Ecosystm research shows that cybersecurity is the most discussed technology at the Board and Management level, driven by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the rapid adoption of AI. While AI enhances security, it also introduces new vulnerabilities. As organisations face an evolving threat landscape, they are adopting a more holistic approach to cybersecurity, covering prevention, detection, response, and recovery.
In 2025, cybersecurity leaders will continue to navigate a complex mix of technological advancements, regulatory pressures, and changing business needs. To stay ahead, organisations will prioritise robust security solutions, skilled professionals, and strategic partnerships.
Ecosystm analysts Darian Bird, Sash Mukherjee, and Simona Dimovski present the key cybersecurity trends for 2025.
Click here to download ‘Securing the AI Frontier: Top 5 Cyber Trends for 2025’ as a PDF
1. Cybersecurity Will Be a Critical Differentiator in Corporate Strategy
The convergence of geopolitical instability, cyber weaponisation, and an interconnected digital economy will make cybersecurity a cornerstone of corporate strategy. State-sponsored cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure, supply chains, and sensitive data have turned cyber warfare into an operational reality, forcing businesses to prioritise security.
Regulatory pressures are driving this shift, mandating breach reporting, data sovereignty, and significant penalties, while international cybersecurity norms compel companies to align with evolving standards to remain competitive.
The stakes are high. Stakeholders now see cybersecurity as a proxy for trust and resilience, scrutinising both internal measures and ecosystem vulnerabilities.

2. Zero Trust Architectures Will Anchor AI-Driven Environments
The future of cybersecurity lies in never trusting, always verifying – especially where AI is involved.
In 2025, the rise of AI-driven systems will make Zero Trust architectures vital for cybersecurity. Unlike traditional networks with implicit trust, AI environments demand stricter scrutiny due to their reliance on sensitive data, autonomous decisions, and interconnected systems. The growing threat of adversarial attacks – data poisoning, model inversion, and algorithmic manipulation – highlights the urgency of continuous verification.
Global forces are driving this shift. Regulatory mandates like the EU’s DORA, the US Cybersecurity Executive Order, and the NIST Zero Trust framework call for robust safeguards for critical systems. These measures align with the growing reliance on AI in high-stakes sectors like Finance, Healthcare, and National Security.

3. Organisations Will Proactively Focus on AI Governance & Data Privacy
Organisations are caught between excitement and uncertainty regarding AI. While the benefits are immense, businesses struggle with the complexities of governing AI. The EU AI Act looms large, pushing global organisations to brace for stricter regulations, while a rise in shadow IT sees business units bypassing traditional IT to deploy AI independently.
In this environment of regulatory ambiguity and organisational flux, CISOs and CIOs will prioritise data privacy and governance, proactively securing organisations with strong data frameworks and advanced security solutions to stay ahead of emerging regulations.
Recognising that AI will be multi-modal, multi-vendor, and hybrid, organisations will invest in model orchestration and integration platforms to simplify management and ensure smoother compliance.

4. Network & Security Stacks Will Streamline Through Converged Platforms
This shift stems from the need for unified management, cost efficiency, and the recognition that standardisation enhances security posture.
Tech providers are racing to deliver comprehensive network and security platforms.
Recent M&A moves by HPE (Juniper), Palo Alto Networks (QRadar SaaS), Fortinet (Lacework), and LogRhythm (Exabeam) highlight this trend. Rising player Cato Networks is capitalising on mid-market demand for single-provider solutions, with many customers planning to consolidate vendors in their favour. Meanwhile, telecoms are expanding their SASE offerings to support organisations adapting to remote work and growing cloud adoption.

5. AI Will Be Widely Used to Combat AI-Powered Threats in Real-time
By 2025, the rise of AI-powered cyber threats will demand equally advanced AI-driven defences.
Threat actors are using AI to launch adaptive attacks like deepfake fraud, automated phishing, and adversarial machine learning, operating at a speed and scale beyond traditional defences.
Real-time AI solutions will be essential for detection and response.
Nation-state-backed advanced persistent threat (APT) groups and GenAI misuse are intensifying these challenges, exploiting vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure and supply chains. Mandatory reporting and threat intelligence sharing will strengthen AI defences, enabling real-time adaptation to emerging threats.


In 2024, technology vendors have heavily invested in AI Agents, recognising their potential to drive significant value. These tools leverage well-governed, small datasets to integrate seamlessly with applications like Workday, Salesforce, ServiceNow, and Dayforce, enhancing processes and outcomes.
2025 is poised to be the year of AI Agent adoption. Designed to automate specific tasks within existing workflows, AI Agents will transform customer experiences, streamline operations, and boost efficiency. Unlike traditional AI deployments, they offer a gradual, non-disruptive approach, augmenting human capabilities without overhauling processes. As organisations adopt new software versions with embedded AI capabilities, 2025 will mark a pivotal shift in customer experience delivery.
Ecosystm analysts Audrey William, Melanie Disse, and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 trends shaping customer experience in 2025.
Click here to download ‘AI-Powered Customer Experience: Top 5 Trends for 2025’ as a PDF
1. AI Won’t Wow Many Customers in 2025
The data is in – the real focus of AI over the next few years will be on productivity and cost savings.
Senior management and boards of directors want to achieve more with less – so even when AI is being used to serve customers, it will be focused on reducing back-end and human costs.
There will be exceptions, such as the adoption of AI agents in contact centres. However, AI agents must match or exceed human performance to see broad adoption.
However, the primary focus in contact centres will be on reducing Average Handling Time (AHT), increasing call volume per agent, accelerating agent onboarding, and automating customer follow-ups.

2. Organisations Will Start Treating CX as a Team Sport
As CX programs mature, 2025 will highlight the need to break down not only data and technology siloes but also organisational and cultural barriers to achieve AI-powered CX and business success.
AI and GenAI have unlocked new sources of customer data, prompting leaders to reorganise and adopt a mindset shift about CX. This involves redefining CX as a collective effort, engaging the entire organisation in the journey.
Technologies and KPIs must be aligned to drive customer AND business needs, not purely driving success in siloed areas.

3. The First “AGI Agents” Will Emerge
AI Agents are set to explode in 2025, but even more disruptive developments in AI are on the horizon.
As conversational computing gains traction, fuelled by advances in GenAI and progress toward AGI, “Complex AI Agents” will emerge.
These “AGI Agents” will mimic certain human-like capabilities, though not fully replicating human cognition, earning their “Agent” designation.
The first use cases will likely be in software development, where these agents will act as intelligent platforms capable of transforming a described digital process or service into reality. They may include design, inbuilt testing, quality assurance, and the ability to learn from existing IP (e.g., “create an app with the same capabilities as X”).

4. Intelligent AI Bots Will Enhance Contact Centre Efficiency
The often-overlooked aspect of CX is the “operational side”, where Operations Managers face significant challenges in maintaining a real-time pulse on contact centre activities.
For most organisations, this remains a highly manual and reactive process. Intelligent workflow bots can revolutionise this by acting as gatekeepers, instantly identifying issues and triggering real-time corrective actions. These bots can even halt processes causing customer dissatisfaction, ensuring problems are addressed proactively.
Operational inefficiencies, such as back-office delays, unanswered emails, and slow issue containment, create constant headaches. Integrating bots into contact centre operations will significantly reduce time wasted on these inefficiencies, enhancing both employee and customer experiences.

5. Employee Experience Will Catch Up to CX Maturity
Employee experience (EX) has traditionally lagged behind CX in focus and technology investment. However, AI-powered technologies are now enabling organisations to apply CX use cases to EX efforts, using advanced data analysis, summaries, and recommendations.
AI and GenAI tools will enhance understanding of employee satisfaction and engagement while predicting churn and retention drivers.
HR teams and leaders will leverage these tools to optimise performance management and improve hiring and retention outcomes.
Additionally, organisations will begin to connect EX with financial performance, identifying key drivers of engagement and linking them to business success. This shift will position EX as a strategic priority, integral to achieving organisational goals.


AI has already had a significant impact on the tech industry, rapidly evolving software development, data analysis, and automation. However, its potential extends into all industries – from the precision of agriculture to the intricacies of life sciences research, and the enhanced customer experiences across multiple sectors.
While we have seen the widespread adoption of AI-powered productivity tools, 2025 promises a bigger transformation. Organisations across industries will shift focus from mere innovation to quantifiable value. In sectors where AI has already shown early success, businesses will aim to scale these applications to directly impact their revenue and profitability. In others, it will accelerate research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and innovations in the years to come. Regardless of the specific industry, one thing is certain: AI will be a driving force, reshaping business models and competitive landscapes.
Ecosystm analysts Alan Hesketh, Clay Miller, Peter Carr, Sash Mukherjee, and Steve Shipley present the top trends shaping key industries in 2025.
Click here to download ‘AI’s Impact on Industry in 2025’ as a PDF
1. GenAI Virtual Agents Will Reshape Public Sector Efficiency
Operating within highly structured, compliance-driven environments, public sector organisations are well-positioned to benefit from GenAI Agents.
These agents excel when powered LLMs tailored to sector-specific needs, informed by documented legislation, regulations, and policies. The result will be significant improvements in how governments manage rising service demands and enhance citizen interactions. From automating routine enquiries to supporting complex administrative processes, GenAI Virtual Agents will enable public sector to streamline operations without compromising compliance. Crucially, these innovations will also address jurisdictional labour and regulatory requirements, ensuring ethical and legal adherence. As GenAI technology matures, it will reshape public service delivery by combining scalability, precision, and responsiveness.

2. Healthcare Will Lead in Innovation; Lag in Adoption
In 2025, healthcare will undergo transformative innovations driven by advancements in AI, remote medicine, and biotechnology. Innovations will include personalised healthcare driven by real-time data for tailored wellness plans and preventive care, predictive AI tackling global challenges like aging populations and pandemics, virtual healthcare tools like VR therapy and chatbots enhancing accessibility, and breakthroughs in nanomedicine, digital therapeutics, and next-generation genomic sequencing.
Startups and innovators will often lead the way, driven by a desire to make an impact.
However, governments will lack the will to embrace these technologies. After significant spending on crisis management, healthcare ministries will likely hesitate to commit to fresh large-scale investments.

3. Agentic AI Will Move from Bank Credit Recommendation to Approval
Through 2024, we have seen a significant upturn in Agentic AI making credit approval recommendations, providing human credit managers with the ability to approve more loans more quickly. Yet, it was still the mantra that ‘AI recommends—humans approve.’ That will change in 2025.
AI will ‘approve’ much more and much larger credit requests.
The impact will be multi-faceted: banks will greatly enhance client access to credit, offering 24/7 availability and reducing the credit approval and origination cycle to mere seconds. This will drive increased consumer lending for high-value purchases, such as major appliances, electronics, and household goods.

4. AI-Powered Demand Forecasting Will Transform Retail
There will be a significant shift away from math-based tools to predictive AI using an organisation’s own data. This technology will empower businesses to analyse massive datasets, including sales history, market trends, and social media, to generate highly accurate demand predictions. Adding external influencing factors such as weather and events will be simplified.
The forecasts will enable companies to optimise inventory levels, minimise stockouts and overstock situations, reduce waste, and increase profitability. Early adopters are already leveraging AI to anticipate fashion trends and adjust production accordingly.
No more worrying about capturing “Demand Influencing Factors” – it will all be derived from the organisation’s data.

5. AI-Powered Custom-Tailored Insurance Will Be the New Norm
Insurers will harness real-time customer data, including behavioural patterns, lifestyle choices, and life stage indicators, to create dynamic policies that adapt to individual needs. Machine learning will process vast datasets to refine risk predictions and deliver highly personalised coverage. This will produce insurance products with unparalleled relevance and flexibility, closely aligning with each policyholder’s changing circumstances. Consumers will enjoy transparent pricing and tailored options that reflect their unique risk profiles, often resulting in cost savings. At the same time, insurers will benefit from enhanced risk assessment, reduced fraud, and increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This evolution will redefine the customer-insurer relationship, making insurance a more dynamic and responsive service that adjusts to life’s changes in real-time.


2024 was a year marked by intense AI-driven innovation. While the hype surrounding AI may have reached a fever pitch, the technology’s transformative potential is undeniable.
The growing interest in AI can be attributed to several factors: the democratisation of AI, with tools and platforms now accessible to businesses of all sizes; AI’s appeal to business leaders, offering actionable insights and process automation; and aggressive marketing by major tech companies, which has amplified the excitement and hype surrounding AI.
2025 will be a year defined by AI, with its transformative impact rippling across industries. However, other geopolitical and social factors will also significantly shape the tech landscape.
Ecosystm analysts Achim Granzen, Alan Hesketh, Audrey William, Clay Miller, Darian Bird, Manish Goenka, Richard Wilkins, Sash Mukherjee, Simona Dimovski, and Tim Sheedy present the key trends and disruptors shaping the tech market in 2025.
Click here to download ‘Key Tech Trends & Disruptors in 2025’ as a PDF
1. Quantum Computing Will Drive Major Transformation in the Tech Industry
Advancements in qubit technology, quantum error correction, and hybrid quantum-classical systems will accelerate breakthroughs in complex problem-solving and machine learning. Quantum communications will revolutionise data security with quantum key distribution, providing nearly unbreakable communication channels. As quantum encryption becomes more widespread, it will replace current cryptographic methods, protecting sensitive data from future quantum-enabled attacks.
With quantum computing threatening encryption standards like RSA and ECC, post-quantum encryption will be critical for data security.
While the full impact of quantum computers is expected within the next few years, 2025 will be pivotal in the transition toward quantum-resistant security measures and infrastructure.

2. Many Will Try, But Few Will Succeed as Platform Companies
Hypergrowth occurs when companies shift from selling products to becoming platform providers. Unlike traditional businesses, platforms don’t own inventory; their value lies in proprietary data and software that connect buyers, sellers, and consumers. Platforms disrupt industries and often outperform legacy businesses, with examples like Uber, Amazon, and Meta, and disruptors like Lemonade in insurance and Wise in international funds transfer.
In 2025, many companies will aim to become platform businesses, with AI seen as a key driver.
They will begin creating platforms and building ecosystems around them – some within existing brands, others launching new ones or even new subsidiaries to seize this opportunity.

3. A Trans-Atlantic Divide Will Emerge in AI Regulation
The EU is poised to continue its rigorous approach to AI regulation, emphasisng ethical considerations and robust governance. This is evident in the recent AI Act, which imposes stringent guidelines and penalties for violations. The EU’s commitment to responsible AI development is likely to lead to a more cautious and controlled innovation landscape.
In contrast, the US, under a new administration, may adopt a more lenient regulatory stance towards AI. This shift could accelerate innovation and foster a more permissive environment for AI development. However, it may also raise concerns about potential risks and unintended consequences.
This divergence in regulatory frameworks could create significant challenges for multinational companies operating in both regions.

4. The Rise of AI-Driven Ecosystem Platforms Will Shape Tech Investments
By 2025, AI-driven ecosystem platforms will dominate tech investments, fueled by technological convergence, market efficiency demands, and evolving regulations. These platforms will integrate AI, IoT, cloud, and data analytics to create seamless, predictive ecosystems that transcend traditional industry boundaries.
Key drivers include advancements in AI, global supply chain disruptions, and rising ESG expectations. Regulatory shifts, such as the EU’s AI Act, will further push for compliant, ethical platforms emphasising transparency and accountability.
For businesses, this shift redefines technology as interconnected ecosystems driving efficiency, innovation, and customer value.

5. AI-Powered Data Fabrics Will be the Foundation for Data-Driven Success
In 2025, AI-powered data fabrics will become a core technology for large organisations.
They will transition from basic data management tools to intelligent systems that deliver value across the entire data lifecycle. Organisations will finally be able to get control of their data governance.
AI’s enhanced role will automate essential data functions, including intelligent data integration and autonomous connection to diverse data sources. AI will also enable proactive data quality management, predicting and preventing errors for improved reliability. AI-driven data fabrics will also offer automated data discovery and mapping, dynamic data quality and governance, intelligent data integration, and enhanced data access and delivery.

6. Focus Will Shift From AI Models to Intelligence Gaps & Performance
While many organisations are investing in AI, only those that started their transformation in 2024 are truly AI-led. Most have become AI-driven through embedded AI in enterprise systems as tech providers continue to evolve their offerings. However, these multi-vendor environments often lack synergy, creating gaps and blind spots.
In 2025, organisations will pause their investments to assess AI capabilities and identify these gaps.
Once they pinpoint the blind spots, investments will refocus not on new AI models, but on areas like model orchestration to manage workflows and ensure peak performance; vendor management to establish unified governance frameworks for flexibility and compliance; and eventually automated AI lifecycle management, with centralised inventories and monitoring to track performance and detect issues like model drift.

7. Specialised Small Language Models Will Gain Traction
GenAI, driven by LLMs, has dominated the spotlight, fueling both excitement and concerns about AI. However, LLM-based GenAI is entering a phase of diminishing returns, both in terms of individual model capabilities and the number of available models. Only a few providers will have the resources to develop LLMs, focusing on a limited number of models.
This will see the increased popularity of small language models (SLMs), that are tailored for a specific purpose, use case, or environment. These models will be developed by startups, organisations, and enterprises with deep domain knowledge and data. They will be fully commercialised driving narrow but distinct ROI.
There will be an increased demand for GPU-as-a-service and SLM-as-a-service, and the platforms which can support these.

8. Multi-agent AI Systems Will Help Manage Complexity and Collaboration
Isolated AI tools that can perform narrow tasks lack the adaptability and coordination required for real-time decision-making. Multi-agent systems, in contrast, consist of decentralised agents that collaborate, share information, and make independent decisions while working toward a common goal. This approach not only improves efficiency but also enhances resilience in rapidly changing conditions.
Early use cases will be in complex environments that require cooperation between multiple stakeholders.
Multi-agent systems will optimise logistics by continuously analysing disruptions and dynamically balancing supply and demand in energy grids. These multi-agent systems will also operate in competitive modes, such as algorithmic trading, ad auctions, and ecommerce recommender systems.

9. Super Apps Will Expand into Rural & Underserved Markets in Asia Pacific
Super apps are set to reshape rural economies, fueled by increased internet access, affordable tech, and heavy government investment in digital infrastructure. Their localised, all-in-one services unlock untapped potential in underserved regions, fostering inclusivity and innovation.
By 2025, super apps will deepen their reach across Asia, integrating communication, payments, and logistics into seamless platforms.
Leveraging affordable mobile devices, cloud-native technologies, and localised services, they will penetrate rural and underserved areas with tailored solutions like agricultural marketplaces, local logistics, and expanded government services. Enterprises investing in agile cloud infrastructure will drive this evolution, bridging the digital divide, boosting economic growth, and enhancing user experiences for millions.

10. Intense Debates Over Remote vs. In-Office Work Will Persist in Asia Pacific
Employers in Asia Pacific will enforce stricter return-to-office policies, linking them to performance metrics and benefits to justify investments in physical spaces and enhance workforce productivity.
However, remote collaboration will remain integral, even for in-office teams.
The push for human-centred tech will grow, focusing on employee well-being and flexibility through AI-powered tools and hybrid platforms. Companies will prioritise enhancing employee experiences with personalised, adaptable workspaces, while office designs will increasingly incorporate biophilic elements, blending nature and technology to support seamless collaboration and remote integration.


In 2024, AI was marked by experimentation, but 2025 will focus on delivering real business value through robust infrastructure, efficient operations, and skilled talent.
This whitepaper explores the emerging AI trends, the critical challenges businesses face, and offers practical insights from 17 leading APAC organizations to help unlock AI’s transformative power while mitigating risks. Explore AI success stories from ANZ, India, Singapore, and more, and uncover practical steps to start or refine your AI journey.
Download Whitepaper – Whitepaper – APAC AI Outlook 2025

(Clicking on this link will take you to the IBM website where you can download the whitepaper)

Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on Public Sector.
Click here to download ‘AI in Government: Success Stories & Insights’ as a PDF
From improving citizen services to infrastructure management, AI is empowering governments to deliver efficient, effective, and equitable public services. While challenges like data privacy and the need for investments in technology infrastructure remain, governments that can overcome these obstacles and harness the power of AI will be well-positioned to shape the future of public service.
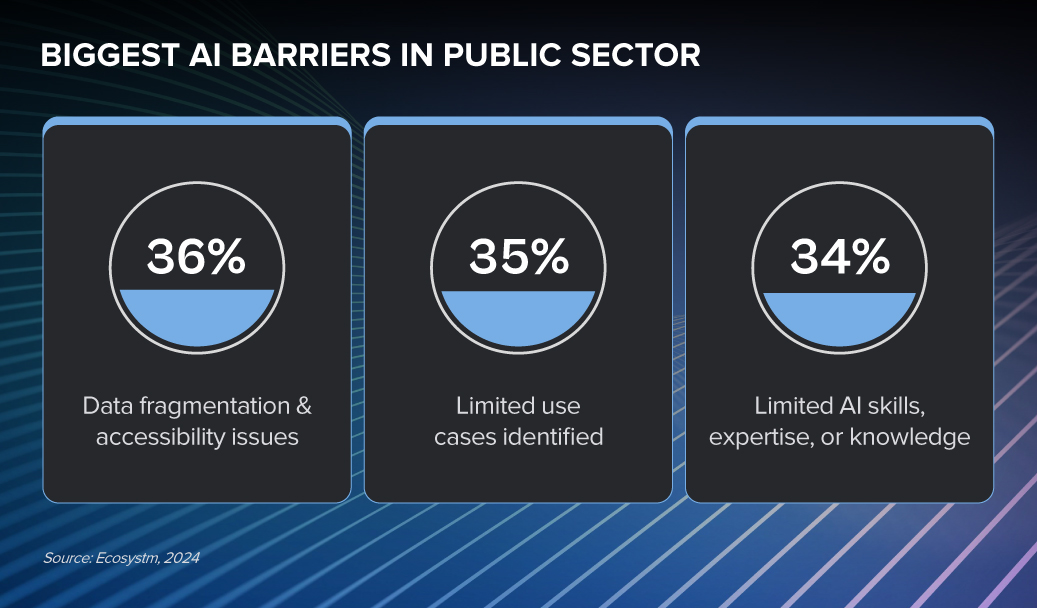
Despite the challenges, Public Sector organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Public Services & Citizen Engagement
- 2. Infrastructure Management & Optimisation
- 3. Internal Operations & Efficiency
Public Services & Citizen Engagement
- Chatbots & Virtual Assistants. Providing citizens with information and support
- Online Services. Delivering government services online, such as healthcare and education
- Citizen Engagement. Gathering and analysing citizen feedback to deepen engagement
“The pandemic accelerated the development of AI-based apps and services, which provide answers to citizen inquiries and manage bookings. Initially introduced for contactless interaction due to health concerns, these technologies are now boosting employee productivity and eliminating bottlenecks.” - CITIZEN SERVICES LEADER
Infrastructure Management & Optimisation
- Traffic Management. Optimising traffic flow and reducing congestion
- Urban Planning. Analysing urban growth patterns and planning for future development
- Asset Management. Managing and maintaining government assets efficiently
“AI solutions have greatly enhanced visibility across multiple key departments – detection of roadblocks and accidents, real-time updates on drainage issues during rainy seasons, remotely monitoring water quality, and so on.” - URBAN DEVELOPMENT LEADER
Internal Operations & Efficiency
- Workflow Automation. Automating various government processes to improve efficiency
- Decision Support. Providing decision-makers with AI-powered insights and recommendations
- Resource Management. Optimising the allocation and management of resources
“We are committed to increase our investments on process efficiency, with the ultimate objective of providing better citizen services.” - CIO, CITIZEN WELFARE ORGANISATION

Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on the Healthcare industry.
Click here to download ‘AI in Healthcare: Success Stories & Insights’ as a PDF
AI is transforming the healthcare industry, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient outcomes and streamline operations. However, the successful implementation of AI in healthcare is not without its challenges. Those who can navigate these complexities and harness the power of AI will emerge as industry leaders, driving innovation and shaping the future of healthcare.

Despite the challenges, Healthcare organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Diagnostics
- 2. Care Management
- 3. Operational Efficiency & Optimisation
Diagnostics
- Image Analysis. Analysing medical images (e.g., X-rays, MRIs) to detect diseases and abnormalities
- Diagnosis. Assisting clinicians in identifying and diagnosing diseases
- Early Detection. Detecting diseases at an early stage for more effective treatment
“Diagnostics is where our AI journey began – starting with image analysis for eye diseases, evolving to x-ray screening tools, and most recently, investing in digital stethoscopes for our doctors and nurses.” – CLINICIAN LEADER
Care Management
- Clinical Decision Support. Providing clinicians with recommendations and insights to improve patient care
- Personalised Treatment Plans. Personalising treatment protocols based on patient data and genetics
- Chronic Disease Management. Monitoring chronic diseases over multiple years
“Clinical decision support isn’t new, but AI has revolutionised it by enabling the system to send alerts and warnings proactively, rather than only when prompted.” – CLINICIAN LEADER
Operational Efficiency & Optimisation
- Supply Chain Management. Optimising inventory and supply chain processes
- Appointment Scheduling. Automating appointment booking and management
- Workflow Optimisation. Streamlining workflows and improving efficiency of clinical staff
“Patient satisfaction extends beyond clinical outcomes. Aspects like shorter waiting times during appointments, the availability of medications, and automated responses to common queries significantly enhance patient satisfaction. These are areas where we have successfully implemented AI.” – COO

As increasing climate chaos creates a disruptive impact on businesses, climate crisis, resource scarcity and environmental destruction are no longer just news stories — they are daily realities affecting all of us. Despite numerous sustainability initiatives, progress is not happening fast enough to meet the demands of a growing population and a rapidly changing planet.
The second edition of The Global Sustainability Barometer study, commissioned by Kyndryl and Microsoft, examines the roles that strategy, data and AI play in achieving sustainability goals and highlights the gaps between organizational intent and action.
Conducted by Ecosystm in August and September of 2024, this study reflects the perspectives of 1,355 global sustainability leaders spanning 20 countries and nine industries. Respondents were evenly split between technology leaders and sustainability leaders from various business lines.
Download Whitepaper – 2024 Global Sustainability Barometer Study

(Clicking on this link will take you to the Kyndryl website where you can download the whitepaper)

Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on the Retail industry.
Click here to download ‘AI in Retail: Success Stories & Insights’ as a PDF
From personalised product recommendations to predictive analytics, AI is helping retailers deliver exceptional customer experiences and optimise their operations. However, many retailers are still grappling with the complexities of AI implementation. Those who can successfully navigate this challenge and harness the power of AI will emerge as industry leaders, driving innovation and shaping the future of retail.
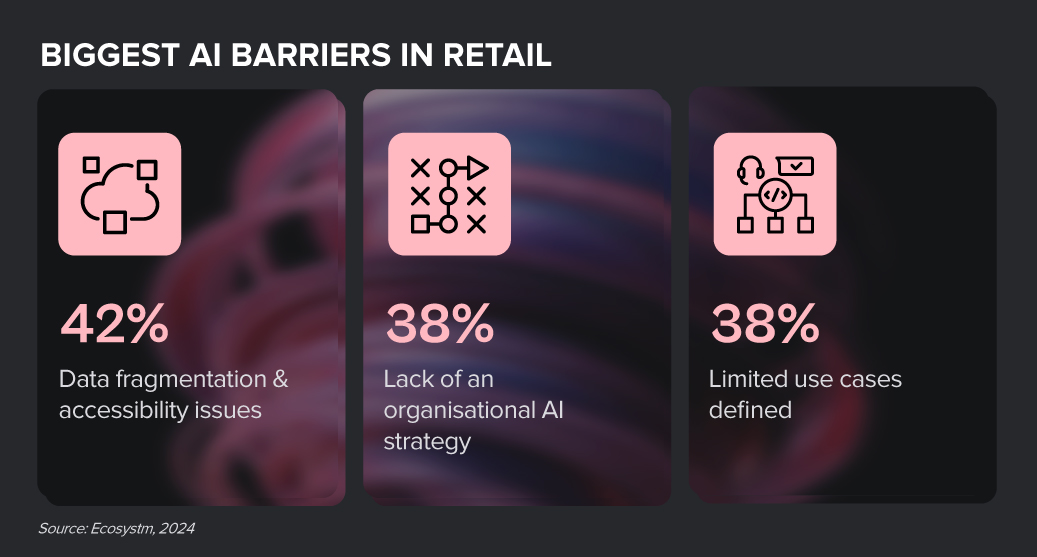
Despite the challenges, Retail organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Customer Experience & Engagement
- 2. Supply Chain Optimisation
- 3. Fraud & Risk Analysis
Customer Experience & Engagement
- Conversational AI. Providing real-time customer support and answering queries
- Personalisation. Offering tailored product suggestions based on customer preferences and behaviour
- Virtual Try-On. Allowing customers to visualise products in different settings using AR
“AI has helped us to refine our customer chatbots to allow for more self-service. We’ve experienced faster customer order processing and quicker resolution of issues, putting control directly in the hands of our customers.” – CX LEADER
Supply Chain Optimisation
- Inventory Management. Automating inventory management processes to ensure optimal stock levels
- Supply Chain Visibility. Monitoring and optimising supply chain operations, including logistics and distribution
- Demand Forecasting. Predicting sales and demand trends to optimise inventory and production planning
“We use AI to optimise the supply chain, saving operational costs. Digital supply chains and cloud-based tracking systems streamline operations and enhance efficiency.” – CFO
Fraud & Risk Analysis
- Fraud Detection. Identify and prevent fraudulent activities, such as online fraud and chargebacks
- Risk Assessment. Assessing risk factors associated with customer transactions and preventing losses
- Customer & Market Insights. Understanding customer behaviour, market trends, and growth opportunities
“With eCommerce as a key market force, understanding customer habits is crucial to ensuring we have the right products in stock and optimising our pricing strategy.” – COO









































































