The challenge of AI is that it is hard to build a business case when the outcomes are inherently uncertain. Unlike a traditional process improvement procedure, there are few guarantees that AI will solve the problem it is meant to solve. Organisations that have been experimenting with AI for some time are aware of this, and have begun to formalise their Proof of Concept (PoC) process to make it easily repeatable by anyone in the organisation who has a use case for AI. PoCs can validate assumptions, demonstrate the feasibility of an idea, and rally stakeholders behind the project.
PoCs are particularly useful at a time when AI is experiencing both heightened visibility and increased scrutiny. Boards, senior management, risk, legal and cybersecurity professionals are all scrutinising AI initiatives more closely to ensure they do not put the organisation at risk of breaking laws and regulations or damaging customer or supplier relationships.
13 Steps to Building an AI PoC
Despite seeming to be lightweight and easy to implement, a good PoC is actually methodologically sound and consistent in its approach. To implement a PoC for AI initiatives, organisations need to:
- Clearly define the problem. Businesses need to understand and clearly articulate the problem they want AI to solve. Is it about improving customer service, automating manual processes, enhancing product recommendations, or predicting machinery failure?
- Set clear objectives. What will success look like for the PoC? Is it about demonstrating technical feasibility, showing business value, or both? Set tangible metrics to evaluate the success of the PoC.
- Limit the scope. PoCs should be time-bound and narrow in scope. Instead of trying to tackle a broad problem, focus on a specific use case or a subset of data.
- Choose the right data. AI is heavily dependent on data. For a PoC, select a representative dataset that’s large enough to provide meaningful results but manageable within the constraints of the PoC.
- Build a multidisciplinary team. Involve team members from IT, data science, business units, and other relevant stakeholders. Their combined perspectives will ensure both technical and business feasibility.
- Prioritise speed over perfection. Use available tools and platforms to expedite the development process. It’s more important to quickly test assumptions than to build a highly polished solution.
- Document assumptions and limitations. Clearly state any assumptions made during the PoC, as well as known limitations. This helps set expectations and can guide future work.
- Present results clearly. Once the PoC is complete, create a clear and concise report or presentation that showcases the results, methodologies, and potential implications for the business.
- Get feedback. Allow stakeholders to provide feedback on the PoC. This includes end-users, technical teams, and business leaders. Their insights will help refine the approach and guide future iterations.
- Plan for the next steps. What actions need to follow a successful PoC demonstration? This might involve a pilot project with a larger scope, integrating the AI solution into existing systems, or scaling the solution across the organisation.
- Assess costs and ROI. Evaluate the costs associated with scaling the solution and compare it with the anticipated ROI. This will be crucial for securing budget and support for further expansion.
- Continually learn and iterate. AI is an evolving field. Use the PoC as a learning experience and be prepared to continually iterate on your solutions as technologies and business needs evolve.
- Consider ethical and social implications. Ensure that the AI initiative respects privacy, reduces bias, and upholds the ethical standards of the organisation. This is critical for building trust and ensuring long-term success.
Customising AI for Your Business
The primary purpose of a PoC is to validate an idea quickly and with minimal risk. It should provide a clear path for decision-makers to either proceed with a more comprehensive implementation or to pivot and explore alternative solutions. It is important for the legal, risk and cybersecurity teams to be aware of the outcomes and support further implementation.
AI initiatives will inevitably drive significant productivity and customer experience improvements – but not every solution will be right for the business. At Ecosystm, we have come across organisations that have employed conversational AI in their contact centres to achieve entirely distinct results – so the AI experience of peers and competitors may not be relevant. A consistent PoC process that trains business and technology teams across the organisation and encourages experimentation at every possible opportunity, would be far more useful.

Generative AI has stolen the limelight in 2023 from nearly every other technology – and for good reason. The advances made by Generative AI providers have been incredible, with many human “thinking” processes now in line to be automated.
But before we had Generative AI, there was the run-of-the-mill “traditional AI”. However, despite the traditional tag, these capabilities have a long way to run within your organisation. In fact, they are often easier to implement, have less risk (and more predictability) and are easier to generate business cases for. Traditional AI systems are often already embedded in many applications, systems, and processes, and can easily be purchased as-a-service from many providers.
Unlocking the Potential of AI Across Industries
Many organisations around the world are exploring AI solutions today, and the opportunities for improvement are significant:
- Manufacturers are designing, developing and testing in digital environments, relying on AI to predict product responses to stress and environments. In the future, Generative AI will be called upon to suggest improvements.
- Retailers are using AI to monitor customer behaviours and predict next steps. Algorithms are being used to drive the best outcome for the customer and the retailer, based on previous behaviours and trained outcomes.
- Transport and logistics businesses are using AI to minimise fuel usage and driver expenses while maximising delivery loads. Smart route planning and scheduling is ensuring timely deliveries while reducing costs and saving on vehicle maintenance.
- Warehouses are enhancing the safety of their environments and efficiently moving goods with AI. Through a combination of video analytics, connected IoT devices, and logistical software, they are maximising the potential of their limited space.
- Public infrastructure providers (such as shopping centres, public transport providers etc) are using AI to monitor public safety. Video analytics and sensors is helping safety and security teams take public safety beyond traditional human monitoring.
AI Impacts Multiple Roles
Even within the organisation, different lines of business expect different outcomes for AI implementations.
- IT teams are monitoring infrastructure, applications, and transactions – to better understand root-cause analysis and predict upcoming failures – using AI. In fact, AIOps, one of the fastest-growing areas of AI, yields substantial productivity gains for tech teams and boosts reliability for both customers and employees.
- Finance teams are leveraging AI to understand customer payment patterns and automate the issuance of invoices and reminders, a capability increasingly being integrated into modern finance systems.
- Sales teams are using AI to discover the best prospects to target and what offers they are most likely to respond to.
- Contact centres are monitoring calls, automating suggestions, summarising records, and scheduling follow-up actions through conversational AI. This is allowing to get agents up to speed in a shorter period, ensuring greater customer satisfaction and increased brand loyalty.
Transitioning from Low-Risk to AI-Infused Growth
These are just a tiny selection of the opportunities for AI. And few of these need testing or business cases – many of these capabilities are available out-of-the-box or out of the cloud. They don’t need deep analysis by risk, legal, or cybersecurity teams. They just need a champion to make the call and switch them on.
One potential downside of Generative AI is that it is drawing unwarranted attention to well-established, low-risk AI applications. Many of these do not require much time from data scientists – and if they do, the challenge is often finding the data and creating the algorithm. Humans can typically understand the logic and rules that the models create – unlike Generative AI, where the outcome cannot be reverse-engineered.
The opportunity today is to take advantage of the attention that LLMs and other Generative AI engines are getting to incorporate AI into every conceivable aspect of a business. When organisations understand the opportunities for productivity improvements, speed enhancement, better customer outcomes and improved business performance, the spend on AI capabilities will skyrocket. Ecosystm estimates that for most organisations, AI spend will be less than 5% of their total tech spend in 2024 – but it is likely to grow to over 20% within the next 4-5 years.

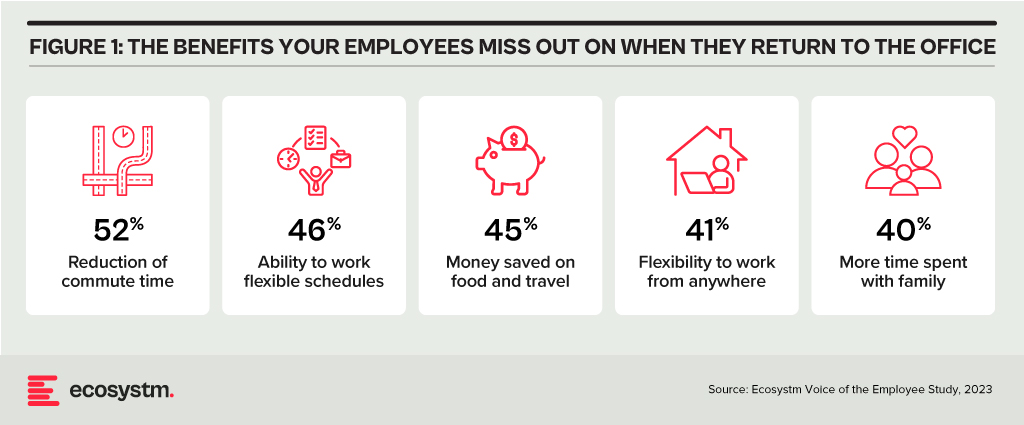
It seems for many employees, the benefits of working from home or even adopting a hybrid model are a thing of the past. Employees are returning to the grind of long commutes and losing hours in transit. What is driving this shift in sentiment? CEOs, who once rooted for remote work, have undergone a change of heart – many say that remote work hampers their ability to innovate.
That may not be the real reason, however. There is a good chance that the CEO and/or other managers feel they have lost control or visibility over their employees. Returning to a more traditional management approach, where everyone is within direct sight, might seem like a simpler solution.
The Myths of Workplace Innovation
I find it ironic that organisations say they want employees to come into the office because they cannot innovate at the same rate. What the last few years have demonstrated – and quite conclusively – is that employees can innovate wherever they are, if they are driven to it and have the right tools. So, organisations need to evaluate whether they have innovated on and evolved their hybrid and remote work solutions effectively, to continue to support hybrid work – and innovation.
What is confusing about this stance that many organisations are taking, is that when an organisation has multiple offices, they are effectively a hybrid business – they have had people working from different locations, but have never felt the need to get all their staff together for 3-5 days every week for organisation-wide innovation that is suddenly so important today.
The CEO of a tech research firm once said – the office used to be considered the place to get together to use the tools we need to innovate; but the reality is that the office is just one of the tools that businesses have, to drive their organisation forward. Ironically, this same CEO has recently called everyone back into the office 3 days a week!
Is Remote Work the Next Step in Employee Rights?
It has become clear that remote and hybrid work is the next step in employees getting greater rights. Many organisations fought against the five-day work weeks, claiming they wouldn’t make as much money as they did when employees worked whenever they were told. They fought against the 40-hour work week (in France some fought against the 35-hour work week!) They fight against the introduction of new public holidays, against increases to the minimum wages, against paid parental leave.
Some industries, companies, unions, and countries are looking to (or already have) formalised hybrid and remote work in their policies and regulations. More unions and businesses will do this – and employees will have choice.
People will have the option to work for an employer who wants their employees to come into the office – or work for someone else. And this will depend on preferences and working styles – some employees enjoy the time spent away from home and like the social nature of office environments. But many also like the extra time, money, and flexibility that remote work allows.
There might be many reasons why leadership teams would want employees to come into the office – and establishing and maintaining a common corporate culture would be a leading reason. But what they need to do is stop pretending it is about “innovation”. Innovation is possible while working remotely, as it is when working from separate offices or even different floors within the same building.
Evolving Employee Experience & Collaboration Needs
Organisations today face a challenge – and it is not the inability to innovate in a hybrid work environment! It is in their ability to deliver the employee experience that their employees want. This is more challenging now because there are more preferences, options, and technologies available. But it is established that organisations need to continue to evolve their employee experience.
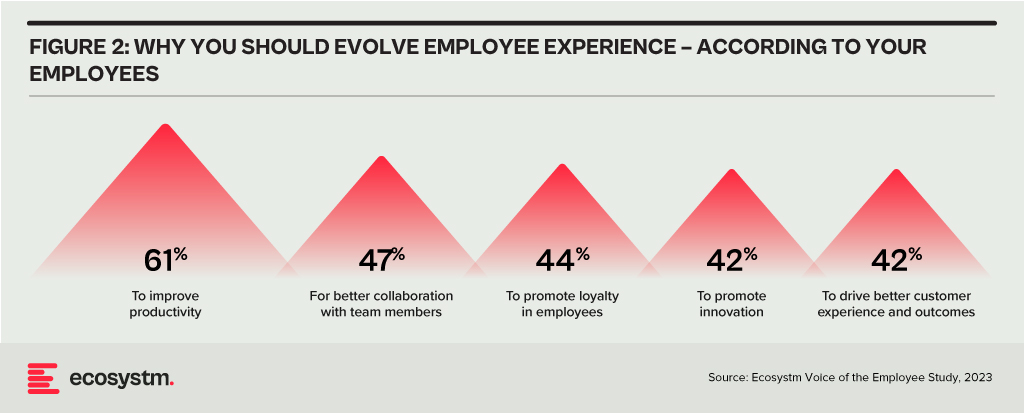
Technology does and will continue to play an important role in keeping our employees connected and productive. AI – such as Microsoft Copilot – will continue to improve our productivity. But the management needs to evolve with the technology. If the senior management feels that connecting people will help to solve the current growth challenges in the business, then it becomes the role of managers to better connect people – not just teams in offices, but virtual teams across the entire organisation.
Organisations that have focused their energies on connecting their employees better, regardless of their location (such as REA in Australia), find that productivity and innovation rates are better than when people are physically together. What do they do differently?
- Managers find their roles have moved from supporting individual employees to connecting employees
- Documentation of progress and challenges means that everyone knows where to focus their energies
- Managed virtual (and in-person) meetings mean that everyone has a voice and gets to contribute (not the loudest, most talkative or most senior person)
Remote and hybrid workers are often well-positioned to come up with new and innovative ideas. Senior management can encourage innovation and risk-taking by creating a safe environment for employees to share their ideas and by providing them with the resources they need to develop and implement their ideas. Sometimes these resources are in an office – but they don’t have to be. Manufacturers are quickly moving to complete digital development, prototyping, and testing of their new and improved products and services. Digital is often faster, better, and more innovative than physical – but employees need to be allowed to embrace these new platforms and tools to drive better organisational and customer outcomes.
What the pandemic has taught us is that people are good at solving problems; they are good at innovating irrespective of whether their managers are watching or not.

A lot gets written about cybersecurity – and organisations spend a lot on it! Ecosystm research finds that 63% of organisations across Asia Pacific are planning to increase their cyber budget for the next year. As budgets continue to rise, the threat landscape continues to get more complex and difficult to navigate. Despite increasing spend, 69% of organisations believe a breach is inevitable. And breaches can be EXPENSIVE! Medibank, in Australia, was breached in (or around) October, 2022. The cost of the breach is expected to reach around USD 52 million when everything is done and dusted – and this does not include the impacts of any potential findings or outcomes from regulatory investigations or litigation.
Recovering Strong
While cybersecurity is still crucially important, the ability to recover from breaches quickly and cost-effectively is also imperative. How you recover from a breach will ultimately determine your organisation’s long-term viability and success. The capabilities needed to recover quickly include:
- A well-documented and practices incident response plan. The plan should outline the roles and responsibilities of all team members, communication protocols, and steps to be taken in the event of a breach.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery (DR) solutions. Regular backups of critical data and systems are essential to quickly recover from a breach. Backup solutions should include offsite or cloud-based options that are isolated from the main network. DR solutions ensure that critical systems can be quickly restored and made operational after a breach.
- Cybersecurity awareness training. Investing in regular training for all employees is crucial to ensure they are aware of the latest threats and know how to respond in the event of a breach.
- Automated response tools. Automation can help speed up the response time during a breach by automatically blocking malicious IPs, quarantining infected devices, or taking other predefined actions based on the nature of the attack.
- Threat intelligence. This can help organisations stay ahead of the latest threats and vulnerabilities and frame quicker responses if a breach occurs.
Backup and Disaster Recovery is Evolving
Most organisations already have backup and disaster recovery capabilities in place – but too often they are older systems, designed more as a “just in case” versus a “will keep us in business” capability. Backup and DR systems are evolving and improving – and with the increased likelihood of a breach, it is a good time to consider what a modern Backup and DR system can provide to your organisation. Here are some of the key trends and considerations that technology leaders should be aware of:
- Cloud-based solutions. More organisations are moving towards cloud-based backup and DR solutions. Cloud solutions offer several advantages, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to access data and systems from anywhere. However, technology leaders need to consider data security, compliance requirements, and the reliability of the cloud service provider.
- Hybrid options. As hybrid cloud becomes the norm for most organisations, hybrid solutions backup and DR that combine on-premises and cloud-based backups are becoming more popular. This approach provides the best of both worlds – the security and control of on-premises backups with the scalability and flexibility of the cloud.
- Increased use of automation. Automation is becoming more prevalent in backup and DR solutions. Automation helps reduce the time it takes to backup data, restore systems, and test DR plans. It also minimises the risk of human error. Technology leaders should look for solutions that offer automation capabilities while also allowing for manual intervention when necessary.
- Cybersecurity integration. With the rise of cyberattacks, especially ransomware, it is crucial that backup and DR solutions are integrated with an organisation’s cybersecurity strategy. Backup data should be encrypted and isolated from the main network to prevent attackers from accessing or corrupting it. Regular testing of backup and DR plans should also include scenarios where a cyberattack, such as ransomware, is involved.
- More frequent backups. Data is becoming more critical to business operations, so there is a trend towards more frequent backups, even continuous backups, to minimise data loss in the event of a disaster. Technology leaders need to balance the need for frequent backups with the cost and complexity involved.
- Super-fast data recovery. Some data recovery platforms can recover data FAST – in as little as 6 seconds. The ability to recover data faster than the bad actors can delete it makes organisations less vulnerable and buys more time to plug the gaps that the attackers are exploiting to gain access to data and systems.
- Monitoring and analytics. Modern backup and DR solutions offer advanced monitoring and analytics capabilities. This allows organisations to track the performance of their backups, identify potential issues before they become critical, and optimise their backup and DR processes. Technology leaders should look for solutions that offer comprehensive monitoring and analytics capabilities.
- Compliance considerations. With the increasing focus on data privacy and protection, organisations need to ensure that backup and DR solutions are compliant with relevant regulations, often dictated at the industry level in each geography. Technology leaders should work with their legal and compliance teams to ensure that their backup and DR solutions meet all necessary requirements.
The sooner you evolve and modernise your backup and disaster recovery capabilities, the more breathing room your cybersecurity team has, to improve the ability to repel threats. New security architectures and postures – such as Zero Trust and SASE are emerging as better ways to build your cybersecurity capabilities – but they won’t happen overnight and require significant investment, training, and business change to implement.

As an industry, the tech sector tends to jump on keywords and terms – and sometimes reshapes their meaning and intention. “Sustainable” is one of those terms. Technology vendors are selling (allegedly!) “sustainable software/hardware/services/solutions” – in fact, the focus on “green” or “zero carbon” or “recycled” or “circular economy” is increasing exponentially at the moment. And that is good news – as I mentioned in my previous post, we need to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions if we want a future for our kids. But there is a significant disconnect between the way tech vendors use the word “sustainable” and the way it is used in boardrooms and senior management teams of their clients.
Defining Sustainability
For organisations, Sustainability is a broad business goal – in fact for many, it is the over-arching goal. A sustainable organisation operates in a way that balances economic, social, and environmental (ESG) considerations. Rather than focusing solely on profits, a sustainable organisation aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
This is what building a “Sustainable Organisation” typically involves:
Economic Sustainability. The organisation must be financially stable and operate in a manner that ensures long-term economic viability. It doesn’t just focus on short-term profits but invests in long-term growth and resilience.
Social Sustainability. This involves the organisation’s responsibility to its employees, stakeholders, and the wider community. A sustainable organisation will promote fair labour practices, invest in employee well-being, foster diversity and inclusion, and engage in ethical decision-making. It often involves community engagement and initiatives that support societal growth and well-being.
Environmental Sustainability. This facet includes the responsible use of natural resources and minimising negative impacts on the environment. A sustainable organisation seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, minimise waste, enhance energy efficiency, and often supports or initiates activities that promote environmental conservation.
Governance and Ethical Considerations. Sustainable organisations tend to have transparent and responsible governance. They follow ethical business practices, comply with laws and regulations, and foster a culture of integrity and accountability.
Security and Resilience. Sustainable organisations have the ability to thwart bad actors – and in the situation that they are breached, to recover from these breaches quickly and safely. Sustainable organisations can survive cybersecurity incidents and continue to operate when breaches occur, with the least impact.
Long-Term Focus. Sustainability often requires a long-term perspective. By looking beyond immediate gains and considering the long-term impact of decisions, a sustainable organisation can better align its strategies with broader societal goals.
Stakeholder Engagement. Understanding and addressing the needs and concerns of different stakeholders (including employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and shareholders) is key to sustainability. This includes open communication and collaboration with these groups to foster relationships based on trust and mutual benefit.
Adaptation and Innovation. The organisation is not static and recognises the need for continual improvement and adaptation. This might include innovation in products, services, or processes to meet evolving sustainability standards and societal expectations.
Alignment with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UNSDGs). Many sustainable organisations align their strategies and operations with the UNSDGs which provide a global framework for addressing sustainability challenges.
Organisations Appreciate Precise Messaging
A sustainable organisation is one that integrates economic, social, and environmental considerations into all aspects of its operations. It goes beyond mere compliance with laws to actively pursue positive impacts on people and the planet, maintaining a balance that ensures long-term success and resilience.
These factors are all top of mind when business leaders, boards and government agencies use the word “sustainable”. Helping organisations meet their emission reduction targets is a good starting point – but it is a long way from all businesses need to become sustainable organisations.
Tech providers need to reconsider their use of the term “sustainable” – unless their solution or service is helping organisations meet all of the features outlined above. Using specific language would be favoured by most customers – telling them how the solution will help them reduce greenhouse gas emissions, meet compliance requirements for CO2 and/or waste reduction, and save money on electricity and/or management costs – these are all likely to get the sale over the line faster than a broad “sustainability” messaging will.

While there has been much speculation about AI being a potential negative force on humanity, what we do know today is that the accelerated use of AI WILL mean an accelerated use of energy. And if that energy source is not renewable, AI will have a meaningful negative impact on CO2 emissions and will accelerate climate change. Even if the energy is renewable, GPUs and CPUs generate significant heat – and if that heat is not captured and used effectively then it too will have a negative impact on warming local environments near data centres.
Balancing Speed and Energy Efficiency
While GPUs use significantly more energy than CPUs, they run many AI algorithms faster than CPUs – so use less energy overall. But the process needs to run – and these are additional processes. Data needs to be discovered, moved, stored, analysed, cleansed. In many cases, algorithms need to be recreated, tweaked and improved. And then that algorithm itself will kick off new digital processes that are often more processor and energy-intensive – as now organisations might have a unique process for every customer or many customer groups, requiring more decisioning and hence more digitally intensive.
The GPUs, servers, storage, cabling, cooling systems, racks, and buildings have to be constructed – often built from raw materials – and these raw materials need to be mined, transported and transformed. With the use of AI exploding at the moment, so is the demand for AI infrastructure – all of which has an impact on the resources of the planet and ultimately on climate change.
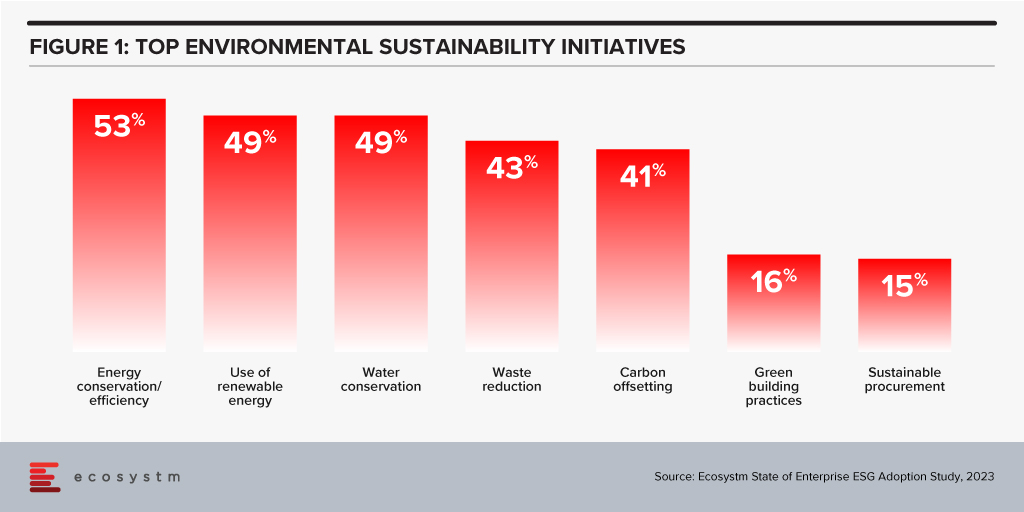
Sustainable Sourcing
Some organisations understand this already and are beginning to use sustainable sourcing for their technology services. However, it is not a top priority with Ecosystm research showing only 15% of organisations focus on sustainable procurement.
Technology Providers Can Help
Leading technology providers are introducing initiatives that make it easier for organisations to procure sustainable IT solutions. The recently announced HPE GreenLake for Large Language Models will be based in a data centre built and run by Qscale in Canada that is not only sustainably built and sourced, but sits on a grid supplying 99.5% renewable electricity – and waste (warm) air from the data centre and cooling systems is funneled to nearby greenhouses that grow berries. I find the concept remarkable and this is one of the most impressive sustainable data centre stories to date.
The focus on sustainability needs to be universal – across all cloud and AI providers. AI usage IS exploding – and we are just at the tip of the iceberg today. It will continue to grow as it becomes easier to use and deploy, more readily available, and more relevant across all industries and organisations. But we are at a stage of climate warming where we cannot increase our greenhouse gas emissions – and offsetting these emissions just passes the buck.
We need more companies like HPE and Qscale to build this Sustainable Future – and we need to be thinking the same way in our own data centres and putting pressure on our own AI and overall technology value chain to think more sustainably and act in the interests of the planet and future generations. Cloud providers – like AWS – are committed to the NetZero goal (by 2040 in their case) – but this is meaningless if our requirement for computing capacity increases a hundred-fold in that period. Our businesses and our tech partners need to act today. It is time for organisations to demand it from their tech providers to influence change in the industry.

I have spent many years analysing the mobile and end-user computing markets. Going all the way back to 1995 where I was part of a Desktop PC research team, to running the European wireless and mobile comms practice, to my time at 3 Mobile in Australia and many years after, helping clients with their end-user computing strategies. From the birth of mobile data services (GPRS, WAP, and so on to 3G, 4G and 5G), from simple phones to powerful foldable devices, from desktop computers to a complex array of mobile computing devices to meet the many and varied employee needs. I am always looking for the “next big thing” – and there have been some significant milestones – Palm devices, Blackberries, the iPhone, Android, foldables, wearables, smaller, thinner, faster, more powerful laptops.
But over the past few years, innovation in this space has tailed off. Outside of the foldable space (which is already four years old), the major benefits of new devices are faster processors, brighter screens, and better cameras. I review a lot of great computers too (like many of the recent Surface devices) – and while they are continuously improving, not much has got my clients or me “excited” over the past few years (outside of some of the very cool accessibility initiatives).
The Force of AI
But this is all about to change. Devices are going to get smarter based on their data ecosystem, the cloud, and AI-specific local processing power. To be honest, this has been happening for some time – but most of the “magic” has been invisible to us. It happened when cameras took multiple shots and selected the best one; it happened when pixels were sharpened and images got brighter, better, and more attractive; it happened when digital assistants were called upon to answer questions and provide context.
Microsoft, among others, are about to make AI smarts more front and centre of the experience – Windows Copilot will add a smart assistant that can not only advise but execute on advice. It will help employees improve their focus and productivity, summarise documents and long chat threads, select music, distribute content to the right audience, and find connections. Added to Microsoft 365 Copilot it will help knowledge workers spend less time searching and reading – and more time doing and improving.
The greater integration of public and personal data with “intent insights” will also play out on our mobile devices. We are likely to see the emergence of the much-promised “integrated app”– one that can take on many of the tasks that we currently undertake across multiple applications, mobile websites, and sometimes even multiple devices. This will initially be through the use of public LLMs like Bard and ChatGPT, but as more custom, private models emerge they will serve very specific functions.
Focused AI Chips will Drive New Device Wars
In parallel to these developments, we expect the emergence of very specific AI processors that are paired to very specific AI capabilities. As local processing power becomes a necessity for some AI algorithms, the broad CPUs – and even the AI-focused ones (like Google’s Tensor Processor) – will need to be complemented by specific chips that serve specific AI functions. These chips will perform the processing more efficiently – preserving the battery and improving the user experience.
While this will be a longer-term trend, it is likely to significantly change the game for what can be achieved locally on a device – enabling capabilities that are not in the realm of imagination today. They will also spur a new wave of device competition and innovation – with a greater desire to be on the “latest and greatest” devices than we see today!
So, while the levels of device innovation have flattened, AI-driven software and chipset innovation will see current and future devices enable new levels of employee productivity and consumer capability. The focus in 2023 and beyond needs to be less on the hardware announcements and more on the platforms and tools. End-user computing strategies need to be refreshed with a new perspective around intent and intelligence. The persona-based strategies of the past have to be changed in a world where form factors and processing power are less relevant than outcomes and insights.

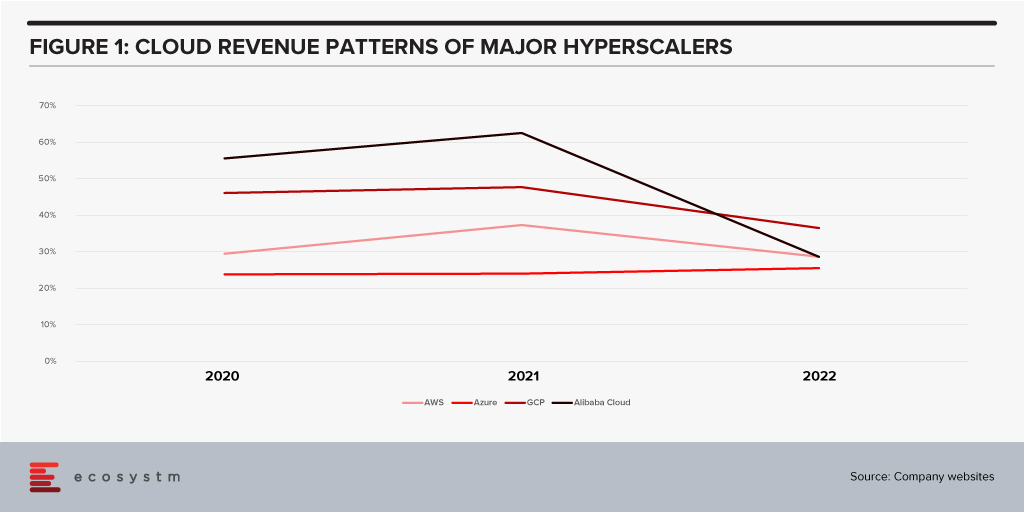
All growth must end eventually. But it is a brave person who will predict the end of growth for the public cloud hyperscalers. The hyperscaler cloud revenues have been growing at between 25-60% the past few years (off very different bases – and often including and counting different revenue streams). Even the current softening of economic spend we are seeing across many economies is only causing a slight slowdown.
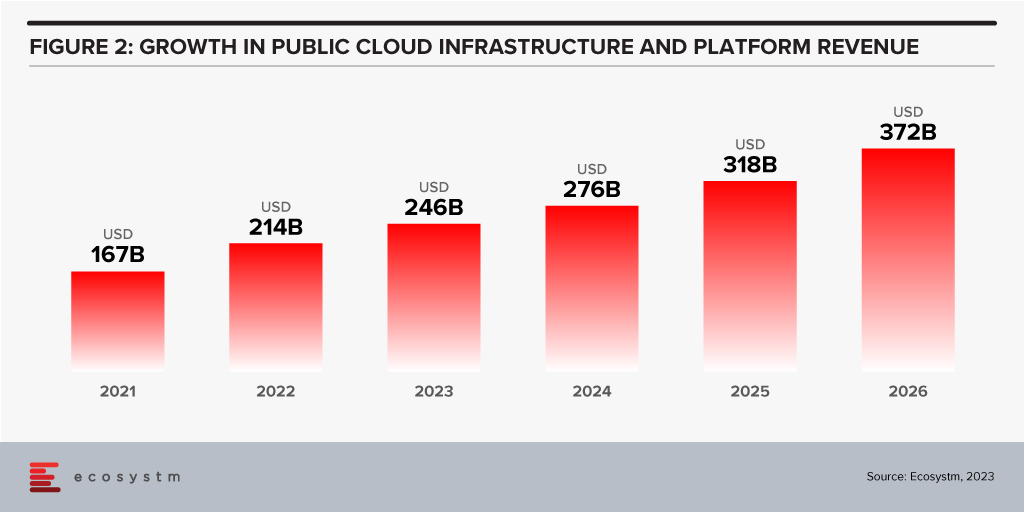
Looking forward, we expect growth in public cloud infrastructure and platform spend to continue to decline in 2024, but to accelerate in 2025 and 2026 as businesses take advantage of new cloud services and capabilities. However, the sheer size of the market means that we will see slower growth going forward – but we forecast 2026 to see the highest revenue growth of any year since public cloud services were founded.
The factors driving this growth include:
- Acceleration of digital intensity. As countries come out of their economic slowdowns and economic activity increases, so too will digital activity. And greater volumes of digital activity will require an increase in the capacity of cloud environments on which the applications and processes are hosted.
- Increased use of AI services. Businesses and AI service providers will need access to GPUs – and eventually, specialised AI chipsets – which will see cloud bills increase significantly. The extra data storage to drive the algorithms – and the increase in CPU required to deliver customised or personalised experiences that these algorithms will direct will also drive increased cloud usage.
- Further movement of applications from on-premises to cloud. Many organisations – particularly those in the Asia Pacific region – still have the majority of their applications and tech systems sitting in data centre environments. Over the next few years, more of these applications will move to hyperscalers.
- Edge applications moving to the cloud. As the public cloud giants improve their edge computing capabilities – in partnership with hardware providers, telcos, and a broader expansion of their own networks – there will be greater opportunity to move edge applications to public cloud environments.
- Increasing number of ISVs hosting on these platforms. The move from on-premise to cloud will drive some growth in hyperscaler revenues and activities – but the ISVs born in the cloud will also drive significant growth. SaaS and PaaS are typically seeing growth above the rates of IaaS – but are also drivers of the growth of cloud infrastructure services.
- Improving cloud marketplaces. Continuing on the topic of ISV partners, as the cloud hyperscalers make it easier and faster to find, buy, and integrate new services from their cloud marketplace, the adoption of cloud infrastructure services will continue to grow.
- New cloud services. No one has a crystal ball, and few people know what is being developed by Microsoft, AWS, Google, and the other cloud providers. New services will exist in the next few years that aren’t even being considered today. Perhaps Quantum Computing will start to see real business adoption? But these new services will help to drive growth – even if “legacy” cloud service adoption slows down or services are retired.
Hybrid Cloud Will Play an Important Role for Many Businesses
Growth in hyperscalers doesn’t mean that the hybrid cloud will disappear. Many organisations will hit a natural “ceiling” for their public cloud services. Regulations, proximity, cost, volumes of data, and “gravity” will see some applications remain in data centres. However, businesses will want to manage, secure, transform, and modernise these applications at the same rate and use the same tools as their public cloud environments. Therefore, hybrid and private cloud will remain important elements of the overall cloud market. Their success will be the ability to integrate with and support public cloud environments.
The future of cloud is big – but like all infrastructure and platforms, they are not a goal in themselves. It is what cloud is and will further enable businesses and customers which is exciting. As the rates of digitisation and digital intensity increase, the opportunities for the cloud infrastructure and platform providers will blossom. Sometimes they will be the driver of the growth, and other times they will just be supporting actors. But either way, in 2026 – 20 years after the birth of AWS – the growth in cloud services will be bigger than ever.

It is not hyperbole to state that AI is on the cusp of having significant implications on society, business, economies, governments, individuals, cultures, politics, the arts, manufacturing, customer experience… I think you get the idea! We cannot understate the impact that AI will have on society. In times gone by, businesses tested ideas, new products, or services with small customer segments before they went live. But with AI we are all part of this experiment on the impacts of AI on society – its benefits, use cases, weaknesses, and threats.
What seemed preposterous just six months ago is not only possible but EASY! Do you want a virtual version of yourself, a friend, your CEO, or your deceased family member? Sure – just feed the data. Will succession planning be more about recording all conversations and interactions with an executive so their avatar can make the decisions when they leave? Why not? How about you turn the thousands of hours of recorded customer conversations with your contact centre team into a virtual contact centre team? Your head of product can present in multiple countries in multiple languages, tailored to the customer segments, industries, geographies, or business needs at the same moment.
AI has the potential to create digital clones of your employees, it can spread fake news as easily as real news, it can be used for deception as easily as for benefit. Is your organisation prepared for the social, personal, cultural, and emotional impacts of AI? Do you know how AI will evolve in your organisation?
When we focus on the future of AI, we often interview AI leaders, business leaders, futurists, and analysts. I haven’t seen enough focus on psychologists, sociologists, historians, academics, counselors, or even regulators! The Internet and social media changed the world more than we ever imagined – at this stage, it looks like these two were just a rehearsal for the real show – Artificial Intelligence.
Lack of Government or Industry Regulation Means You Need to Self-Regulate
These rapid developments – and the notable silence from governments, lawmakers, and regulators – make the requirement for an AI Ethics Policy for your organisation urgent! Even if you have one, it probably needs updating, as the scenarios that AI can operate within are growing and changing literally every day.
- For example, your customer service team might want to create a virtual customer service agent from a real person. What is the policy on this? How will it impact the person?
- Your marketing team might be using ChatGPT or Bard for content creation. Do you have a policy specifically for the creation and use of content using assets your business does not own?
- What data is acceptable to be ingested by a public Large Language Model (LLM). Are are you governing data at creation and publishing to ensure these policies are met?
- With the impending public launch of Microsoft’s Co-Pilot AI service, what data can be ingested by Co-Pilot? How are you governing the distribution of the insights that come out of that capability?
If policies are not put in place, data tagged, staff trained, before using a tool such as Co-Pilot, your business will be likely to break some privacy or employment laws – on the very first day!
What do the LLMs Say About AI Ethics Policies?
So where do you go when looking for an AI Ethics policy? ChatGPT and Bard of course! I asked the two for a modern AI Ethics policy.
You can read what they generated in the graphic below.
I personally prefer the ChatGPT4 version as it is more prescriptive. At the same time, I would argue that MOST of the AI tools that your business has access to today don’t meet all of these principles. And while they are tools and the ethics should dictate the way the tools are used, with AI you cannot always separate the process and outcome from the tool.
For example, a tool that is inherently designed to learn an employee’s character, style, or mannerisms cannot be unbiased if it is based on a biased opinion (and humans have biases!).
LLMs take data, content, and insights created by others, and give it to their customers to reuse. Are you happy with your website being used as a tool to train a startup on the opportunities in the markets and customers you serve?
By making content public, you acknowledge the risk of others using it. But at least they visited your website or app to consume it. Not anymore…
A Policy is Useless if it Sits on a Shelf
Your AI ethics policy needs to be more than a published document. It should be the beginning of a conversation across the entire organisation about the use of AI. Your employees need to be trained in the policy. It needs to be part of the culture of the business – particularly as low and no-code capabilities push these AI tools, practices, and capabilities into the hands of many of your employees.
Nearly every business leader I interview mentions that their organisation is an “intelligent, data-led, business.” What is the role of AI in driving this intelligent business? If being data-driven and analytical is in the DNA of your organisation, soon AI will also be at the heart of your business. You might think you can delay your investments to get it right – but your competitors may be ahead of you.
So, as you jump head-first into the AI pool, start to create, improve and/or socialise your AI Ethics Policy. It should guide your investments, protect your brand, empower your employees, and keep your business resilient and compliant with legacy and new legislation and regulations.















