As one of Asia’s most digitally mature economies, Singapore was an early mover in national digital transformation and is now turning that head start into resilient, innovation-led economic value. Today, the conversation across boardrooms, regulators, and industry circles has evolved: it’s no longer just about adopting technology but about embedding digital as a systemic driver of competitiveness, inclusion, and sustained growth.
Singapore’s approach offers a model for the region, with its commitment to building a holistic digital ecosystem. This goes beyond infrastructure, it includes nurturing digital talent, fostering a vibrant innovation and startup culture, enabling trusted cross-border data flows, and championing public-private collaboration. Crucially, its forward-looking regulatory stance balances support for experimentation with the need to uphold public trust.
Through our conversations with leaders in Singapore and Ecosystm’s broader research, we see a country intentionally architecting its digital future, focused on real-world outcomes, regional relevance, and long-term economic resilience.
Here are five insights that capture the pulse of Singapore’s digital transformation.
Theme 1: Digital Governance as Strategy: Setting the Pace for Innovation & Trust
Singapore’s approach to digital governance goes beyond policy. It’s a deliberate strategy to build trust, accelerate innovation, and maintain economic competitiveness. The guiding principle is clear: technology must be both transformative and trustworthy.
This vision is clearly visible in the public sector, where digital platforms and services are setting the pace for the rest of the economy. Public service apps are designed to be citizen-centric, secure, and efficient, demonstrating how digital delivery can work at scale. The Government Tech Stack allows agencies to rapidly build and integrate services using shared APIs, cloud infrastructure, and secure data layers. Open data initiatives like Data.gov.sg unlock thousands of datasets, while tools such as FormSG and SG Notify make it easy for any organisation to digitise services and engage users in real time.
By leading with well-designed digital infrastructure and standards, the public sector creates blueprints that others can adopt, lowering the barriers to innovation for businesses of all sizes. For SMEs in particular, these tools and frameworks offer a practical foundation to modernise operations and participate more fully in the digital economy.
Singapore is also setting clear rules for responsible tech. IMDA’s Trusted Data Sharing Framework and AI Verify establish standards for secure data use and transparent AI, giving businesses the certainty they need to innovate with confidence. All of this is underpinned by strategic investments in digital infrastructure, including a new generation of sustainable, high-capacity data centres to meet growing regional demand. In Singapore, digital governance isn’t a constraint, it’s a catalyst.

Theme 2: AI in Singapore: From Experimentation to Accountability
Few places have embraced AI’s potential as strongly as Singapore. In 2022 and 2023, fuelled by the National AI Strategy and commercial pressure to deliver results, organisations across industries rushed into pilots in 2022 and 2023. Ecosystm research shows that by 2024, nearly 82% of large enterprises in Singapore were experimenting with AI, with 37% deploying it across multiple departments.
However, that initial wave of excitement soon gave way to realism. Leaders now speak candidly about AI fatigue and the growing demand for measurable returns. The conversation has shifted from “What can we automate?” to “What’s actually worth scaling?” Organisations are scrutinising whether their AI projects deliver tangible value, integrate into daily operations, and meet evolving regulatory expectations.
This maturity is especially visible in Singapore’s banking sector, where the stakes are high and scrutiny is intense. Banks were among the first to embrace AI aggressively and are now leading the shift toward disciplined prioritisation. From actively hunting down use cases, they’ve pivoted to focusing on the select few that deliver real business outcomes. With increasing pressure to ensure transparency, auditability, and alignment with global standards, finance leaders are setting the tone for AI accountability across the economy.
The result: a more grounded, impact-focused AI strategy. While many regional peers are still chasing pilots, Singapore is entering a new phase, defined by fewer but better AI initiatives, built to solve real problems and deliver meaningful ROI.

Theme 3: The Cyber Imperative: Trust, Recovery, and Resilience
Singapore’s digital leadership brings not only opportunities but also increased exposure to cyber threats. In 2024 alone, the country faced 21 million cyberattacks, ranking eighth globally as both a target and a source. High-profile breaches, from vendor compromises affecting thousands of banking customers to earlier incidents like the SingHealth data breach, have exposed vulnerabilities across critical sectors.
These incidents have sparked a fundamental shift in Singapore’s cybersecurity mindset from building impenetrable digital fortresses to embracing digital resilience. The government recognises that breaches are inevitable and prioritises rapid containment and recovery over prevention alone. Regulatory bodies like MAS have tightened incident reporting rules, demanding quicker, more transparent responses from affected organisations.
For enterprises in Singapore, cybersecurity has moved beyond a technical challenge to become a strategic imperative deeply tied to customer trust and business continuity. Leaders are investing heavily in real-time threat detection, incident response, and crisis management capabilities. In a landscape where vulnerabilities are real and constant, cyber resilience is now a critical competitive advantage because in Singapore’s digital economy, trust and operational reliability are non-negotiable.

Theme 4: Beyond Coding: Singapore’s Quest for Hybrid Digital Talent
Singapore’s digital ambitions increasingly depend on its human capital. While consistently ranking high in global talent competitiveness, the city-state faces a projected shortfall of over 1.2 million digitally skilled workers, particularly in fields like cybersecurity, data science, and AI engineering.
But the challenge isn’t purely technical. Organisations now demand talent that bridges technology, business strategy, and regulatory insight. Many digital initiatives stall not from technology limitations, but from a lack of professionals who can translate complex digital concepts into business value and ensure regulatory compliance.
To address this, government initiatives like the TechSkills Accelerator (TeSA) offer training subsidies and career conversion programmes. Meanwhile, leading tech providers including AWS, Microsoft, Google, and IBM, are stepping up, partnering with government and industry to deliver specialised training, certification programmes, and talent pipelines that help close the skills gap.
Still, enterprises grapple with keeping pace amid rapid technological change, balancing reskilling local talent with attracting specialised professionals from abroad. The future of Singapore’s digital economy will be defined as much by people as by technology; and by the partnerships that help bridge this critical gap.

Theme 5: Tracking Impact, Driving Change: Singapore’s Sustainability and Tech Synergy
Sustainability remains a core pillar of Singapore’s digital ambitions, driven by the government’s unwavering focus and supportive green financing options unlike in some markets where momentum has slowed. Anchored by the Singapore Green Plan 2030, the nation aims to double solar energy capacity and reduce landfill waste per capita by 30% by 2030.
Digital technology plays a critical role in this vision. Initiatives like the Green Data Centre Roadmap promote energy-efficient infrastructure and sustainable cooling technologies, balancing growth in the digital economy with carbon footprint management. Singapore is also emerging as a regional hub for carbon services, leveraging digital platforms such as the Carbon Services Platform to track, verify, and trade emissions, fostering credible and transparent carbon markets.
Government-backed green financing schemes, including the Green Bond Grant Scheme and Sustainability-Linked Loans, are accelerating investments in eco-friendly projects, enabling enterprises to fund sustainable innovation while meeting global ESG standards.
Despite these advances, leaders highlight challenges such as the lack of standardised sustainability metrics and rising risks of greenwashing, which complicate scaling green finance and cross-border sustainability reporting. Still, Singapore’s ability to integrate sustainability with digital innovation underscores its ambition to be more than a tech hub. It aims to be a trusted leader in building a responsible, future-ready economy.

From Innovation to Lasting Impact
Singapore stands at a critical inflection point. Already recognised as one of the world’s most advanced digital economies, its greatest test now is execution transforming cutting-edge technology from promise into real, everyday impact. The nation must balance rapid innovation with robust security, while shaping global standards that reflect its unique blend of ambition and pragmatism.
With deep-rooted trust across government, industry, and society, Singapore is uniquely equipped to lead not just in developing technology, but in embedding it responsibly to create lasting value for its people and the wider region. The next chapter will define whether Singapore can move from digital leadership to digital legacy.

Over the past year of moderating AI roundtables, I’ve had a front-row seat to how the conversation has evolved. Early discussions often centred on identifying promising use cases and grappling with the foundational work, particularly around data readiness. More recently, attention has shifted to emerging capabilities like Agentic AI and what they mean for enterprise workflows. The pace of change has been rapid, but one theme has remained consistent throughout: ROI.
What’s changed is the depth and nuance of that conversation. As AI moves from pilot projects to core business functions, the question is no longer just if it delivers value, but how to measure it in a way that captures its true impact. Traditional ROI frameworks, focused on immediate, measurable returns, are proving inadequate when applied to AI initiatives that reshape processes, unlock new capabilities, and require long-term investment.
To navigate this complexity, organisations need a more grounded, forward-looking approach that considers not only direct gains but also enablement, scalability, and strategic relevance. Getting this right is key to both validating today’s investments and setting the stage for meaningful, sustained transformation.
Here is a summary of the key thoughts around AI ROI from multiple conversations across the Asia Pacific region.
1. Redefining ROI Beyond Short-Term Wins
A common mistake when adopting AI is using traditional ROI models that expect quick, obvious wins like cutting costs or boosting revenue right away. But AI works differently. Its real value often shows up slowly, through better decision-making, greater agility, and preparing the organisation to compete long-term.
AI projects need big upfront investments in things like improving data quality, upgrading infrastructure, and managing change. These costs are clear from the start, while the bigger benefits, like smarter predictions, faster processes, and a stronger competitive edge, usually take years to really pay off and aren’t easy to measure the usual way.
Ecosystm research finds that 60% of organisations in Asia Pacific expect to see AI ROI over two to five years, not immediately.
The most successful AI adopters get this and have started changing how they measure ROI. They look beyond just money and track things like explainability (which builds trust and helps with regulations), compliance improvements, how AI helps employees work better, and how it sparks new products or business models. These less obvious benefits are actually key to building strong, AI-ready organisations that can keep innovating and growing over time.

2. Linking AI to High-Impact KPIs: Problem First, Not Tech First
Successful AI initiatives always start with a clearly defined business problem or opportunity; not the technology itself. When a precise pain point is identified upfront, AI shifts from a vague concept to a powerful solution.
An industrial firm in Asia Pacific reduced production lead time by 40% by applying AI to optimise inspection and scheduling. This result was concrete, measurable, and directly tied to business goals.
This problem-first approach ensures every AI use case links to high-impact KPIs – whether reducing downtime, improving product quality, or boosting customer satisfaction. While this short-to-medium-term focus on results might seem at odds with the long-term ROI perspective, the two are complementary. Early wins secure executive buy-in and funding, giving AI initiatives the runway needed to mature and scale for sustained strategic impact.
Together, these perspectives build a foundation for scalable AI value that balances immediate relevance with future resilience.

3. Tracking ROI Across the Lifecycle
A costly misconception is treating pilot projects as the final success marker. While pilots validate concepts, true ROI only begins once AI is integrated into operations, scaled organisation-wide, and sustained over time.
Ecosystm research reveals that only about 32% of organisations rigorously track AI outcomes with defined success metrics; most rely on ad-hoc or incomplete measures.
To capture real value, ROI must be measured across the full AI lifecycle. This includes infrastructure upgrades needed for scaling, ongoing model maintenance (retraining and tuning), strict data governance to ensure quality and compliance, and operational support to monitor and optimise deployed AI systems.
A lifecycle perspective acknowledges the real value – and hidden costs – emerge beyond pilots, ensuring organisations understand the total cost of ownership and sustained benefits.

4. Strengthening the Foundations: Talent, Data, and Strategy
AI success hinges on strong foundations, not just models. Many projects fail due to gaps in skills, data quality, or strategic focus – directly blocking positive ROI and wasting resources.
Top organisations invest early in three pillars:
- Data Infrastructure. Reliable, scalable data pipelines and quality controls are vital. Poor data leads to delays, errors, higher costs, and compliance risks, hurting ROI.
- Skilled Talent. Cross-functional teams combining technical and domain expertise speed deployment, improve quality, reduce errors, and drive ongoing innovation – boosting ROI.
- Strategic Roadmap. Clear alignment with business goals ensures resources focus on high-impact projects, secures executive support, fosters collaboration, and enables measurable outcomes through KPIs.
Strengthening these fundamentals turns AI investments into consistent growth and competitive advantage.

5. Navigating Tool Complexity: Toward Integrated AI Lifecycle Management
One of the biggest challenges in measuring AI ROI is tool fragmentation. The AI lifecycle spans multiple stages – data preparation, model development, deployment, monitoring, and impact tracking – and organisations often rely on different tools for each. MLOps platforms track model performance, BI tools measure KPIs, and governance tools ensure compliance, but these systems rarely connect seamlessly.
This disconnect creates blind spots. Metrics sit in silos, handoffs across teams become inefficient, and linking model performance to business outcomes over time becomes manual and error prone. As AI becomes more embedded in core operations, the need for integration is becoming clear.
To close this gap, organisations are adopting unified AI lifecycle management platforms. These solutions provide a centralised view of model health, usage, and business impact, enriched with governance and collaboration features. By aligning technical and business metrics, they enable faster iteration, responsible scaling, and clearer ROI across the lifecycle.

Final Thoughts: The Cost of Inaction
Measuring AI ROI isn’t just about proving cost savings; it’s a shift in how organisations think about value. AI delivers long-term gains through better decision-making, improved compliance, more empowered employees, and the capacity to innovate continuously.
Yet too often, the cost of doing nothing is overlooked. Failing to invest in AI leads to slower adaptation, inefficient processes, and lost competitive ground. Traditional ROI models, built for short-term, linear investments, don’t account for the strategic upside of early adoption or the risks of falling behind.
That’s why leading organisations are reframing the ROI conversation. They’re looking beyond isolated productivity metrics to focus on lasting outcomes: scalable governance, adaptable talent, and future-ready business models. In a fast-evolving environment, inaction carries its own cost – one that may not appear in today’s spreadsheet but will shape tomorrow’s performance.

Organisations are finding that the ways to do work and conduct business are evolving rapidly. It is evident that we cannot use the perspectives from the past as a guide to the future. As a consequence both leaders and employees are discovering and adapting both their work and their expectations from it. In general, while job security concerns still command a big mindshare, the simpler productivity measures are evolving to more nuanced wellness measures. This puts demands on the CHRO and the leadership team to think about company, customer and people strategy as one holistic way of working and doing business.
Organisations will have to re-think their people and technology to evolve their Future of Work policies and strategise their Future of Talent. There are multiple dimensions that will require attention.
Hybrid is Becoming Mainstream
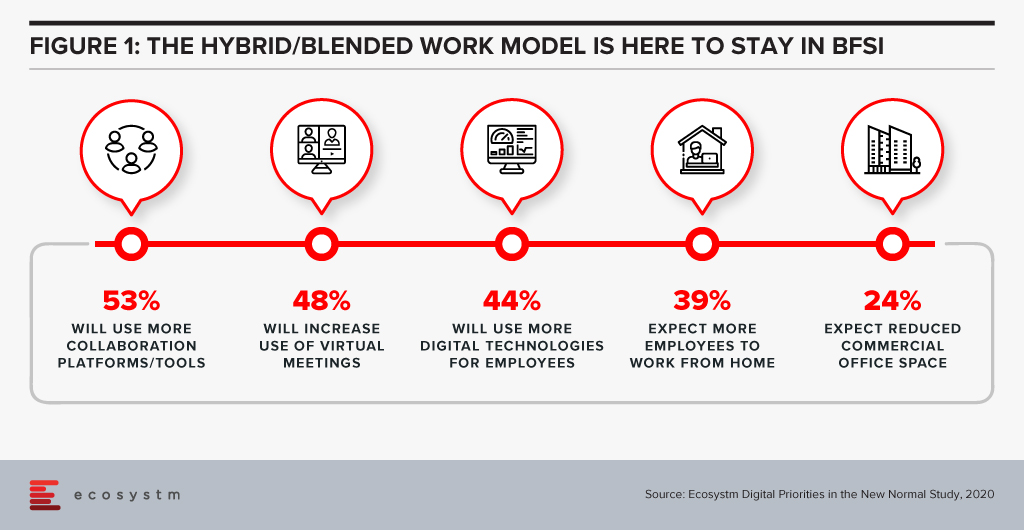
It is clear that hybrid workplaces are here to stay. Ecosystm research finds that in 2021 BFSI organisations will use more collaboration tools and platforms, and virtual meetings (Figure 1). Nearly 40% expect more employees to work from home, but only about a quarter of organisations are looking to reduce their physical workspaces. Organisations will give more choice to employees in the location of their work – and employees will choose to work from where they are more productive. The Hybrid model will be more mainstream than it has been in the last few months.
Companies are coming to terms with the fact that there is no single answer to operating in the new world. Experimentation and learnings are continuously captured to create the right workforce and workplace model that works best. Agility both in terms of being able to undersand the market as well as quickly adapt is becoming quite important. Thus being able to use different models and ways of working at the same time is the new norm.
Technology and Talent are Core
Talent and tech are the two core pillars that companies need to look at to be successful against their competition. It is becoming imperative to create synergy between the two to deliver a superior value proposition to customers. Companies that are able to bring the customer and employee experience journeys together will be able to create better value. HR tech stacks need to evolve to be more deliberate in the way they link the employee experience, customer experience, and the culture of the organisation. That’s how the Employee Value Proposition (EVP) comes to life on a day-to-day basis to the employers. With evolving work models, the tech stack is a key EVP pillar.
Governments will also need to partner with industry to make such talent available. Singapore is rolling out a new “Tech.Pass” to support the entry of up to 500 proven founders, leaders and experts from top tech companies into Singapore. Its an extension of the Tech@SG program launched in 2019, to provide fast-growing companies greater assurance and access to the talent they need. The EDB will administer the pass, supported by the Ministry of Manpower.
Attracting the Right Talent
Talent has always been difficult to find. Even with globalisation, significant investment of time and resources is needed to find and relocate talent to the right geography. In many instances this was not possible given the preferences of the candidates and/or the hiring managers. COVID-19 has changed this drastically. Remote working and distributed teams have become acceptable. With limitations on immigration and travel for work, there is a lot more openness to finding and hiring talent from outside the traditional talent pool.
However it is not as simple as it seems. The cost per applicant (CPA) – the cost to convert a job seeker to a job applicant – had been averaging US$11-12 throughout 2019 according to recruiting benchmark data from programmatic recruitment advertising provider, Appcast. But, the impact of COVID-19 saw the CPA reach US$19 in June – a 60% increase. I expect that finding right talent is going to be a “needle in a haystack” issue. But this is only one side of the coin – the other aspect is that the talent profile needed to be successful in roles that are all remote or hybrid is also significantly different from what it was before. Companies need to pay special attention to what kind of people they would like to hire in these new roles. Without this due consideration it is very likely that there would be difficulty in on-boarding and making these new hires successful within the organisation.
Automation Augmentation and Skills
The pace at which companies are choosing to automate or apply AI is increasing. This is changing the work patterns and job requirements for many roles within the industry. According to the BCG China AI study on the financial sector 23% of the roles will be replaced by AI by 2027. The roles that will not be replaced will need a higher degree of soft skills, critical thinking and creativity. However, automation is not the endgame. Firms that go ahead with automation without considering the implications on the business process, and the skills and roles it impacts will end up disrupting the business and customer experience. Firms will have to really design their customer journeys, their business processes along with roles and capabilities needed. Job redesign and reskilling will be key to ensuring a great customer experience
Analytics is Inadequate Without the Right Culture
Data-driven decision-making as well as modelling is known to add value to business. We have great examples of analytics and data modelling being used successfully in Attrition, Recruitment, Talent Analytics, Engagement and Employee Experience. The next evolution is already underway with advanced analytics, sentiment analysis, organisation network analysis and natural language processing (NLP) being used to draw better insights and make people strategies predictive. Being able to use effective data models to predict and and draw insights will be a key success factor for leadership teams. Data and bots do not drive engagement and alignment to purpose – leaders do. Working to promote transparency of data insights and decisions, for faster response, to champion diversity, and give everyone a voice through inclusion will lead to better co-creation, faster innovation and an overall market agility.
Creating a Synergy
We are seeing a number of resets to what we used to know, believe and think about the ways of working. It is a good time to rethink what we believe about the customer, business talent and tech. Just like customer experience is not just about good sales skills or customer service – the employee experience and role of Talent is also evolving rapidly. As companies experiment with work models, technology and work environment, there will a need to constantly recalibrate business models, job roles, job technology and skills. With this will come the challenge of melding the pieces together within the context of the entire business without falling into the trap of siloed thinking. Only by bringing together businesses processes, talent, capability evolution, culture and digital platforms together as one coherent ecosystem can firms create a winning formula to create a competitive edge.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Talent Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics on Founders success and failure stories, pandemic impact on founders and talent development, upskilling and reskilling for the future of work.