In 2024, technology vendors have heavily invested in AI Agents, recognising their potential to drive significant value. These tools leverage well-governed, small datasets to integrate seamlessly with applications like Workday, Salesforce, ServiceNow, and Dayforce, enhancing processes and outcomes.
2025 is poised to be the year of AI Agent adoption. Designed to automate specific tasks within existing workflows, AI Agents will transform customer experiences, streamline operations, and boost efficiency. Unlike traditional AI deployments, they offer a gradual, non-disruptive approach, augmenting human capabilities without overhauling processes. As organisations adopt new software versions with embedded AI capabilities, 2025 will mark a pivotal shift in customer experience delivery.
Ecosystm analysts Audrey William, Melanie Disse, and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 trends shaping customer experience in 2025.
Click here to download ‘AI-Powered Customer Experience: Top 5 Trends for 2025’ as a PDF
1. AI Won’t Wow Many Customers in 2025
The data is in – the real focus of AI over the next few years will be on productivity and cost savings.
Senior management and boards of directors want to achieve more with less – so even when AI is being used to serve customers, it will be focused on reducing back-end and human costs.
There will be exceptions, such as the adoption of AI agents in contact centres. However, AI agents must match or exceed human performance to see broad adoption.
However, the primary focus in contact centres will be on reducing Average Handling Time (AHT), increasing call volume per agent, accelerating agent onboarding, and automating customer follow-ups.

2. Organisations Will Start Treating CX as a Team Sport
As CX programs mature, 2025 will highlight the need to break down not only data and technology siloes but also organisational and cultural barriers to achieve AI-powered CX and business success.
AI and GenAI have unlocked new sources of customer data, prompting leaders to reorganise and adopt a mindset shift about CX. This involves redefining CX as a collective effort, engaging the entire organisation in the journey.
Technologies and KPIs must be aligned to drive customer AND business needs, not purely driving success in siloed areas.

3. The First “AGI Agents” Will Emerge
AI Agents are set to explode in 2025, but even more disruptive developments in AI are on the horizon.
As conversational computing gains traction, fuelled by advances in GenAI and progress toward AGI, “Complex AI Agents” will emerge.
These “AGI Agents” will mimic certain human-like capabilities, though not fully replicating human cognition, earning their “Agent” designation.
The first use cases will likely be in software development, where these agents will act as intelligent platforms capable of transforming a described digital process or service into reality. They may include design, inbuilt testing, quality assurance, and the ability to learn from existing IP (e.g., “create an app with the same capabilities as X”).

4. Intelligent AI Bots Will Enhance Contact Centre Efficiency
The often-overlooked aspect of CX is the “operational side”, where Operations Managers face significant challenges in maintaining a real-time pulse on contact centre activities.
For most organisations, this remains a highly manual and reactive process. Intelligent workflow bots can revolutionise this by acting as gatekeepers, instantly identifying issues and triggering real-time corrective actions. These bots can even halt processes causing customer dissatisfaction, ensuring problems are addressed proactively.
Operational inefficiencies, such as back-office delays, unanswered emails, and slow issue containment, create constant headaches. Integrating bots into contact centre operations will significantly reduce time wasted on these inefficiencies, enhancing both employee and customer experiences.

5. Employee Experience Will Catch Up to CX Maturity
Employee experience (EX) has traditionally lagged behind CX in focus and technology investment. However, AI-powered technologies are now enabling organisations to apply CX use cases to EX efforts, using advanced data analysis, summaries, and recommendations.
AI and GenAI tools will enhance understanding of employee satisfaction and engagement while predicting churn and retention drivers.
HR teams and leaders will leverage these tools to optimise performance management and improve hiring and retention outcomes.
Additionally, organisations will begin to connect EX with financial performance, identifying key drivers of engagement and linking them to business success. This shift will position EX as a strategic priority, integral to achieving organisational goals.


AI has already had a significant impact on the tech industry, rapidly evolving software development, data analysis, and automation. However, its potential extends into all industries – from the precision of agriculture to the intricacies of life sciences research, and the enhanced customer experiences across multiple sectors.
While we have seen the widespread adoption of AI-powered productivity tools, 2025 promises a bigger transformation. Organisations across industries will shift focus from mere innovation to quantifiable value. In sectors where AI has already shown early success, businesses will aim to scale these applications to directly impact their revenue and profitability. In others, it will accelerate research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and innovations in the years to come. Regardless of the specific industry, one thing is certain: AI will be a driving force, reshaping business models and competitive landscapes.
Ecosystm analysts Alan Hesketh, Clay Miller, Peter Carr, Sash Mukherjee, and Steve Shipley present the top trends shaping key industries in 2025.
Click here to download ‘AI’s Impact on Industry in 2025’ as a PDF
1. GenAI Virtual Agents Will Reshape Public Sector Efficiency
Operating within highly structured, compliance-driven environments, public sector organisations are well-positioned to benefit from GenAI Agents.
These agents excel when powered LLMs tailored to sector-specific needs, informed by documented legislation, regulations, and policies. The result will be significant improvements in how governments manage rising service demands and enhance citizen interactions. From automating routine enquiries to supporting complex administrative processes, GenAI Virtual Agents will enable public sector to streamline operations without compromising compliance. Crucially, these innovations will also address jurisdictional labour and regulatory requirements, ensuring ethical and legal adherence. As GenAI technology matures, it will reshape public service delivery by combining scalability, precision, and responsiveness.

2. Healthcare Will Lead in Innovation; Lag in Adoption
In 2025, healthcare will undergo transformative innovations driven by advancements in AI, remote medicine, and biotechnology. Innovations will include personalised healthcare driven by real-time data for tailored wellness plans and preventive care, predictive AI tackling global challenges like aging populations and pandemics, virtual healthcare tools like VR therapy and chatbots enhancing accessibility, and breakthroughs in nanomedicine, digital therapeutics, and next-generation genomic sequencing.
Startups and innovators will often lead the way, driven by a desire to make an impact.
However, governments will lack the will to embrace these technologies. After significant spending on crisis management, healthcare ministries will likely hesitate to commit to fresh large-scale investments.

3. Agentic AI Will Move from Bank Credit Recommendation to Approval
Through 2024, we have seen a significant upturn in Agentic AI making credit approval recommendations, providing human credit managers with the ability to approve more loans more quickly. Yet, it was still the mantra that ‘AI recommends—humans approve.’ That will change in 2025.
AI will ‘approve’ much more and much larger credit requests.
The impact will be multi-faceted: banks will greatly enhance client access to credit, offering 24/7 availability and reducing the credit approval and origination cycle to mere seconds. This will drive increased consumer lending for high-value purchases, such as major appliances, electronics, and household goods.

4. AI-Powered Demand Forecasting Will Transform Retail
There will be a significant shift away from math-based tools to predictive AI using an organisation’s own data. This technology will empower businesses to analyse massive datasets, including sales history, market trends, and social media, to generate highly accurate demand predictions. Adding external influencing factors such as weather and events will be simplified.
The forecasts will enable companies to optimise inventory levels, minimise stockouts and overstock situations, reduce waste, and increase profitability. Early adopters are already leveraging AI to anticipate fashion trends and adjust production accordingly.
No more worrying about capturing “Demand Influencing Factors” – it will all be derived from the organisation’s data.

5. AI-Powered Custom-Tailored Insurance Will Be the New Norm
Insurers will harness real-time customer data, including behavioural patterns, lifestyle choices, and life stage indicators, to create dynamic policies that adapt to individual needs. Machine learning will process vast datasets to refine risk predictions and deliver highly personalised coverage. This will produce insurance products with unparalleled relevance and flexibility, closely aligning with each policyholder’s changing circumstances. Consumers will enjoy transparent pricing and tailored options that reflect their unique risk profiles, often resulting in cost savings. At the same time, insurers will benefit from enhanced risk assessment, reduced fraud, and increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This evolution will redefine the customer-insurer relationship, making insurance a more dynamic and responsive service that adjusts to life’s changes in real-time.


2024 was a year marked by intense AI-driven innovation. While the hype surrounding AI may have reached a fever pitch, the technology’s transformative potential is undeniable.
The growing interest in AI can be attributed to several factors: the democratisation of AI, with tools and platforms now accessible to businesses of all sizes; AI’s appeal to business leaders, offering actionable insights and process automation; and aggressive marketing by major tech companies, which has amplified the excitement and hype surrounding AI.
2025 will be a year defined by AI, with its transformative impact rippling across industries. However, other geopolitical and social factors will also significantly shape the tech landscape.
Ecosystm analysts Achim Granzen, Alan Hesketh, Audrey William, Clay Miller, Darian Bird, Manish Goenka, Richard Wilkins, Sash Mukherjee, Simona Dimovski, and Tim Sheedy present the key trends and disruptors shaping the tech market in 2025.
Click here to download ‘Key Tech Trends & Disruptors in 2025’ as a PDF
1. Quantum Computing Will Drive Major Transformation in the Tech Industry
Advancements in qubit technology, quantum error correction, and hybrid quantum-classical systems will accelerate breakthroughs in complex problem-solving and machine learning. Quantum communications will revolutionise data security with quantum key distribution, providing nearly unbreakable communication channels. As quantum encryption becomes more widespread, it will replace current cryptographic methods, protecting sensitive data from future quantum-enabled attacks.
With quantum computing threatening encryption standards like RSA and ECC, post-quantum encryption will be critical for data security.
While the full impact of quantum computers is expected within the next few years, 2025 will be pivotal in the transition toward quantum-resistant security measures and infrastructure.

2. Many Will Try, But Few Will Succeed as Platform Companies
Hypergrowth occurs when companies shift from selling products to becoming platform providers. Unlike traditional businesses, platforms don’t own inventory; their value lies in proprietary data and software that connect buyers, sellers, and consumers. Platforms disrupt industries and often outperform legacy businesses, with examples like Uber, Amazon, and Meta, and disruptors like Lemonade in insurance and Wise in international funds transfer.
In 2025, many companies will aim to become platform businesses, with AI seen as a key driver.
They will begin creating platforms and building ecosystems around them – some within existing brands, others launching new ones or even new subsidiaries to seize this opportunity.

3. A Trans-Atlantic Divide Will Emerge in AI Regulation
The EU is poised to continue its rigorous approach to AI regulation, emphasisng ethical considerations and robust governance. This is evident in the recent AI Act, which imposes stringent guidelines and penalties for violations. The EU’s commitment to responsible AI development is likely to lead to a more cautious and controlled innovation landscape.
In contrast, the US, under a new administration, may adopt a more lenient regulatory stance towards AI. This shift could accelerate innovation and foster a more permissive environment for AI development. However, it may also raise concerns about potential risks and unintended consequences.
This divergence in regulatory frameworks could create significant challenges for multinational companies operating in both regions.

4. The Rise of AI-Driven Ecosystem Platforms Will Shape Tech Investments
By 2025, AI-driven ecosystem platforms will dominate tech investments, fueled by technological convergence, market efficiency demands, and evolving regulations. These platforms will integrate AI, IoT, cloud, and data analytics to create seamless, predictive ecosystems that transcend traditional industry boundaries.
Key drivers include advancements in AI, global supply chain disruptions, and rising ESG expectations. Regulatory shifts, such as the EU’s AI Act, will further push for compliant, ethical platforms emphasising transparency and accountability.
For businesses, this shift redefines technology as interconnected ecosystems driving efficiency, innovation, and customer value.

5. AI-Powered Data Fabrics Will be the Foundation for Data-Driven Success
In 2025, AI-powered data fabrics will become a core technology for large organisations.
They will transition from basic data management tools to intelligent systems that deliver value across the entire data lifecycle. Organisations will finally be able to get control of their data governance.
AI’s enhanced role will automate essential data functions, including intelligent data integration and autonomous connection to diverse data sources. AI will also enable proactive data quality management, predicting and preventing errors for improved reliability. AI-driven data fabrics will also offer automated data discovery and mapping, dynamic data quality and governance, intelligent data integration, and enhanced data access and delivery.

6. Focus Will Shift From AI Models to Intelligence Gaps & Performance
While many organisations are investing in AI, only those that started their transformation in 2024 are truly AI-led. Most have become AI-driven through embedded AI in enterprise systems as tech providers continue to evolve their offerings. However, these multi-vendor environments often lack synergy, creating gaps and blind spots.
In 2025, organisations will pause their investments to assess AI capabilities and identify these gaps.
Once they pinpoint the blind spots, investments will refocus not on new AI models, but on areas like model orchestration to manage workflows and ensure peak performance; vendor management to establish unified governance frameworks for flexibility and compliance; and eventually automated AI lifecycle management, with centralised inventories and monitoring to track performance and detect issues like model drift.

7. Specialised Small Language Models Will Gain Traction
GenAI, driven by LLMs, has dominated the spotlight, fueling both excitement and concerns about AI. However, LLM-based GenAI is entering a phase of diminishing returns, both in terms of individual model capabilities and the number of available models. Only a few providers will have the resources to develop LLMs, focusing on a limited number of models.
This will see the increased popularity of small language models (SLMs), that are tailored for a specific purpose, use case, or environment. These models will be developed by startups, organisations, and enterprises with deep domain knowledge and data. They will be fully commercialised driving narrow but distinct ROI.
There will be an increased demand for GPU-as-a-service and SLM-as-a-service, and the platforms which can support these.

8. Multi-agent AI Systems Will Help Manage Complexity and Collaboration
Isolated AI tools that can perform narrow tasks lack the adaptability and coordination required for real-time decision-making. Multi-agent systems, in contrast, consist of decentralised agents that collaborate, share information, and make independent decisions while working toward a common goal. This approach not only improves efficiency but also enhances resilience in rapidly changing conditions.
Early use cases will be in complex environments that require cooperation between multiple stakeholders.
Multi-agent systems will optimise logistics by continuously analysing disruptions and dynamically balancing supply and demand in energy grids. These multi-agent systems will also operate in competitive modes, such as algorithmic trading, ad auctions, and ecommerce recommender systems.

9. Super Apps Will Expand into Rural & Underserved Markets in Asia Pacific
Super apps are set to reshape rural economies, fueled by increased internet access, affordable tech, and heavy government investment in digital infrastructure. Their localised, all-in-one services unlock untapped potential in underserved regions, fostering inclusivity and innovation.
By 2025, super apps will deepen their reach across Asia, integrating communication, payments, and logistics into seamless platforms.
Leveraging affordable mobile devices, cloud-native technologies, and localised services, they will penetrate rural and underserved areas with tailored solutions like agricultural marketplaces, local logistics, and expanded government services. Enterprises investing in agile cloud infrastructure will drive this evolution, bridging the digital divide, boosting economic growth, and enhancing user experiences for millions.

10. Intense Debates Over Remote vs. In-Office Work Will Persist in Asia Pacific
Employers in Asia Pacific will enforce stricter return-to-office policies, linking them to performance metrics and benefits to justify investments in physical spaces and enhance workforce productivity.
However, remote collaboration will remain integral, even for in-office teams.
The push for human-centred tech will grow, focusing on employee well-being and flexibility through AI-powered tools and hybrid platforms. Companies will prioritise enhancing employee experiences with personalised, adaptable workspaces, while office designs will increasingly incorporate biophilic elements, blending nature and technology to support seamless collaboration and remote integration.


Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on the Retail industry.
Click here to download ‘AI in Retail: Success Stories & Insights’ as a PDF
From personalised product recommendations to predictive analytics, AI is helping retailers deliver exceptional customer experiences and optimise their operations. However, many retailers are still grappling with the complexities of AI implementation. Those who can successfully navigate this challenge and harness the power of AI will emerge as industry leaders, driving innovation and shaping the future of retail.
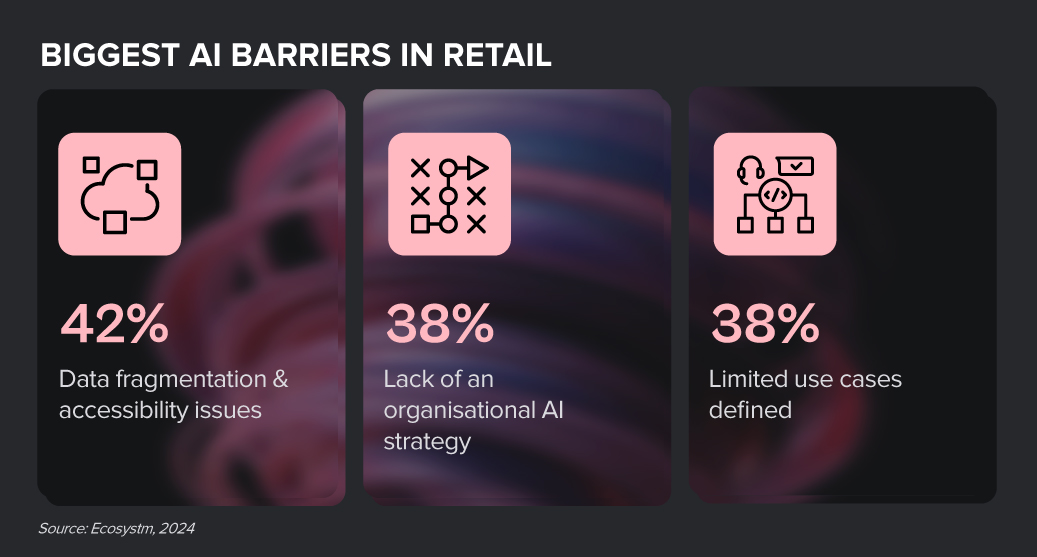
Despite the challenges, Retail organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Customer Experience & Engagement
- 2. Supply Chain Optimisation
- 3. Fraud & Risk Analysis
Customer Experience & Engagement
- Conversational AI. Providing real-time customer support and answering queries
- Personalisation. Offering tailored product suggestions based on customer preferences and behaviour
- Virtual Try-On. Allowing customers to visualise products in different settings using AR
“AI has helped us to refine our customer chatbots to allow for more self-service. We’ve experienced faster customer order processing and quicker resolution of issues, putting control directly in the hands of our customers.” – CX LEADER
Supply Chain Optimisation
- Inventory Management. Automating inventory management processes to ensure optimal stock levels
- Supply Chain Visibility. Monitoring and optimising supply chain operations, including logistics and distribution
- Demand Forecasting. Predicting sales and demand trends to optimise inventory and production planning
“We use AI to optimise the supply chain, saving operational costs. Digital supply chains and cloud-based tracking systems streamline operations and enhance efficiency.” – CFO
Fraud & Risk Analysis
- Fraud Detection. Identify and prevent fraudulent activities, such as online fraud and chargebacks
- Risk Assessment. Assessing risk factors associated with customer transactions and preventing losses
- Customer & Market Insights. Understanding customer behaviour, market trends, and growth opportunities
“With eCommerce as a key market force, understanding customer habits is crucial to ensuring we have the right products in stock and optimising our pricing strategy.” – COO

The cryptocurrency industry is no longer just a niche market; it’s a burgeoning global financial force, poised to reach a staggering USD 11.7 billion by 2030. Fuelled by rapid technological advancements, evolving regulatory landscapes, and increased mainstream adoption, the sector is facing both unprecedented challenges and exciting opportunities. As blockchain and digital currencies continue to disrupt traditional finance, understanding the key trends driving these changes is essential for anyone navigating the crypto ecosystem.
#1 AI’s Game-Changing Impact on Crypto Exchanges
AI is revolutionising the way crypto exchanges operate – from enhanced efficiency and security to a more personalised user experience.
One of the most significant contributions of AI is the use of automated trading bots. These bots can analyse vast amounts of market data, predict price movements, and execute trades with precision, often outperforming human traders. By operating 24/7 and eliminating emotional biases, AI-powered bots offer a significant advantage in the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency trading.
AI also plays a crucial role in improving security on crypto exchanges. By using machine learning algorithms to monitor and analyse transaction patterns, AI can identify and mitigate the risks of hacks and fraud, which have plagued the cryptocurrency space for years. For example, in 2023 alone, crypto scams led to losses of over USD 5.6 billion in the US.
AI personalises the user experience by offering tailored recommendations based on individual trading behaviour. Additionally, AI performs market sentiment analysis by processing unstructured data from social media, news outlets, and other online platforms, providing valuable insights into market trends. AI also plays a crucial role in improving security on crypto exchanges.
#2 Global Cryptocurrency Regulations: A Maturing Landscape
Cryptocurrency regulations are evolving rapidly around the world as governments strive to manage risks and protect consumers. The Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation in the EU is a significant milestone, requiring licensing for all crypto firms operating within the bloc and mandating stringent consumer protection measures, including capital requirements for stablecoins.
In the US, efforts like the Financial Innovation and Technology (FIT) for the 21st Century Act and the Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act are expanding oversight of the industry and clarifying the roles of different regulatory bodies. Similar regulatory movements are underway across Asia. Japan has recognised crypto as legal property, and South Korea passed the Virtual Asset Users Protection Act to increase transparency. However, countries like China and India maintain restrictive approaches, with bans on trading and mining.
Brazil’s 2023 Cryptoassets Act demonstrates the global trend towards more robust regulation, aiming to prevent fraud in the crypto sector.
#3 Mergers and Acquisitions: A Strategic Play in the Crypto Space
As traditional financial institutions race to embrace the digital asset revolution, mergers and acquisitions are becoming a strategic tool to gain a foothold in the cryptocurrency market. By acquiring crypto companies with real-world applications and robust infrastructure, these institutions aim to expand their digital asset capabilities and stay ahead of the curve.
Examples like Ripple’s acquisition of Metaco and Coinbase’s purchase of One River Digital highlight the growing interest in integrating traditional financial services with blockchain technology. These M&A deals not only enhance service offerings but also facilitate entry into new markets and the development of innovative solutions.
Looking ahead, we can expect to see even larger financial institutions playing a more active role in crypto mergers and acquisitions. As the demand for scalable, compliant blockchain solutions continues to grow, strategic partnerships and acquisitions will become increasingly important in paving the way for broader adoption of digital assets.
#4 CBDCs and Stablecoins: A New Era in Digital Finance
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are gaining significant traction, with 86% of central banks actively exploring their potential. Major economies like the UK, EU, and US are in various stages of CBDC research and development, carefully considering privacy concerns, financial stability, and the impact on commercial banks. Smaller nations like the Bahamas, Nigeria, and Jamaica have taken the lead, launching CBDCs to serve as digital alternatives to traditional fiat currencies.
In the private sector, stablecoins have experienced substantial adoption. Major financial institutions and payment providers are integrating stablecoins like USDC and Tether (USDT) into their services, processing billions in daily transaction volume. This growth has prompted regulators worldwide to develop comprehensive frameworks, such as the EU’s MiCA regulation and similar efforts in the UK and US. These regulatory initiatives aim to provide clear guidelines while fostering innovation.
As traditional financial institutions explore stablecoin integration for both retail and wholesale applications, the future of digital finance looks increasingly promising.
#5 The Focus on User Experience and Security
As the crypto landscape continues to evolve, the focus on user experience and security has never been more critical. Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, targeting crypto exchanges and DeFi platforms alike. Historically, the industry has been developer-centric, with little attention paid to creating intuitive platforms for everyday users. However, as more consumers embrace blockchain-based financial services, there is a growing demand for seamless, user-friendly interfaces.
Security is another major concern. High-profile hacks and fraud have tarnished the reputation of the crypto industry, leading to skepticism among users and regulators. DeFi platforms, in particular, have been frequent targets due to vulnerabilities in smart contracts. To foster widespread trust and adoption, the industry must prioritise integrating security features by design, such as blockchain analytics for detecting fraudulent activities and advanced risk management tools.
Emerging technologies like social recovery wallets, which help users regain access to lost funds, and improvements in blockchain scalability and efficiency, will be instrumental in attracting more mainstream users.
Crypto’s Future: A Balancing Act
The future of the crypto industry hinges on its ability to strike a delicate balance between innovation, regulation, and security. As digital assets become more deeply integrated into mainstream finance, we can expect to see a surge in tokenised real-world assets, stablecoins, and central bank digital currencies.
Collaboration between regulators, financial institutions, and tech innovators will be essential in shaping a secure and inclusive ecosystem. Ultimately, the success of crypto will depend on its ability to build trust while delivering the efficiency and transparency that define a rapidly evolving digital economy.

Southeast Asia’s banking sector is poised for significant digital transformation. With projected Net Interest Income reaching USD 148 billion by 2024, the market is ripe for continued growth. While traditional banks still hold a dominant position, digital players are making significant inroads. To thrive in this evolving landscape, financial institutions must adapt to rising customer expectations, stringent regulations, and the imperative for resilience. This will require a seamless collaboration between technology and business teams.
To uncover how banks in Southeast Asia are navigating this complex landscape and what it takes to succeed, Ecosystm engaged in in-depth conversations with senior banking executives and technology leaders as part of our research initiatives. Here are the highlights of the discussions with leaders across the region.
#1 Achieving Hyper-Personalisation Through AI
As banks strive to deliver highly personalised financial services, AI-driven models are becoming increasingly essential. These models analyse customer behaviour to anticipate needs, predict future behaviour, and offer relevant services at the right time. AI-powered tools like chatbots and virtual assistants further enhance real-time customer support.

Hyper-personalisation, while promising, comes with its challenges – particularly around data privacy and security. To deliver deeply tailored services, banks must collect extensive customer information, which raises the question: how can they ensure this sensitive data remains protected?

AI projects require a delicate balance between innovation and regulatory compliance. Regulations often serve as the right set of guardrails within which banks can innovate. However, banks – especially those with cross-border operations – must establish internal guidelines that consider the regulatory landscape of multiple jurisdictions.
#2 Beyond AI: Other Emerging Technologies
AI isn’t the only emerging technology reshaping Southeast Asian banking. Banks are increasingly adopting technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and blockchain to boost efficiency and engagement. RPA is automating repetitive tasks, such as data entry and compliance checks, freeing up staff for higher-value work. CIMB in Malaysia reports seeing a 35-50% productivity increase thanks to RPA. Blockchain is being explored for secure, transparent transactions, especially cross-border payments. The Asian Development Bank successfully trialled blockchain for faster, safer bond settlements. While AR and VR are still emerging in banking, they offer potential for enhanced customer engagement. Banks are experimenting with immersive experiences like virtual branch visits and interactive financial education tools.
The convergence of these emerging technologies will drive innovation and meet the rising demand for seamless, secure, and personalised banking services in the digital age. This is particularly true for banks that have the foresight to future-proof their tech foundation as part of their ongoing modernisation efforts. Emerging technologies offer exciting opportunities to enhance customer engagement, but they shouldn’t be used merely as marketing gimmicks. The focus must be on delivering tangible benefits that improve customer outcomes.

#3 Greater Banking-Fintech Collaboration
The digital payments landscape in Southeast Asia is experiencing rapid growth, with a projected 10% increase between 2024-2028. Digital wallets and contactless payments are becoming the norm, and platforms like GrabPay, GoPay, and ShopeePay are dominating the market. These platforms not only offer convenience but also enhance financial inclusion by reaching underbanked populations in remote areas.
The rise of digital payments has significantly impacted traditional banks. To remain relevant in this increasingly cashless society, banks are collaborating with fintech companies to integrate digital payment solutions into their services. For instance, Indonesia’s Bank Mandiri collaborated with digital credit services provider Kredivo to provide customers with access to affordable and convenient credit options.
Partnerships between traditional banks and fintechs are essential for staying competitive in the digital age, especially in areas like digital payments, data analytics, and customer experience.

While these collaborations offer opportunities, they also pose challenges. Banks must invest in advanced fraud detection, AI monitoring, and robust authentication to secure digital payments. Once banks adopt a mindset of collaboration with innovators, they can leverage numerous innovations in the cybersecurity space to address these challenges.
#4 Agile Infrastructure for an Agile Business
While the banking industry is considered a pioneer in implementing digital technologies, its approach to cloud has been more cautious. While interest remained high, balancing security and regulatory concerns with cloud agility impacted the pace. Hybrid multi-cloud environments has accelerated banking cloud adoption.

Leveraging public and private clouds optimises IT costs, offering flexibility and scalability for changing business needs. Hybrid cloud allows resource adjustments for peak demand or cost reductions off-peak. Access to cloud-native services accelerates innovation, enabling rapid application development and improved competitiveness. As the industry adopts GenAI, it requires infrastructure capable of handling vast data, massive computing power, advanced security, and rapid scalability – all strengths of hybrid cloud.
Replicating critical applications and data across multiple locations ensures disaster recovery and business continuity. A multi-cloud strategy also helps avoid vendor lock-in, diversifies cloud providers, and reduces exposure to outages.

Hybrid cloud adoption offers benefits but also presents challenges for banks. Managing the environment is complex, needing coordination across platforms and skilled personnel. Ensuring data security and compliance across on-prem and public cloud infrastructure is demanding, requiring robust measures. Network latency and performance issues can arise, making careful design and optimisation crucial. Integrating on-prem systems with public cloud services is time-consuming and needs investment in tools and expertise.
#5 Cyber Measures to Promote Customer & Stakeholder Trust
The banking sector is undergoing rapid AI-driven digital transformation, focusing on areas like digital customer experiences, fraud detection, and risk assessment. However, this shift also increases cybersecurity risks, with the majority of banking technology leaders anticipate inevitable data breaches and outages.

Key challenges include expanding technology use, such as cloud adoption and AI integration, and employee-related vulnerabilities like phishing. Banks in Southeast Asia are investing heavily in modernising infrastructure, software, and cybersecurity.
Banks must update cybersecurity strategies to detect threats early, minimise damage, and prevent lateral movement within networks.

Employee training, clear security policies, and a culture of security consciousness are critical in preventing breaches.
Regulatory compliance remains a significant concern, but banks are encouraged to move beyond compliance checklists and adopt risk-based, intelligence-led strategies. AI will play a key role in automating compliance and enhancing Security Operations Centres (SOCs), allowing for faster threat detection and response. Ultimately, the BFSI sector must prioritise cybersecurity continuously based on risk, rather than solely on regulatory demands.
Breaking Down Barriers: The Role of Collaboration in Banking Transformation
Successful banking transformation hinges on a seamless collaboration between technology and business teams. By aligning strategies, fostering open communication, and encouraging cross-functional cooperation, banks can effectively leverage emerging technologies to drive innovation, enhance customer experience, and improve efficiency.
A prime example of the power of collaboration is the success of AI initiatives in addressing specific business challenges.

This user-centric approach ensures that technology addresses real business needs.
By fostering a culture of collaboration, banks can promote continuous learning, idea sharing, and innovation, ultimately driving successful transformation and long-term growth in the competitive digital landscape.

India is undergoing a remarkable transformation across various industries, driven by rapid technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and a dynamic economic landscape. From the integration of new-age technologies like GenAI to the adoption of sustainable practices, industries in India are redefining their operations and strategies to stay competitive and relevant.
Here are some organisations that are leading the way.
Download ‘From Tradition to Innovation: Industry Transformation in India’ as a PDF
Redefining Customer Experience in the Financial Sector
Financial inclusion. India’s largest bank, the State Bank of India, is leading financial inclusion with its YONO app, to enhance accessibility. Initial offerings include five core banking services: cash withdrawals, cash deposits, fund transfers, balance inquiries, and mini statements, with plans to include account opening and social security scheme enrollments.
Customer Experience. ICICI Bank leverages RPA to streamline repetitive tasks, enhancing customer service with its virtual assistant, iPal, for handling queries and transactions. HDFC Bank customer preference insights to offer tailored financial solutions, while Axis Bank embraces a cloud-first strategy to digitise its platform and improve customer interfaces.
Indian banks are also collaborating with fintechs to harness new technologies for better customer experiences. YES Bank has partnered with Paisabazaar to simplify loan applications, and Canara HSBC Life Insurance has teamed up with Artivatic.AI to enhance its insurance processes via an AI-driven platform.
Improving Healthcare Access
Indian healthcare organisations are harnessing technology to enhance efficiency, improve patient experiences, and enable remote care.
Apollo Hospitals has launched an automated patient monitoring system that alerts experts to health deteriorations, enabling timely interventions through remote monitoring. Manipal Hospitals’ video consultation app reduces emergency department pressure by providing medical advice, lab report access, bill payments, appointment bookings, and home healthcare requests, as well as home medication delivery and Fitbit monitoring. Omni Hospitals has also implemented AI-based telemedicine for enhanced patient engagement and remote monitoring.
The government is also driving the improvement of healthcare access. eSanjeevani is the world’s largest government-owned telemedicine system, with the capacity to handle up to a million patients a day.
Driving Retail Agility & Consumer Engagement
India’s Retail sector, the fourth largest globally, contributes over 10% of the nation’s GDP. To stay competitive and meet evolving consumer demands, Indian retailers are rapidly adopting digital technologies, from eCommerce platforms to AI.
Omnichannel Strategies. Reliance Retail integrates physical stores with digital platforms like JioMart to boost sales and customer engagement. Tata CLiQ’s “phygital” approach merges online and offline shopping for greater convenience while Shoppers Stop uses RFID and data analytics for improved in-store experiences, online shopping, and targeted marketing.
Retail AI. Flipkart’s AI-powered shopping assistant, Flippi uses ML for conversational product discovery and intuitive guidance. BigBasket employs IoT-led AI to optimise supply chain and improve product quality.
Reshaping the Automotive Landscape
Tech innovation, from AI/ML to connected vehicle technologies, is revolutionising the Automotive sector. This shift towards software-defined vehicles and predictive supply chain management underscores the industry’s commitment to efficiency, transparency, safety, and environmental sustainability.
Maruti Suzuki’s multi-pronged approach includes collaborating with over 60 startups through its MAIL program and engaging Accenture to drive tech change. Maruti has digitised 24 out of 26 customer touchpoints, tracking every interaction to enhance customer service. In the Auto OEM space, they are shifting to software-defined vehicles and operating models.
Tata Motors is leveraging cloud, AI/ML, and IoT to enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and driving sustainability across its operations. Key initiatives include connected vehicles, automated driving, dealer management, cybersecurity, electric powertrains, sustainability, and supply chain optimisation.
Streamlining India’s Logistics Sector
India’s logistics industry is on the cusp of a digital revolution as it embraces cutting-edge technologies to streamline processes and reduce environmental impact.
Automation and Predictive Analytics. Automation is transforming warehousing operations in India, with DHL India automating sortation centres to handle 6,000 shipments per hour. Predictive analytics is reshaping logistics decision-making, with Delhivery optimising delivery routes to ensure timely service.
Sustainable Practices. The logistics sector contributes one-third of global carbon emissions. To combat this, Amazon India will convert its delivery fleet to 100% EVs by 2030 to reduce emissions and fuel costs. Blue Energy Motors is also producing 10,000 heavy-duty LNG trucks annually for zero-emission logistics.

At a recently held Ecosystm roundtable, in partnership with Qlik and 121Connects, Ecosystm Principal Advisor Manoj Chugh, moderated a conversation where Indian tech and data leaders discussed building trust in data strategies. They explored ways to automate data pipelines and improve governance to drive better decisions and business outcomes. Here are the key takeaways from the session.

Data isn’t just a byproduct anymore; it’s the lifeblood of modern businesses, fuelling informed decisions and strategic growth. But with vast amounts of data, the challenge isn’t just managing it; it’s building trust. AI, once a beacon of hope, is now at risk without a reliable data foundation. Ecosystm research reveals that a staggering 66% of Indian tech leaders doubt their organisation’s data quality, and the problem of data silos is exacerbating this trust crisis.
At the Leaders Roundtable in Mumbai, I had the opportunity to moderate a discussion among data and digital leaders on the critical components of building trust in data and leveraging it to drive business value. The consensus was that building trust requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses the complexities of data management and positions the organisation for future success. Here are the key strategies that are essential for achieving these goals.
1. Adopting a Unified Data Approach
Organisations are facing a growing wave of complex workloads and business initiatives. To manage this expansion, IT teams are turning to multi-cloud, SaaS, and hybrid environments. However, this diverse landscape introduces new challenges, such as data silos, security vulnerabilities, and difficulties in ensuring interoperability between systems.

A unified data strategy is crucial to overcome these challenges. By ensuring platform consistency, robust security, and seamless data integration, organisations can simplify data management, enhance security, and align with business goals – driving informed decisions, innovation, and long-term success.
Real-time data integration is essential for timely data availability, enabling organisations to make data-driven decisions quickly and effectively. By integrating data from various sources in real-time, businesses can gain valuable insights into their operations, identify trends, and respond to changing market conditions.
Organisations that are able to integrate their IT and operational technology (OT) systems find their data accuracy increasing. By combining IT’s digital data management expertise with OT’s real-time operational insights, organisations can ensure more accurate, timely, and actionable data. This integration enables continuous monitoring and analysis of operational data, leading to faster identification of errors, more precise decision-making, and optimised processes.
2. Enhancing Data Quality with Automation and Collaboration
As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, ensuring high data quality is essential for organisations to make accurate decisions and to drive trust in data-driven solutions. Automated data quality tools are useful for cleansing and standardising data to eliminate errors and inconsistencies.

As mentioned earlier, integrating IT and OT systems can help organisations improve operational efficiency and resilience. By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can identify bottlenecks, optimise workflows, and proactively address potential issues before they escalate. This can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and improved customer satisfaction.
However, while automation technologies can help, organisations must also invest in training employees in data management, data visualisation, and data governance.
3. Modernising Data Infrastructure for Agility and Innovation
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, agility is paramount. Modernising data infrastructure is essential to remain competitive – the right digital infrastructure focuses on optimising costs, boosting capacity and agility, and maximising data leverage, all while safeguarding the organisation from cyber threats. This involves migrating data lakes and warehouses to cloud platforms and adopting advanced analytics tools. However, modernisation efforts must be aligned with specific business goals, such as enhancing customer experiences, optimising operations, or driving innovation. A well-modernised data environment not only improves agility but also lays the foundation for future innovations.

Technology leaders must assess whether their data architecture supports the organisation’s evolving data requirements, considering factors such as data flows, necessary management systems, processing operations, and AI applications. The ideal data architecture should be tailored to the organisation’s specific needs, considering current and future data demands, available skills, costs, and scalability.
4. Strengthening Data Governance with a Structured Approach
Data governance is crucial for establishing trust in data, and providing a framework to manage its quality, integrity, and security throughout its lifecycle. By setting clear policies and processes, organisations can build confidence in their data, support informed decision-making, and foster stakeholder trust.
A key component of data governance is data lineage – the ability to trace the history and transformation of data from its source to its final use. Understanding this journey helps organisations verify data accuracy and integrity, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies, improve data quality by proactively addressing issues, and enhance decision-making through context and transparency.
A tiered data governance structure, with strategic oversight at the executive level and operational tasks managed by dedicated data governance councils, ensures that data governance aligns with broader organisational goals and is implemented effectively.
Are You Ready for the Future of AI?
The ultimate goal of your data management and discovery mechanisms is to ensure that you are advancing at pace with the industry. The analytics landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, promising to revolutionise how organisations interact with data. A key innovation, the data fabric, is enabling organisations to analyse unstructured data, where the true value often lies, resulting in cleaner and more reliable data models.

GenAI has emerged as another game-changer, empowering employees across the organisation to become citizen data scientists. This democratisation of data analytics allows for a broader range of insights and fosters a more data-driven culture. Organisations can leverage GenAI to automate tasks, generate new ideas, and uncover hidden patterns in their data.
The shift from traditional dashboards to real-time conversational tools is also reshaping how data insights are delivered and acted upon. These tools enable users to ask questions in natural language, receiving immediate and relevant answers based on the underlying data. This conversational approach makes data more accessible and actionable, empowering employees to make data-driven decisions at all levels of the organisation.
To fully capitalise on these advancements, organisations need to reassess their AI/ML strategies. By ensuring that their tech initiatives align with their broader business objectives and deliver tangible returns on investment, organisations can unlock the full potential of data-driven insights and gain a competitive edge. It is equally important to build trust in AI initiatives, through a strong data foundation. This involves ensuring data quality, accuracy, and consistency, as well as implementing robust data governance practices. A solid data foundation provides the necessary groundwork for AI and GenAI models to deliver reliable and valuable insights.

India’s digital economy is on a meteoric rise, expected to reach USD 1 trillion by 2025. This surge in digital activity is fuelling the rapid expansion of its data centre market, positioning the country as a global player. With a projected market value of USD 4.5 billion by 2025, India’s data centre industry is set to surpass traditional regional hubs like Malaysia, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
This growth is driven by factors such as the proliferation of smartphones, internet connectivity, and digital services, generating massive amounts of data that need storage and processing. Government initiatives like Digital India and the National e-Governance Plan have promoted digitalisation, while favourable market conditions, including cost-effective infrastructure, skilled talent, and a large domestic market, make India an attractive destination for data centre investments.
As companies continue to invest, India is solidifying its role as a critical hub for Asia’s digital revolution, driving economic development and creating new opportunities for innovation and job creation.
What is Fuelling India’s Data Centre Growth?
India’s data centre industry is experiencing rapid growth in 2024, driven by a combination of strategic advantages and increasing demand. The country’s abundance of land and skilled workforce are key factors contributing to this boom.
- Digitisation push. The digital revolution is fueling the need for more sophisticated data centre infrastructure. The rise of social media, online gaming, and streaming apps has created a surge in demand for faster networks, better data storage options, and increased data centre services.
- Internet and mobile penetration. With 1.1 billion mobile phone subscribers, Indians use an average of 8.3 GB of data per month. As more people come online, businesses need to expand their data infrastructure to handle increased traffic, enhance service delivery, and support a growing digital economy.
- Increasing tech adoption. India’s AI market is projected to reach around USD 17 billion by 2027. As businesses integrate AI, IoT, cloud, and other technologies, data centres will become instrumental in supporting the vast computational and storage requirements.
- Government & regulatory measures. Apart from India being one of the world’s largest data consumption economies, government initiatives have also accelerated the ‘data based’ environment in the country. Additionally, states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu have implemented favourable real estate policies that reduce the costs of setting up data centres.
A Growing Network of Hubs
India’s data centre landscape is rapidly evolving, with major cities and emerging hotspots vying for a piece of the pie.
Mumbai-Navi Mumbai remains the undisputed leader, boasting a combined 39 data centres. Its strategic location with excellent submarine cable connectivity to Europe and Southeast Asia makes it a prime destination for global and domestic players.
Bangalore, India’s IT capital, is not far behind with 29 data centres. The city’s thriving tech ecosystem and skilled talent pool make it an attractive option for businesses looking to set up data centres.
Chennai, located on the east coast, has emerged as a crucial hub with 17 data centres. Its proximity to Southeast Asia and growing digital economy make it a strategic location. The Delhi-NCR region also plays a significant role, with 27 data centres serving the capital and surrounding areas.
Smaller cities like Pune, Jaipur, and Patna are rapidly emerging as data centre hotspots. As businesses seek to serve a growing but distributed user base across India, these cities offer more cost-effective options. Additionally, the rise of edge data centres in these smaller cities is further decentralising the data centre landscape.

A Competitive Market
India ranks 13th globally in the number of operational data centres, with 138 facilities in operation and an additional 45 expected to be completed by the end of 2025. Key initiatives include:
- AWS. AWS is investing USD 12.7 billion to establish four new data centres over the next two years.
- Meta. Meta is set to build a small data centre, potentially focused on cache with a 10-20 MW capacity.
- AdaniConnex. In partnership with EdgeConneX, AdaniConnex aims to develop a 1 GW network of hyperscale data centres over the next decade, all powered by 100% renewable energy.
- Google. Google is set to build an 80-storey data centre by 2025 and is in advanced talks to acquire a 22.5-acre land parcel for its first captive data centre.
- NTT. NTT is investing USD 241 million in a data campus, which will feature three data centres.
Data Centres: Driving Digital India’s Success
The Digital India initiative has transformed government services through improved online infrastructure and increased connectivity. Data centres play a pivotal role in supporting this vision by managing, storing, and processing the vast amounts of data that power essential services like Aadhaar and BharatNet.
Aadhaar, India’s biometric ID system, relies heavily on data centres to store and process biometric information, enabling seamless identification and authentication. BharatNet, the government’s ambitious project to connect rural areas with high-speed internet, also depends on data centres to provide the necessary infrastructure and support.
The impact of data centres on India’s digital transformation is far-reaching. Here are some key areas where data centres have made a significant contribution:
- Enabling Remote Work and Education. Data centres have been instrumental in supporting the surge in remote work and online learning during the pandemic. By providing the necessary infrastructure and connectivity, data centres have ensured business continuity and uninterrupted education.
- Fostering Start-Up Innovation. Data centres provide the essential infrastructure for start-ups to thrive. By offering reliable and scalable computing resources, data centres enable rapid growth and innovation, contributing to the expansion of India’s SaaS market.
- Supporting Government Services. Data centres underpin key government initiatives, including e-governance platforms and digital identity systems. They enhance the accessibility, transparency, and efficiency of government services, bridging the urban-rural divide and improving public service delivery.
Securing India’s Data Centre Future
Data centres are the backbone of India’s digital transformation, fuelling economic growth, government services, innovation, remote work, and technological progress. The Indian government’s ambitious plan to invest over USD 1 billion in hyperscale data centres over the next five years underscores the country’s commitment to building a robust digital infrastructure.
To secure the long-term success of India’s data centre industry, alignment with global standards and strategic investment are crucial. Prioritising reliability, efficiency, and sustainability will attract global providers and position India as a prime destination for digital infrastructure investments. Addressing challenges like legacy upgrades, modernisation, and cybersecurity risks will require collaboration across stakeholders, with government support and technological innovation playing key roles.
A unified effort from central and state governments is vital to enhance competitiveness. By fostering a favourable regulatory environment and offering incentives, the government can accelerate the development of world-class data centres. As India advances digitally, data centres will be instrumental in driving economic growth, improving quality of life, and solidifying India’s status as a global digital leader.

























































