such as the banking sector. Building a customer-centric capability is not simple and involves a substantial operational and technological shift.
On the other hand, as they bring newer products to market and change their business models, they are being forced to shift focus away from horizontal technologies and connecting people – to industry solutions and connecting machines. As their business becomes more solution-based, they are being forced to address their offerings at new buying centres, beyond IT infrastructure and Facilities. Their new customer base within organisations wants to talk about a variety of managed services such as VoIP, IoT, Edge computing, AI and automation.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for telecom service providers, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the top priorities are driving customer loyalty (through better coverage, smart billing and competitive pricing) and process optimisation (including asset maintenance).
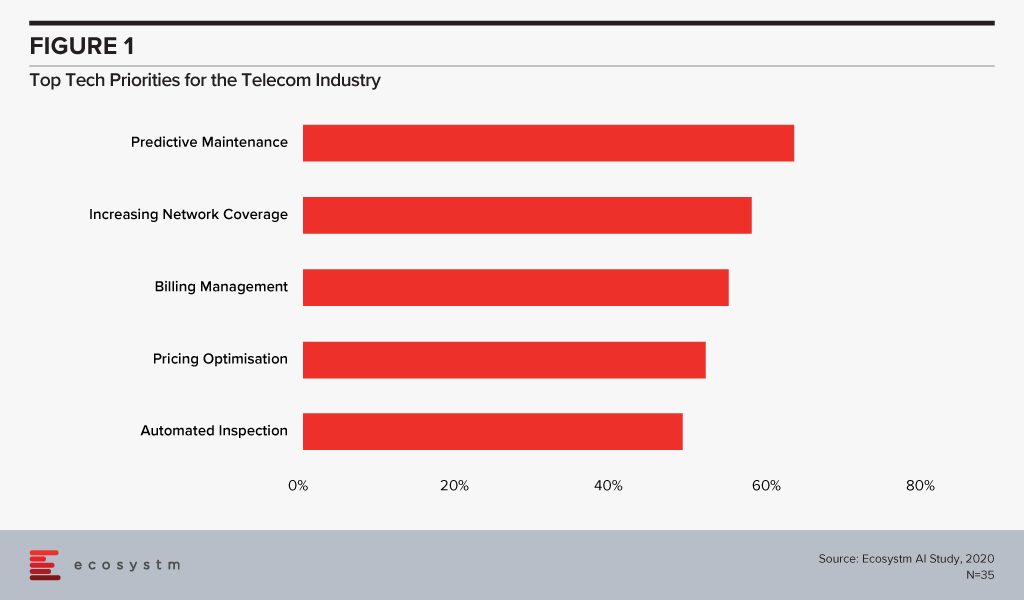
Technology as an Enabler of Telecom Transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used internally by telecom service providers as they look towards DX to remain competitive. They are transforming both asset and customer management in the telecom industry.
IoT & AI
Telecom infrastructure includes expensive equipment, towers and data centres, and providers are embedding IoT devices to monitor and maintain the equipment while ensuring minimal downtime. The generators, meters, towers are being fitted with IoT sensors for remote asset management and predictive maintenance, which has cost as well as customer service benefits. AI is also unlocking advanced network traffic optimisation capabilities to extend network coverage intelligently, and dynamically distribute frequencies across users to improve network experience.
Chatbots and virtual assistants are used by operators to improve customer service and assist customers with equipment set-up, troubleshooting and maintenance. These AI investments see tremendous improvement in customer satisfaction. This also has an impact on employee experience (EX) as these automation tools free workforce from repetitive tasks and they be deployed to more advanced tasks.
Telecom providers have access to large volumes of customer data that can help them predict customer usage patterns. This helps them in price optimisation and last-minute deals, giving them a competitive edge. More data is being collected and used as several operators provide location-based services and offerings.
In the end, the IoT data and the AI/Analytics solutions are enabling telecom service providers to improve products and solutions and offer their customers the innovation that they want. For instance, Vodafone partnered with BMW to incorporate an in-built SIM that enables vehicle tracking and provides theft protection. In case of emergencies, alerts can also be sent to emergency services and contacts. AT&T designed a fraud detection application to look for patterns and detect suspected fraud, spam and robocalls. The system looks for multiple short-duration calls from a single source to numbers on the ‘Do Not Call’ registry. This enables them to block calls and prevent scammers, telemarketers and identity theft issues.
Cybersecurity
Talking about the significance of increasing investments in cybersecurity solutions by telecom service providers, Amanullah says, “Telecom operators have large customer databases and provide a range of services which gives criminals a great incentive to steal identity and payment information, damage websites and cause loss of reputation. They have to ramp up their investment in cybersecurity technology, processes and people. A telecom operator’s compromised security can have country-wide, and even global consequences. As networks become more complex with numerous partnerships, there is a need for strategic planning and implementation of security, with clear accountability defined for each party.”
One major threat to the users is the attack on infrastructure or network equipment, such as routers or DDoS attacks through communication lines. Once the equipment has been compromised, hackers can use it to steal data, launch other anonymous attacks, store exfiltrated data or access expensive services such as international phone calls. To avoid security breaches, telecom companies are enhancing cybersecurity in such devices. However, what has become even more important for the telecom providers is to actually let their consumers know the security features they have in place and incorporate it into their go-to-market messaging. Comcast introduced an advanced router to monitor connected devices, inform security threats and block online threats to provide automatic seamless protection to connected devices.
Blockchain
Blockchain can bring tremendous benefits to the telecom industry, according to Amanullah. “It will undeniably increase security, transparency and reduce fraud in areas including billing and roaming services, and in simply knowing your customer better. With possibilities of 5G, IoT and Edge computing, more and more devices are on the network – and identity and security are critical. Newer business models are expected, including those provided for by 5G network slicing, which involves articulation in the OSS and BSS.”
Blockchain will be increasingly used for supply chain and SLA management. Tencent and China Unicom launched an eSIM card which implements new identity authentication standards. The blockchain-based authentication system will be used in consumer electronics, vehicles, connected devices and smart city applications.
Adoption of emerging technologies for DX may well be the key to survival for many telecom operators, over the next few years.

Governments across the globe are realising the true potential of emerging technologies to provide better citizen services and to ensure transparency and accountability. Blockchain is one of the emerging technologies that is helping and will continue to help governments to achieve transformation. Government departments and agencies are being increasingly pushed to be collaborative and share data across agencies, while at the same time maintain the security of the data in their care. A distributed ledger that can share information based on agreed-upon protocols helps governments immensely in collaborating without losing accountability.
What are the key priorities of public sector organisations? The global Ecosystm CX study finds that citizens and employees are the top priorities for government agencies and departments.
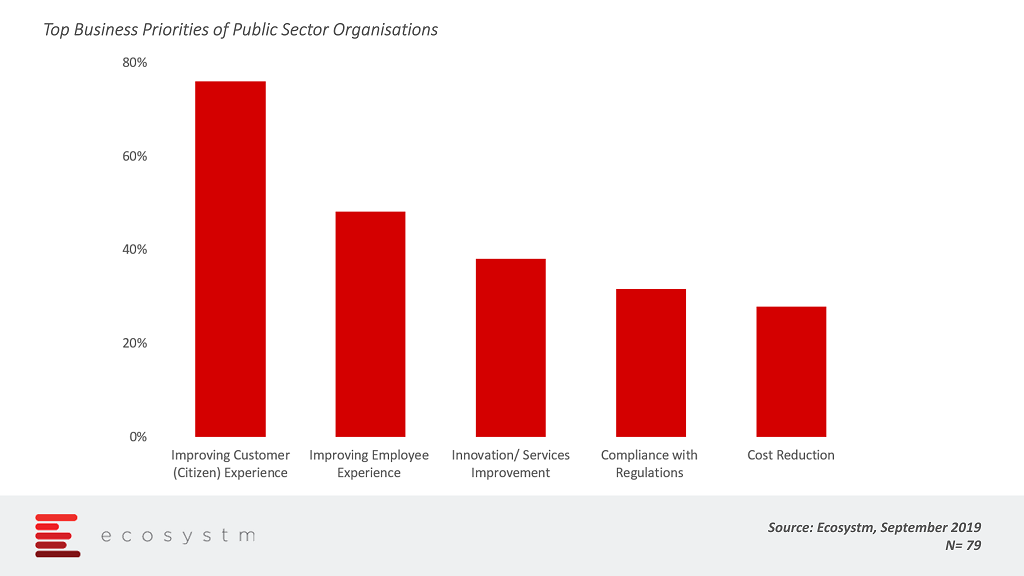
Blockchain can help the public sector achieve many of its goals –
Improving Citizen Services
As more countries aim to be eGovernments, there is a need for real-time data access, information management, and fraud prevention. Blockchain is enabling governments to provide innovative services to citizens. It is possible now to decentralise the citizen database, reducing the time and cost of fetching records. Moreover, Blockchain enhances transparency and makes the highly regulated public sector audit-ready by creating a single source of truth for all connected devices and stakeholders.
One of the earliest use cases we see is in records management. Population records are useful for several agencies from healthcare to civil services to welfare departments. In Myanmar, UNICEF has collaborated with the industry to introduce a mobile birth and death registration system based on Blockchain. This digital mobile recording system is maintained on an integrated platform controlled by several parties who maintain birth and death records of Myanmar’s citizens and is a step towards achieving universal registration.
Citizen services such as notarisation, recording and time-stamping events, transactional real-estate contracts, online storing and verification of academic degrees, identity management and so on are benefiting from Blockchain deployment.
In Georgia, the government department of Land, Property and Housing Management is using Blockchain to maintain land and property records. The blockchain-based land registry allows speedier approvals with no involvement of paperwork or multi-party signatures on physical documents. This is enhancing service quality while offering better security measures as the data is digitally stored in the National Agency of Public Registry’s land title database.
Improving Employee Experience
Maintaining massive records about individuals, organisations, assets, activities, location and national information by the government department employees is a time-consuming process. In addition to this, managing and updating the ever-growing records is made more difficult by data silos and information management protocols and of course errors creep in.
Blockchain is streamlining the workflow and information management system at an individual as well as at a departmental level. In government departments, Blockchain can redefine processes by including events and agents in a block-based system where each activity can be easily managed and accounted for. This prevents issues such as miscounts, delayed processes and slipped deadlines.
The Chilean National Energy Commission has piloted a Blockchain platform to regulate the energy sector such as installed capacity, average market price, marginal costs, hydrocarbons and more. To implement this, first the energy data was stored on an Open Energy database which was then distributed across hundreds of secure servers countrywide. Later the employees verified anomalies which minimised their workload and made it convenient to edit the central database. The information added to open ledger is readily available to employees and citizens.
Compliance with Regulations
One of the primary benefits of Blockchain technology in the public sector is compliance. The transactions recorded on distributed ledgers are documented in a central ledger providing a comprehensive, precise, irreversible, permanent and secure trail. For instance, Blockchain is used to streamline cross-border compliance adherence by matching the data with the actual trade transactions. This creates an efficient and secure system ensuring real-time compliance, significant reduction of transaction costs, elimination of customs evasion and fraud from the outset.
In June, the Chinese Customs deployed its cross-border Blockchain compliance solution. The platform aims to increase efficiency by monitoring the flow of imports and exports and helping with risk assessments and document management. As transaction information can be stored safely and transparently on a Blockchain, the platform enables easy identification of documents to be checked, making compliance easier.
Data Management and Privacy
Blockchain acts as a default record keeper for society and governments and prevents the data from being misused by criminals and hackers. Through the responsible deployment of Blockchain data structures, governments can strengthen network security by reducing risks of single points-of-failure and preventing data breaches.
Democracy Earth – a Blockchain-based community has established a decentralised online governance platform, entirely built on open source technologies. The website helps users to cast votes on various policies based on tokens assigned to the users. This also minimises expenses and creates a secure information flow in a Blockchain-based voting system.
Government agencies, such as the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS), are also getting serious about Blockchain applications in data management and privacy. DHS is funding R&D in Blockchain start-ups to explore new approaches to cybersecurity. The U.S. military is also utilising Blockchain (SIMBA Chain) to secure its military communication, messaging and applications. Blockchain is used for communication between ground troops and their headquarters. In addition to securing communications, the US Airforce is using Blockchain to track 3D printed components throughout their life cycle. With SIMBA, the top-secret printing blueprints are shared without much surveillance – this has enabled the Department of Defense to maintain a digital library of parts.
Cost Reductions
The government has clear citizen responsibilities and fulfilling them with a limited set of resources is one of the prime challenges for public departments. Reconciling expenditure with the budget is a time-consuming, and expensive procedure. Blockchain-based payment and accounting systems can help governments to reduce process costs by removing redundancies, streamlining processes, decreasing audit burden and ensuring systems integrity. By removing the requirement for third-party agencies to handle operations and maintain records, Blockchain technology is helping governments to reduce costs.
Blockchain is still an emerging concept with significant benefits. The Ecosystm IoT study finds that only 20% of public sector IT decision-makers are fully aware of the capabilities and limitations of Blockchain. Adopters and developers are still resolving the challenges. On the technology side, there are concerns on platform scalability, integration, standardisation and validation methods. On the management side, there are concerns about business models, transaction scale, maturity, and structure. However, government agencies will benefit immensely from the technology in the near future.
It can often be difficult to keep track of assets and transactions in a business, and that is where Blockchain is unleashing its potential. It is revolutionising enterprises with its shared ledger technology. There are numerous, and specialised, use cases of Blockchain but the adoption is nascent in most industries. There are a few early adoption use cases of Blockchain, however, which have the potential to replace traditional systems and processes.
In the global Ecosystm Mobility study, organisations are asked about the adoption of Blockchain as a means of authentication. Industries that appear most open to Blockchain adoption are those that have also embraced IoT for tracking and traceability.
Adoption of Blockchain for Authentication – An Industry Comparison
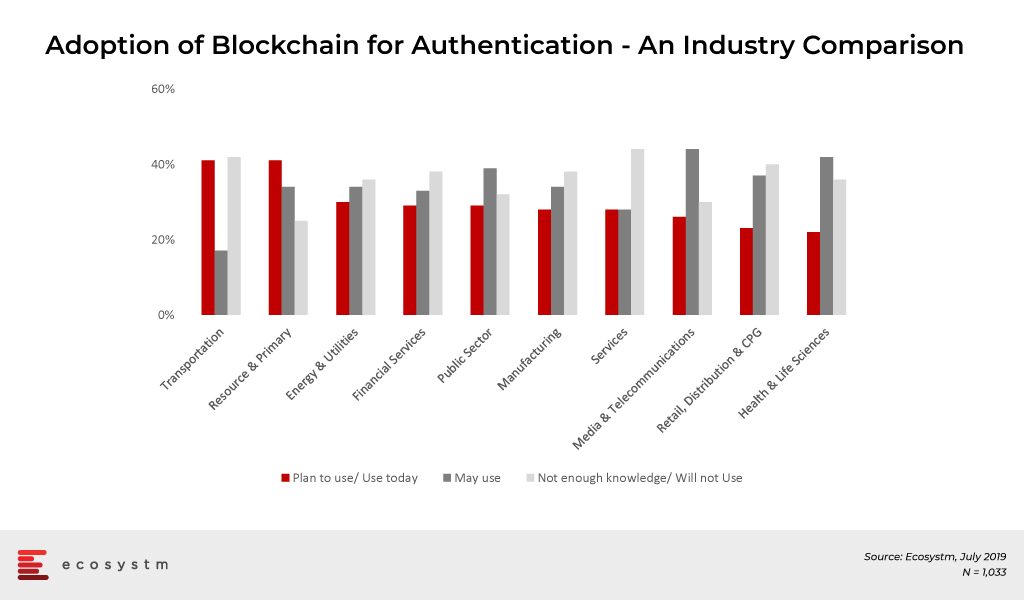
Across industries Blockchain technology is being used primarily for these use cases:
Supply Chain Traceability
Supply chain traceability allows producers, retailers, and consumers to track products from source to consumer. It connects all points in the supply chain, creating transparency and trust in the product. When a business comprises complex processes, a large and dispersed workforce, multiple locations and different operations, a lot of administrative and regulatory frameworks are required to manage and control the supply chain. Functions such as order management, procurement, import, delivery, tracking, and invoicing have their own unique set of requirements and processes. In several cases, especially across primary and retail industries, business complexity has been reduced with the use of Blockchain. The technology allows for improving digital assets and inventory tracking for better services and processes.
Blockchain is ensuring food safety by providing a complete view of the supply chain and creating a real-time trail of products – allowing a ‘farm to fork’ view. Walmart is a good example of how retailers can use Blockchain technology to ensure that they sell fresh produce. Fresh produce shipments can be tracked as they change hands from the farmers to the middlemen, to the distributor and finally to the store. This can have an enormous impact on containing food-borne diseases and food contamination. Not only does Blockchain increase food safety, it ensures fresher food since it secures production and packing dates.
Intellectual Property Intermediary (IPI), an organisation established under Singapore’s Ministry of Trade and Industry, is an affiliate of Enterprise Singapore and focuses on technology innovations in the industry that can empower enterprises to develop new processes, products, and services. IPI has identified Blockchain Technology for Food as an area where the industry can benefit from innovation. The ecosystem will also benefit from the information gathered, with the potential to further improve the production chain.
Fraud Prevention
Taking supply chain visibility a step further, Blockchain technology is being used for fraud prevention – especially payment fraud. Financial transactions are complex and involve multi-step processes and human intervention – involving collaterals, settlement, currency denominations, third-party mediation, and so on. It is often the prime target for fraudsters. The most common instances of fraud involve bank to bank transactions, mobile payments, and digital identity fraud, essentially by tampering with ID or using it an unsanctioned way – providing unauthorised access to digital systems and falsifying information.
Blockchain helps automate preventive measures enabling real-time information sharing which is transmitted on a chain of connected devices where all the nodes in a system verify the transaction. Since it stores the data on several nodes and every other user on the network has a copy of the entire data on the Blockchain, it is virtually impossible to hack or destroy it completely.
Earlier this year, Standard Chartered Singapore showcased their cross-border trade finance transaction which digitalises trade processes and financing documentation. Blockchain enabled the transaction between parties by digitally streamlining the documentation process while providing security and transparency between the partners. Not only does it support the clients’ entire supply chain, but it also creates a transparent way to provide same-day trade financing.
Non-profit organisation BitGive Foundation uses Blockchain technology to provide greater visibility to their donors into the receipt of funds and how they are used by sharing financial information and project results in real-time. The GiveTrack project is built on Bitcoin and Blockchain and is a user-friendly, data-centered and comprehensive user interface. People making donations can precisely track the donations and how the funds were used.
Legal & Compliance
In industries that have higher Compliance & Regulatory requirements, Blockchain can enable safe, secure, and scalable data-sharing. The industry is seeing instances of self-executing contracts, smart registries, secure and time-stamped documents with Blockchain. Blockchain is introducing abilities to record events for a long duration which might include indisputable claims, criminal records, case procedures to support the potential legal work.
Dubai launched a city wide blockchain strategy. Dubai Land Department is implementing blockchain to make property transactions secure, transparent and immutable, thereby reducing fraud and eliminating reams of physical documents. This impacts the entire ecosystem – customers, developers, the land department, utility providers, payment channels, and municipalities – to work in collaboration.
Shipping companies that need to enforce global contracts daily are also benefitting from Blockchain. However, the biggest use cases will eventually come from the Public Sector – across citizen services and criminal justice systems. For instance, National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) is testing Blockchain e-voting facilities. The project is still at the pilot stage and aims to tokenised voting which makes it easy to conduct test and audit for the votes. This allows the regulating authorities to access real-time data, and at the same time, provides means to audit the regulators.
Cybersecurity
73% of global organisations believe that a data breach is inevitable, according to the Ecosystem Cybersecurity Study, and only 18% of them use some form of tokenisation and other cryptographic tools. Blockchain technology offers several capabilities in mitigating cybersecurity risks and detecting and combating cyber attacks. For example, Blockchain can be used to prevent DDoS attacks, and crypto secured biometric keys can replace passwords providing robust ID authentication systems, more secure DNS and decentralised storage. Blockchain implementation can also prevent man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks by encrypting the data in transit so it is not manipulated during the transmission or accessed by unauthorised parties – thus maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
Lockheed Martin, a US security company, is implementing Blockchain into their protocol. The company is enhancing Blockchain cybersecurity protocol measures in engineering systems, supply chain risk management, and software development. This includes researching on expanding on Blockchain capabilities protect their weapons development unit and make it incorruptible.
eGovernment initiatives will also benefit from Blockchain. The biggest stumbling block for providing eservices has always been cybersecurity, where the Government cannot be sure that the citizens are able to access their own records in a secure manner. It has always been a question of responsibility and liability – is the Government liable for a data breach that happens because of a citizen’s fault? Estonia is using Blockchain to protect their digital services such as electronic health records, legal records, police records, banking information, covering data and devices from attacks, misuse, and corruption.
Customer Experience
The ultimate benefit of Blockchain will be realised when it is used to enhance Customer Experience (CX). It brings transparency in doing business, gives on-demand data visibility and fosters trust in customers. A company that shows all transactions between the company and the customer, and in a secure manner, can create a better relationship, increase overall customer satisfaction and retain their customers in a competitive market. For example, Blockchain technology can allow more secure and transparent loyalty programmes, through token creation that can be redeemed on-demand, without customer service intervention. Singapore Airlines’ KrisFlyer structures their payments and loyalty programme with Blockchain. Their digital wallet enables members to convert KrisFlyer miles into KrisPay miles instantly to pay for their purchases at partner merchants. The users can pay through an application by scanning a QR code at a merchant’s location .
Customers will increasingly look for ease of use and security in their transactions. Bank of America has filed a patent for Blockchain powered ATM, for securing records and authenticating business and personal data. This will boost the transaction rate and facilitate various transaction experience with full encryption and security. Blockchain-enabled transactions can be registered and completed with greater easy while lowering the transaction costs for customers and keeping the network safe.
While Blockchain technology is continuing to evolve for a range of applications and industries, it comes with its own share of risks. Adoption should not be based on the hype around the technology but should be evaluated carefully. The starting point should obviously be a real business needs analysis.
Speak with an expert today to evaluate whether your organisation can benefit from Blockchain.
With understanding and acceptance of blockchain increasing, enterprises have started adopting blockchain to store digital records in a secure and auditable manner. In May 2018, we saw Microsoft’s blockchain workbench focused on integrating data and systems and deployment of contracts and blockchain networks. In October 2018, Microsoft Azure joined forces with Nasdaq to integrate blockchain technology into Nasdaq’s framework with an expectancy to speed-up transactions on the stock exchange.
Following these announcements, this month Microsoft unveiled its fully managed Azure Blockchain Service, a package designed to simplify the processes and eliminate the pain points of blockchain networks. Microsoft Azure blockchain service will provide the required infrastructure, connection to services to develop, run and take advantage of applications on its Cloud-based platform.
To leverage blockchain Microsoft and J.P. Morgan announced a partnership to accelerate the adoption of enterprise blockchain. Quorum, an Ethereum-based distributed ledger protocol developed by J.P. Morgan will be the first ledger available through Azure Blockchain Service, on the cloud.
Joining the bandwagon, Starbucks will use Azure and the Ethereum blockchain to track coffee from farm to the cup. In the same way, with a forward-thinking approach, Microsoft and GE Aviation collaborated to bring blockchain into aviation. GE Aviation has built a supply chain track-and-trace blockchain with the help of Microsoft Azure to monitor and collate data in relation to aircraft engine parts, life cycle, when to repair, this technology that the group has come up with is termed as ‘TRUEngine’.
Unfolding blockchain for “regular” businesses and SMEs
Blockchain technology, by its very nature leads itself to the digital transformation journey of an enterprise. Blockchain can address some of the pitfalls of digital transformation such as identity, security, and trust. From digital identity to tokenisation to using smart contracts to automate businesses, blockchain technology is swiftly establishing itself as a key enabler of the emerging digitised enterprise.
 |
Speaking on the subject, Ecosystm’s Principal Advisor, Amit Sharma thinks that “For Small and Mid-Size Enterprise (SMEs), blockchain can simplify and automate processes related to Trade Finance which would mean less paperwork and automation in supply chains and it also opens up a huge alternative finance channel to deal with their cash flow challenges.” |
Overall the blockchain network should facilitate the interworking between IT systems, financial systems and ledgers that are today primarily managed in silos and require heavy manual processes.
Are we already there?
“All disruptive technology has a ‘tipping point’ – the exact moment when it moves from early adopters to widespread acceptance. We are now approaching the tipping point for blockchain. Even though the development of blockchain for business is still in its early stages, business leaders have swiftly moved from understanding blockchain and its potential uses to running pilots,” says Sharma.
Blockchain has attracted attention across industries such as financial services, transportation and shipping, healthcare, energy and utilities, and supply chain management.
These share some common themes. Blockchain is a natural fit for use cases that are transactional but with a high degree of process complexity or volume. Blockchain will become the default technology wherever there is a need to ensure the integrity of data.
Blockchain Adoption by Organisations
Despite the flurry of activity and promising initial developments, blockchain faces a number of obstacles that will need to be overcome before companies choose to adopt it on a broader scale. Its decentralised network runs counter to the current business emphasis on centralising data or functions to support security efforts. Users and operators alike must shift their mindset to embrace and trust the system.“Among blockchain’s selling points is its security: high encryption and protocols. Since the general public largely doesn’t understand how the technology works, many still have concerns with data privacy and cyber security” says Sharma. “As with all new technology, when it comes to blockchain, business leaders should view any initial use cases as part of their enterprise risk management. Executives are attuned to the business and risk implications of blockchain. And in many cases, blockchain, like other technology platforms and systems, can be covered under existing insurance programs.”
Implementation by the large technology providers
“With the large technology providers such as Microsoft and AWS now offering BaaS (Blockchain-as-a-Service) over multiple frameworks supported by a ‘Pay as you use’ model, this technology is much more accessible. Pre-built integrations to the network and infrastructure services that are being offered by some of these players will significantly reduce the development time and cost for enterprise customers” says Sharma.
The next several years could see blockchain move from testbed to becoming an essential business tool, so staying abreast of the latest developments and how it is being used will be critical.





