Organisations are finding that the ways to do work and conduct business are evolving rapidly. It is evident that we cannot use the perspectives from the past as a guide to the future. As a consequence both leaders and employees are discovering and adapting both their work and their expectations from it. In general, while job security concerns still command a big mindshare, the simpler productivity measures are evolving to more nuanced wellness measures. This puts demands on the CHRO and the leadership team to think about company, customer and people strategy as one holistic way of working and doing business.
Organisations will have to re-think their people and technology to evolve their Future of Work policies and strategise their Future of Talent. There are multiple dimensions that will require attention.
Hybrid is Becoming Mainstream
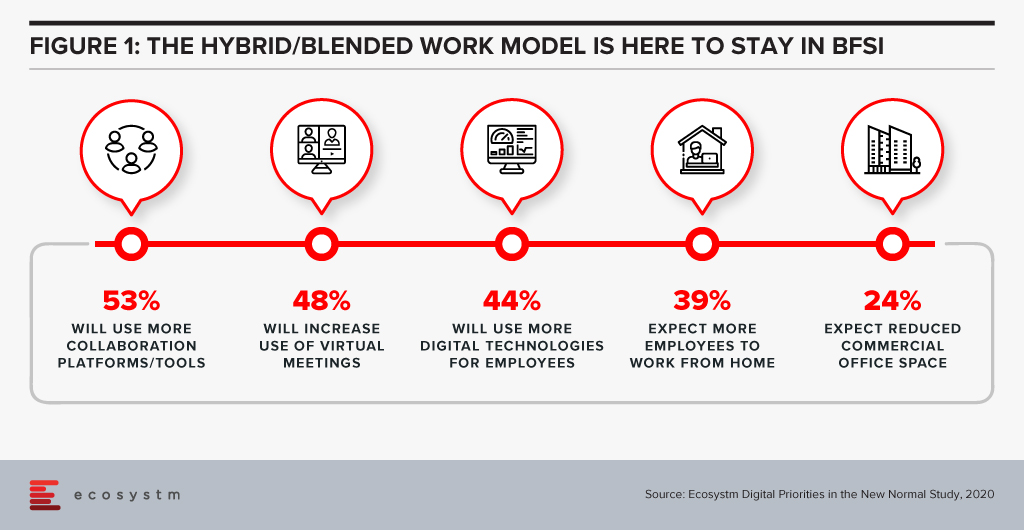
It is clear that hybrid workplaces are here to stay. Ecosystm research finds that in 2021 BFSI organisations will use more collaboration tools and platforms, and virtual meetings (Figure 1). Nearly 40% expect more employees to work from home, but only about a quarter of organisations are looking to reduce their physical workspaces. Organisations will give more choice to employees in the location of their work – and employees will choose to work from where they are more productive. The Hybrid model will be more mainstream than it has been in the last few months.
Companies are coming to terms with the fact that there is no single answer to operating in the new world. Experimentation and learnings are continuously captured to create the right workforce and workplace model that works best. Agility both in terms of being able to undersand the market as well as quickly adapt is becoming quite important. Thus being able to use different models and ways of working at the same time is the new norm.
Technology and Talent are Core
Talent and tech are the two core pillars that companies need to look at to be successful against their competition. It is becoming imperative to create synergy between the two to deliver a superior value proposition to customers. Companies that are able to bring the customer and employee experience journeys together will be able to create better value. HR tech stacks need to evolve to be more deliberate in the way they link the employee experience, customer experience, and the culture of the organisation. That’s how the Employee Value Proposition (EVP) comes to life on a day-to-day basis to the employers. With evolving work models, the tech stack is a key EVP pillar.
Governments will also need to partner with industry to make such talent available. Singapore is rolling out a new “Tech.Pass” to support the entry of up to 500 proven founders, leaders and experts from top tech companies into Singapore. Its an extension of the Tech@SG program launched in 2019, to provide fast-growing companies greater assurance and access to the talent they need. The EDB will administer the pass, supported by the Ministry of Manpower.
Attracting the Right Talent
Talent has always been difficult to find. Even with globalisation, significant investment of time and resources is needed to find and relocate talent to the right geography. In many instances this was not possible given the preferences of the candidates and/or the hiring managers. COVID-19 has changed this drastically. Remote working and distributed teams have become acceptable. With limitations on immigration and travel for work, there is a lot more openness to finding and hiring talent from outside the traditional talent pool.
However it is not as simple as it seems. The cost per applicant (CPA) – the cost to convert a job seeker to a job applicant – had been averaging US$11-12 throughout 2019 according to recruiting benchmark data from programmatic recruitment advertising provider, Appcast. But, the impact of COVID-19 saw the CPA reach US$19 in June – a 60% increase. I expect that finding right talent is going to be a “needle in a haystack” issue. But this is only one side of the coin – the other aspect is that the talent profile needed to be successful in roles that are all remote or hybrid is also significantly different from what it was before. Companies need to pay special attention to what kind of people they would like to hire in these new roles. Without this due consideration it is very likely that there would be difficulty in on-boarding and making these new hires successful within the organisation.
Automation Augmentation and Skills
The pace at which companies are choosing to automate or apply AI is increasing. This is changing the work patterns and job requirements for many roles within the industry. According to the BCG China AI study on the financial sector 23% of the roles will be replaced by AI by 2027. The roles that will not be replaced will need a higher degree of soft skills, critical thinking and creativity. However, automation is not the endgame. Firms that go ahead with automation without considering the implications on the business process, and the skills and roles it impacts will end up disrupting the business and customer experience. Firms will have to really design their customer journeys, their business processes along with roles and capabilities needed. Job redesign and reskilling will be key to ensuring a great customer experience
Analytics is Inadequate Without the Right Culture
Data-driven decision-making as well as modelling is known to add value to business. We have great examples of analytics and data modelling being used successfully in Attrition, Recruitment, Talent Analytics, Engagement and Employee Experience. The next evolution is already underway with advanced analytics, sentiment analysis, organisation network analysis and natural language processing (NLP) being used to draw better insights and make people strategies predictive. Being able to use effective data models to predict and and draw insights will be a key success factor for leadership teams. Data and bots do not drive engagement and alignment to purpose – leaders do. Working to promote transparency of data insights and decisions, for faster response, to champion diversity, and give everyone a voice through inclusion will lead to better co-creation, faster innovation and an overall market agility.
Creating a Synergy
We are seeing a number of resets to what we used to know, believe and think about the ways of working. It is a good time to rethink what we believe about the customer, business talent and tech. Just like customer experience is not just about good sales skills or customer service – the employee experience and role of Talent is also evolving rapidly. As companies experiment with work models, technology and work environment, there will a need to constantly recalibrate business models, job roles, job technology and skills. With this will come the challenge of melding the pieces together within the context of the entire business without falling into the trap of siloed thinking. Only by bringing together businesses processes, talent, capability evolution, culture and digital platforms together as one coherent ecosystem can firms create a winning formula to create a competitive edge.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Talent Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics on Founders success and failure stories, pandemic impact on founders and talent development, upskilling and reskilling for the future of work.

In this blog, our guest author Chandru Pingali talks about the potential benefits of the Blended working model and the impact it will have on FinTech and financial services organisations. “FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.”

When under pressure to reduce costs and survive, we reimagine everything we do to build resilience and thrive. Never before have the buzzwords frugality, prudence and agility gained as much prominence – not just in one country or industry, but across global economies simultaneously (a phenomenon not seen since the Great Depression). And these words have sliced through the employment opportunities ruthlessly, leaving an abundance of talent to be gainfully employed differently.
So, is the freelance economy surging? Statistics appear to say yes. In 2018, freelancers had contributed almost USD 1.40 trillion to the US economy; 162 million freelancers work across US and EU-15. So, who are these people? Why is blended workforce new or relevant for the Asia Pacific? Why is it gaining more prominence now? How can enterprises create and implement a blended workforce strategy to reduce costs more permanently, while running and scaling businesses? What does the Future of Work and workforce mean? How can FinTech enterprises successfully implement a blended workforce strategy?
Let us take Singapore as an example. With 1000+ FinTech firms and increasing investments, the “smart financial centre” initiative of Singapore is a huge success story, recognised globally. To sustain this, apart from innovation and technology, the main ingredient is consistent availability of talent as the demand for expertise in technology and financial services increases, while the supply is inconsistent, uncurated and fragmented. Recent data from the Singapore government job portals reveal that there are several hundred jobs at any point in time posted by FinTech companies that are open for months! This invariably slows down the ability to build businesses, innovate or scale. Interestingly, while the local talent for technology and BFSI may be limited in Singapore, the crisis this year presented a significant opportunity to reimagine the Future of Work and workforce. While efforts should continue to upskill and reskill local talent, it is now possible to create dedicated local and cross-border talent hubs to work part-time, fulltime-short term with the option of working physically or remotely. We expect the plug and play of freelance management experts and expertise to cost 25-30% less to an enterprise, keeps costs flexible and dramatically shortens time to “hire and deploy” from an average of 120 days to 15 days.

Gigs and Generations – Conceptual Clarity of Who We Need
Culturally, the US and Europe are more accepting of freelancing as full-time careers compared to the Asia Pacific. It is predicted that by 2027 the majority of the workforce in the US will be freelancers overtaking traditional employment. The buzz in the Asia Pacific has just started with both employers and employable talent accepting a new reality – learning to run businesses with a blended workforce, starting at the top of the pyramid. Particularly, since the ratio of new jobs to lost jobs is skewed in the wrong direction.
Power of Blended Workforce
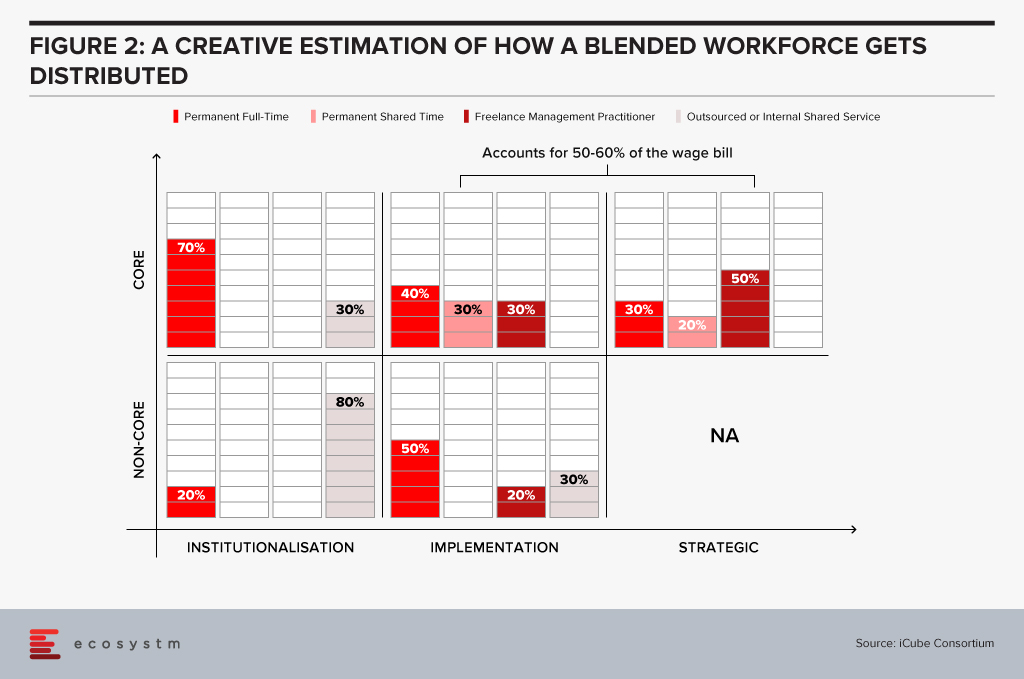
A blended workforce is a combination of permanent, part-time, full time-short term and turnkey practitioners, working as a single collaborative workforce. It is built around business activity clusters – Strategy, Implementation and Institutionalisation, applied to create a plan for core and non-core workforce to drive business.
A creative estimation of how a blended workforce gets distributed across the three business clusters is depicted below (Figure 2). What is important here is to recognise that the ratio of permanent to flexible workforce has to start at 10-15% across different levels. Enterprises will gain the most on cost optimisation when they focus on the management layer to go blended. Not an easy change to drive but then change is often driven by some tough calls and some low hanging fruits to build a sustainable cost model.
Developing & Implementing a Blended Workforce Strategy: What to Consider
Fix the core and flex the non-core should be the mantra
- Identify roles by each business and function
- Segregate core and non-core roles by job profiles
- Classify them into buckets of permanent full time, permanent part time, cyclical, and freelance on demand, based on:
- Time demand for the roles
- Importance to business goals
- Criticality to daily business output
- Criticality to daily or weekly business continuity
- Set up a process to engage and create a blended workforce strategy
- Implement the plan with a blend of a common self-service platform and a central client service team to source, engage and deploy workforces
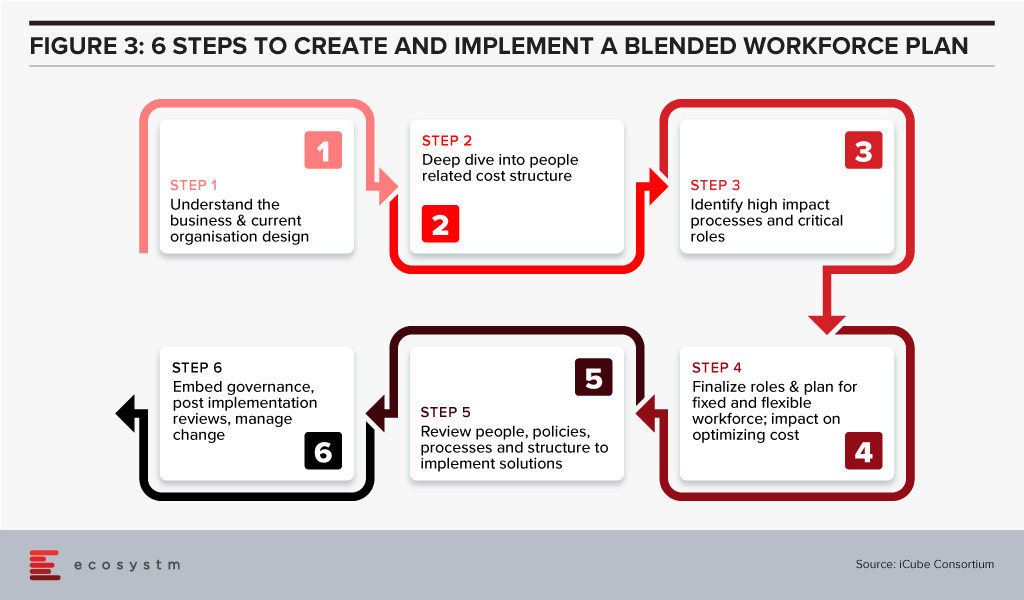
Once the process review is completed, the organisation structures will be finalised. Creation of a strategy and the process are the easier parts. A disciplined fulfilment of the plan is critical to success. So, is this the new normal? Pretty much yes, if organisations need to optimise costs and be agile to reduce or scale with freelance experts and shared talent pools.
The Potential Benefits of a Blended Workforce
A Blended Workforce will help reduce your talent scarcity gap, while providing thousands of work opportunities to locals who are freelance experts. So, what are these benefits that can make you sleep better at night better?
- Cost optimisation. Freelance experts do not need the fully loaded costs. They can work remotely or physically and do not need investment in regular training, insurance, or other related benefits.
- Targeted purpose-hire for short term. With deliverables specified upfront, measurable, results focused and tracked for closure.
- Job Sharing. Two or may be three, for the prize of one! Jobs can be dismantled to tasks or activity clusters to hire more than one expert in place of a full-time role. Enables razor sharp focus on sourcing for expertise, increases employment opportunities and accelerates productivity.
- Boundaryless with an opportunity to find cross-border talent pools to work on-demand, remotely. It cuts both ways- Singaporean talent finding work opportunities outside the country whilst the best talent from other countries made available to grow Singapore’s economy.
- Speed of hire is dramatically reduced (we have several client cases, with a reduction from an average of 120 days to 15 days, to clients’ delight!)
- Reduced infrastructure costs because the workforce works remotely or at best part-time physically. Easy to implement with hot desking, if needed but enables permanent cost reduction.
- Builds resilience by staying agile and nimble in the cost line, with an ability to scale up or down rapidly based on business needs.
How Open is the Financial Services Industry to Blended Workforce and Future of Work?
SolvecubeHR conducted a recent survey with CXOs across 22 countries, predominantly focused on the Asia Pacific region. Some key findings for the financial services industry are:
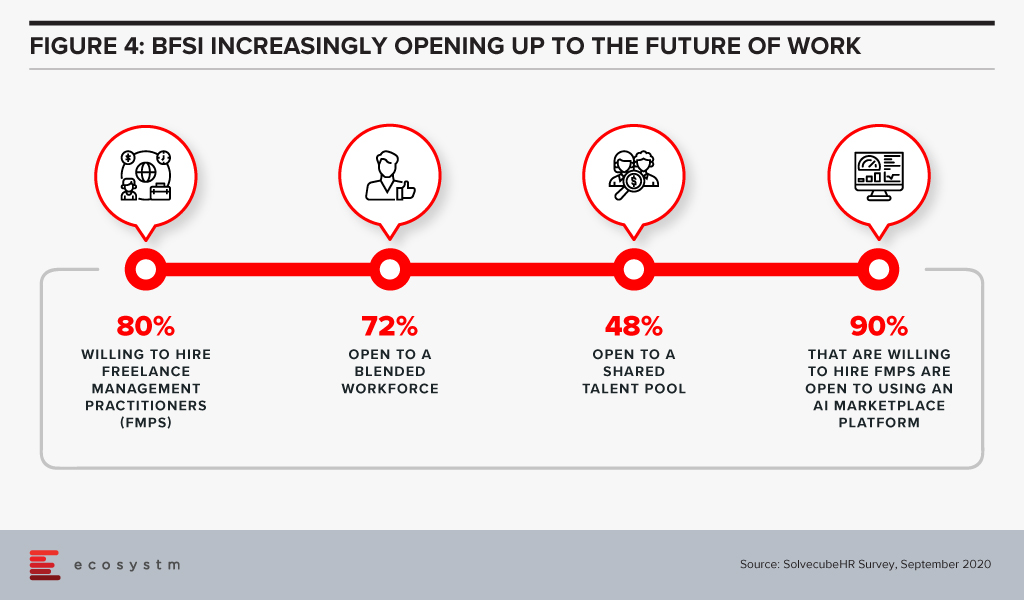
In summary, a blended workforce is the Future of Work. Asia Pacific will see a massive shift in its mindset from “jobs to work opportunities”. Employers and talent pools will embrace new ways of working to remain agile and prudent. The power of aggregation, curation, and collaboration by leveraging an AI matchmaking platform, backed by creation of shared talent pools, will be a game changer.
FinTech innovation and performance is here to stay and thrive. It needs to be backed by a well-oiled machine to support implementation of a blended workforce plan to institutionalise and scale.
We can build technologies to disintermediate people dependency, but we cannot take humans out of the human capital needed to build these technologies.
About iCube: iCube Consortium is a Singapore based, Human Capital Management (HCM) solutions firm, with an award-winning AI platform to source and manage freelance management experts and execute turnkey assignments in Asia and Middle East
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Talent Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics on Founders success and failure stories, pandemic impact on founders and talent development, upskilling and reskilling for the future of work.

COVID has delivered to many companies around the world a knock-out punch which has put them on the mat. They aren’t knocked out; just dazed, as any experienced fighter would be when caught off guard with a hard blow.
One way companies have dealt with the hard blow is in their Work Environment. At the beginning of the pandemic, many businesses simply sent office workers home. Some had corporate guidance and IT support; others simply were told to “make it work”. Post COVID, there will be a New Natural State of Equilibrium in the Work Environment and the business world. In this blog, I will talk more about the Work Environment.
First let me explain my interest in the subject. I have been a full-time mobile and part-time remote worker for over 13 years with a global technology company. I have designed many mobile office environments throughout Asia, working with business units to understand their needs and to educate them on the changes required and the change management process. For over 10 years I have taught this subject around the world to fellow professionals – across industries – in Asia, Australia/New Zealand, Europe and the USA. I was based in Hong Kong during the 2003 SARS outbreak. These experiences have given me a keen understanding and perspective on what happened in the early days of COVID-19, and insights on what the future could look like for many businesses.
Let’s look at some basic Work Environment facts:
- It costs a company an average of over US$10,000/year per employee for their physical space.
- Remote working happened very quickly at the start of COVID-19, almost overnight for some companies and employees.
- There are many venues available to conduct work from, over the long term: Office, Home, the 3rd Space (coffee shops, etc) and other venues.
I recently read the Harvard Business School (HBS) working paper titled, What Jobs are Being Done at Home During the COVID-19 Crisis? Evidence from Firm Level Surveys. Key findings from the report include:
- While overall levels of remote work are high, there is considerable variation across industries.
- Remote work is much more common in industries with better educated and better paid workers.
- Employers think that there has been less productivity loss from remote working in better educated and higher paid industries.
- More than one-third of firms that had employees switch to remote work believe that it will remain more common at their company even after the COVID crisis ends.
The Emergence of the Future of Work
Mobile & Remote Work. The cost of housing a worker in an office environment has always been a concern for senior management. The cost quickly adds up, even for a small or medium-sized firm. The physical cost of the office is typically the second largest expense for a company, after employees’ salaries. This is one reason that “densification” has occurred in the office environment over the past 10 years or so. It is also a reason remote working (working outside the office – from home, coffee shop, hotel, airport lounge, etc.) has been attractive to companies. If the office environment is designed with multiple work-type spaces (e.g. collaborative, non-collaborative, quiet, etc.), a permanently designated workspace is not required for a worker. This type of Work Environment is known as a mobile environment. Both of these Work Environments – remote and mobile – have been the trend for many companies (especially technology and financial firms).
Co-working. Beginning a few years ago, another Work Environment emerged: Co-working. One of the early market leaders was WeWork. Co-working is very similar to the mobile environment. It has the added benefit of not requiring any capital cost for the fit-out (tenant improvements). The company or individual rents a desk or space in a co-working environment and just pays the monthly fee. There is no delay to find the space, sign the lease, design, or construct the space, and no capital required for the construction cost. It is a “plug and play” space.
Blended Model. Given the selection, worker typology, and flexibility of space, all these alternatives will be used in some capacity in the Future of Work (FoW). The Work Environment will be a blend of these environments. Some have predicted the death of the office building. Ecosystm research finds that only 16% of organisations are looking to reduce their commercial office space, going into 2021. People are social creatures and need interaction with others, either for effective work collaboration or just to socialise.
The Future of the Work Environment
Figure 1 shows a compilation of the various type of Work Environments which office workers use and how they came about.
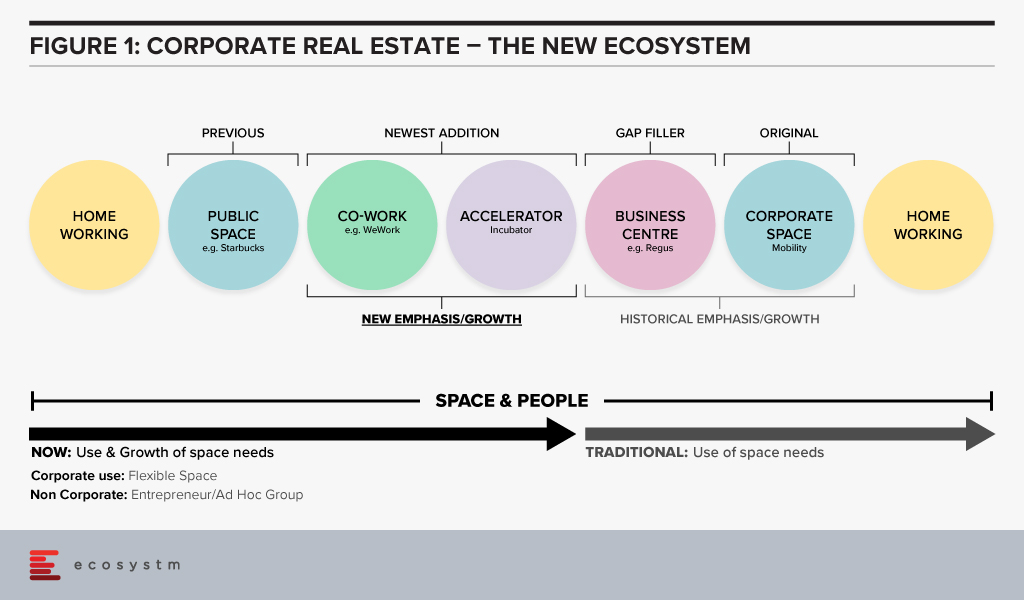
Each company, especially post-COVID, will have to look at their business strategy and determine how they will best solution their Work Environment to get the maximum benefits. These are the main questions each company has to ask and answer at a strategic level:
- What is the best workspace solution for my company and employees?
- Do employees want the corporate leased space? Does it help make them more productive?
- How is the marketplace (landlords) responding to this demand if a company is leasing space?
Role-dependent Remote Workers. Returning to the larger topic of the Work Environment, the HBS paper states there are different rates of remoteness across industries. I would assert that in addition there are different rates of remoteness among the types of workers. A salesperson needs to interact differently with fellow company employees compared to an accountant or an administrative person. Workers in the Banking industry interact differently compared to workers in the Technology industry. The article also points out that a better educated and better paid worker – or a knowledge worker – can more easily be a remote worker. For those of us who have been working in the mobile/remote Work Environment for many years, we know and understand this. Knowledge workers are not employed for their physical skills. For example, an assembly line worker in an auto factory cannot be remote.
Determining Work Typology. The paper also states that remote working will be more common in the companies that have not experienced a dramatic decrease in productivity from remote working. This has been asserted and demonstrated by us, the professionals in the corporate Real Estate industry. The industry has been experiencing increased productivity for many years. We have also conducted in-house studies of the various business groups that have experienced remote working. We have even gone so far as to provide work typologies for the various types of workers. Each typology uses the office Work Environment differently and has varying levels of remote abilities.
Need for Change Management. A critical component of remote work effectiveness is the mindset shift by both the employee and the manager. The managers have to modify their style to more of a “management by performance”, versus just walking around and checking whether people are busy. Similarly, employees have to understand they are being trusted to work unsupervised but will have to accomplish the required work and be held responsible. The manager and employee relationship will require new performance measures to hold people accountable and determine whether they are being effective and productive in their remote environment. All of this requires a change management program to educate both without compromising the corporate culture.
When the pendulum finally comes to rest in the near future at what will be the New Normal, the Work Environment will be modified. But, more importantly, the mindset of employees and managers will have to be adjusted. This new mindset will be required so each company can be more agile to meet the new challenges that will be awaiting every company and industry throughout the world. This will enable a company to not only survive but thrive in the next wave of quantum shifts. And yes, there will be another wave of quantum shifts in the future, lest we forget the examples of the past (eg. the 2007 Global Financial Crisis, 2003 SARS, etc.).
This article has focused on the Work Environment. The Work Environment is one of the four components of the 360o Future of Work practice at Ecosystm. The other three components are: People, Technology, and Business. All four are required to be in balance to enable companies to meet future challenges, competitors, and unknown black swans.