Undersea cables form the invisible backbone of the modern internet, carrying vast amounts of data across continents and connecting billions of people. These vital arteries of global communication are, however, surprisingly vulnerable.
Hybrid Warfare at Sea
Recent incidents have highlighted the vulnerability of undersea infrastructure, particularly in the Baltic Sea. In the latest case, a fibre optic cable between Latvia and Sweden was reportedly severed by the dragging anchor of the cargo ship Vezhen, originating from Russia’s Ust-Luga port. Swedish authorities boarded and seized the vessel.
In December, the Eagle S Panamax oil tanker, sailing from St. Petersburg, allegedly damaged a power cable and three fibre optic cables between Estonia and Finland, as well as another connection between Finland and Germany. Finnish authorities seized the ship for investigation. A similar incident occurred in November when the Yi Peng 3, also from Ust-Luga, was linked to cable ruptures connecting Sweden to Lithuania and Finland to Germany. Although shadowed by the Royal Danish Navy, the vessel was ultimately allowed to continue its voyage.
The suspected sabotage of 11 undersea cables in 15 months has alarmed NATO countries, prompting increased surveillance around Europe. Patrols will focus on protecting critical assets like fibre optic cables, power lines, gas pipelines, and environmental sensors. Dubbed Baltic Sentry, the mission will deploy frigates, patrol aircraft, and unmanned naval drones, supported by NATO’s Maritime Centre for the Security of Critical Undersea Infrastructure. An AI system will monitor unusual shipping activity, such as loitering near cables or erratic course changes, aiming to cut response times to 30-60 minutes. Meanwhile, Operation Nordic Warden will analyse satellite imagery, patrol data, and Automatic Identification System (AIS) signals to assess risks in 22 key areas.
The primary concern is damage to infrastructure in the shallow waters of the Baltic Sea, but suspicious activity elsewhere has caught the attention of tech giants. Ireland, a critical hub for Europe’s cloud data centres, hosts undersea cables owned by companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon, linking it to the US and UK. As a non-NATO country, Ireland faces the challenge of monitoring over 3,000km of coastline. Recently, both the Irish Defence Forces and Royal Navy shadowed a Russian spy ship in the Irish Sea and English Channel. While cable damage is often immediately evident, the risk of communication taps is more alarming and harder to detect.
How Resilient Are Undersea Cable Networks?
There are about 400 undersea cables spanning over 1.3 million kms globally. According to the International Cable Protection Committee, around 200 incidents of cable damage occur annually, mostly caused by dragged anchors or trawling. Only about 10% result from natural causes like weather or wildlife. Near shorelines, cables are heavily protected and often buried under several metres of sand in shallow waters. However, in deeper seas, they are harder to monitor and safeguard.
Highly developed regions, such as the Baltic Sea, North Sea, and Irish Sea, rely on multiple redundant cables to maintain connections between countries. While severing a single link may reduce capacity and cause inconvenience, major disruptions are rare, even for remote European islands served by multiple cables.
Fibre optic cable repairs typically take days to weeks, faster than the lengthy timelines for fixing power cables or gas pipelines. Repair costs range from USD 1-3 million depending on the damage. Faults are located using test pulses, and specialised ships lift the damaged sections to the surface for splicing. However, with only 22 repair-designated cable ships worldwide, simultaneous outages could significantly delay restoration.
In regions with less cooperative neighbours, obtaining permissions can further slow repairs. For instance, cables crossing the South China Sea face increasing challenges in deployment and maintenance, complicating connections between ASEAN nations. Routing cables along longer coastal paths raises costs and impacts latency, adding further strain to the network.
Responding to Escalating Incidents
Plausible deniability and the opaque nature of maritime operations make attributing these events challenging. Nonetheless, NATO countries view them as part of Russia’s broader hybrid warfare strategy, which avoids direct confrontation while instilling fear and uncertainty by showcasing an adversary’s reach. Attacks on undersea cables undermine public trust in a government’s ability to protect critical infrastructure.
European governments initially downplayed the impact of these attacks, likely to minimise psychological effects and avoid escalation. While this cautious approach, coupled with rapid repairs, proved effective in the short term, it may have emboldened adversaries, leading to further incidents. In response, Sweden and Finland are now more willing to seize vessels in their territorial waters to deter both intentional and negligent actions.
Implications for Enterprise Networks
While enterprises cannot prevent damage to undersea infrastructure, they can mitigate risks and build resilient networks:
- Satellite Connectivity. Satellite internet services like Starlink and Eutelsat may not be ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications but can support critical services requiring international connections. An SD-WAN enables automatic failover to a redundant circuit if a land-based or undersea cable is disrupted.
- Dynamic Path Selection. Modern WAN architectures with dynamic path selection can reroute traffic to alternate cloud regions when primary paths are down. Locally available services can continue operating on domestic networks unaffected by international outages.
- Edge Computing. Adopting an edge-to-cloud strategy allows the running of select workloads closer to the edge or in local data centres. This reduces reliance on international links, improves resilience, and lowers latency.
- Disaster Recovery Planning. Enterprises should incorporate extended network outages into their disaster recovery plans, assessing the potential impact on operations and distinguishing between land-based, undersea, and other types of connections.

Ecosystm recently partnered with Asavie to conduct a study on the opportunity and outlook for the “Branch of One“. The results of the study make us question whether organisations’ mobile security strategies are appropriate for the evolving business priorities, the ever-changing threat landscape, and a seamless employee experience.
To answer this question, organisations will need to examine their security frameworks.
COVID-19 has forced organisations to realise that cybersecurity is not only a business enabler – it is a business prerequisite. Our research shows that businesses world-wide no longer see the pandemic as something that we need to get through to get back to “business as usual”. Most acknowledge that remote working and access from anywhere will be the new normal for many employees and that means they need to revisit and reprioritise their spending and their focus.
In many cases, existing procedures and policies are not sufficient to cover this new working environment – and often the policies have not been clearly communicated to all employees. Moreover, many organisations still rely on legacy WAN technologies that make secure and flexible access difficult – something that my colleague, Tim Sheedy touched upon in his recent blog post.
The choice of WAN technology is an important part of any mobile security strategy, but so is the approach to securing endpoints on the WAN and – what is perhaps the weakest link – the behaviour of employees.
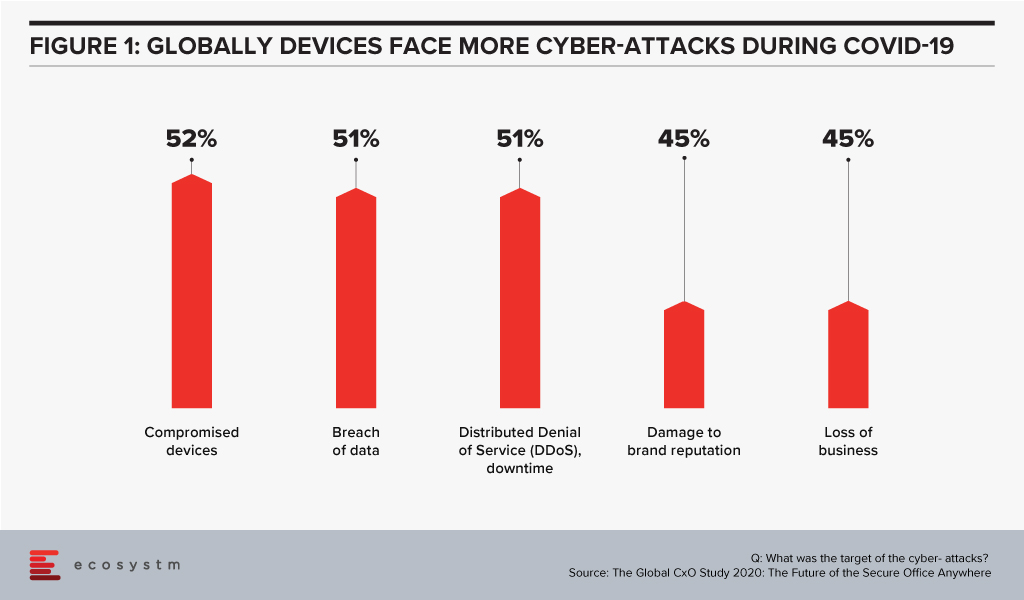
The Global CxO Study 2020: The Future of Secure Office Anywhere showed us that when it came to mobile security, organisations were mostly worried about phishing and malware – but 4 out of the top 5 mobile security concerns involved human error and failure to follow corporate IT security policies and guidelines (Figure 1).

Time to Evaluate New Mobile Security Features
This highlights the importance of a couple of “security features” that many IT organisations still tend to overlook – convenience and ease-of-use. When employees ignore IT policies, bypass security steps, use unsanctioned personal devices to process work data etc., they tend to do so for mainly one reason: because it is convenient for them. Employees just want to get the work done and following security protocols, making sure that devices have the right security software installed etc. is simply seen as too cumbersome or as slowing down the work process.
To counter this, ease-of-use and convenience need to an integral part of any security framework – especially when employees are no longer working in the office. IT managers tend to be a bit ego-centric when they think of these terms, i.e. for them ease-of-use relates to their experience in implementing and running the systems, but they really need to be extending the ease to their users – the employees – as well.
This is where Branch of One comes to the fore. It offers the convenience of employees not having to install or connect software or hardware on the mobile device and it allows administrators to easily scale and manage their mobile security framework. Security frameworks do not have to be in the way of getting the work done. Branch of One shows us that comprehensive mobile security can be nearly seamless.
Download the report based on ‘The Global CxO Study 2020: The Future of the Secure Office Anywhere’, conducted by Ecosystm on behalf of Asavie. The report presents the key findings of the study and analyses the market perceptions of Office Anywhere and the need for a ‘Branch of One’, which will be the foundation of enterprise mobile security in the future.

Ecosystm recently partnered with Asavie to conduct a study into the opportunity and outlook for the “Branch of One”. One of the challenges was actually defining what the Branch of One is. Here’s what we came up with:
Branch of One enables Office Anywhere by delivering secure, frictionless access to all business resources, with full mobility – meeting the security and manageability requirements of CIOs and CISOs.
Basically it is all the data and systems you need to get your job done, in your pocket. Secure. Easy to manage.
What I really like about the idea is that it describes what business is trying to achieve and it gives a common language and outcome for IT and business leaders. Consider all the things that IT and security teams need to do to enable access to applications and data in remote branches – from connectivity to security to data and system access. Often it takes days, weeks or months to open a new office or branch, or to provision a new retail store. Now, imagine having the ability to roll out all of these systems and services in seconds. To a single user or to thousands. Without consideration for location. Business leaders will understand this benefits and will support it.
It also has the opportunity to help nearly every business today. Of the 1005 businesses we interviewed across the globe in our Global CxO Study 2020, 44% admitted to suffering cyber-attack incidents during COVID-19 due to employees working from home – and over half of these attacks were on mobile devices. Compromised devices were the number one target for cyber-attacks in 2020.
Businesses need a new way to manage the devices and applications of their remote employees. They need to be able to extend the benefits of the WAN to them without the downsides of VPNs. Every business we interviewed saw benefits of bringing devices, locations and offices inside the WAN. Turning every device and office into a Branch of One.
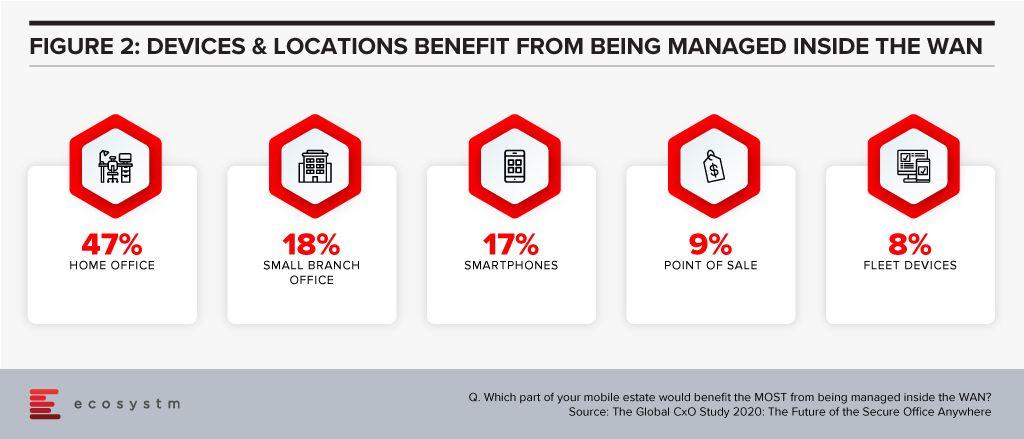
A few security and network technologies have promised this capability – SDNs can offer a similar service, but they require client software to be installed. 78% of businesses we interviewed are using VPNs to bring devices inside the WAN – but again, they require client software, and can be inconsistent (and insecure!) on mobile devices.
Companies that embrace the Branch of One can provision new users in a few clicks. No software to install, no cables to connect, no hardware to provision – it makes life easier for technology and security professionals. The Branch of One gives your employees the systems and data they need to get their job done – delivered securely across the mobile network.
Download the report based on ‘The Global CxO Study 2020: The Future of the Secure Office Anywhere’, conducted by Ecosystm on behalf of Asavie. The report presents the key findings of the study and analyses the market perceptions of Office Anywhere and the need for a ‘Branch of One’, which will be the foundation of enterprise mobile security in the future.





