Operations leaders are on the front lines of the AI revolution. They see the transformative potential of AI and are actively driving its adoption to streamline processes, boost efficiency, and unlock new levels of performance. The value is clear: AI is no longer a futuristic concept, but a present-day necessity.
Over the past two years, Ecosystm’s research – including surveys and deep dives with business and tech leaders has confirmed this: AI is the dominant theme.
Here are some insights for Operations Leaders from our research.
Click here to download “AI Stakeholders: The Operations Perspective” as a PDF
From Streamlined Workflows to Smarter Decisions
AI is already making a tangible difference in operations. A significant 60% of operations leaders are currently leveraging AI for intelligent document processing, freeing up valuable time and resources. But this is just the beginning. The vision extends far beyond, with plans to expand AI’s reach into crucial areas like workflow analysis, fraud detection, and streamlining risk and compliance processes. Imagine AI optimising transportation routes in real-time, predicting equipment maintenance needs before they arise, or automating complex scheduling tasks. This is the operational reality AI is creating.
Real-World Impact, Real-World Examples
The impact of AI is not just theoretical. Operations leaders are witnessing firsthand how AI is driving tangible improvements. “With AI-powered vision and sensors, we’ve boosted efficiency, accuracy, and safety in our manufacturing processes,” shares one leader. Others highlight the security benefits: “From fraud detection to claims processing, AI is safeguarding our transactions and improving trust in our services.” Even complex logistical challenges are being conquered: “Our AI-driven logistics solution has cut costs, saved time, and turned complex operations into seamless processes.” These real-world examples showcase the power of AI to deliver concrete results across diverse operational functions.
Operations Takes a Seat at the AI Strategy Table (But Faces Challenges)
With 54% of organisations prioritising cost savings from AI, operations leaders are rightfully taking a seat at the AI strategy table, shaping use cases and driving adoption. A remarkable 56% of operations leaders are actively involved in defining high-value AI applications. However, a disconnect exists. Despite their influence on AI strategy, only a small fraction (7%) of operations leaders have direct data governance responsibilities. This lack of control over the very fuel that powers AI – data – creates a significant hurdle.
Further challenges include data access across siloed systems, limiting the ability to gain a holistic view, difficulty in identifying and prioritising the most impactful AI use cases, and persistent skills shortages. These barriers, while significant, are not deterring operations leaders.
The Future is AI-Driven
Despite these challenges, operations leaders are doubling down on AI. A striking 7 out of 10 plan to prioritise AI investments in 2025, driven by the pursuit of greater cost savings. And the biggest data effort on the horizon? Identifying and prioritising better use cases for AI. This focus on practical applications demonstrates a clear understanding: the future of operations is inextricably linked to the power of AI. By addressing the challenges they face and focusing on strategic implementation, operations leaders are poised to unlock the full potential of AI and transform their organisations.

AI is reshaping the tech infrastructure landscape, demanding a fundamental rethinking of organisational infrastructure strategies. Traditional infrastructure, once sufficient, now struggles to keep pace with the immense scale and complexity of AI workloads. To meet these demands, organisations are turning to high-performance computing (HPC) solutions, leveraging powerful GPUs and specialised accelerators to handle the computationally intensive nature of AI algorithms.
Real-time AI applications, from fraud detection to autonomous vehicles, require lightning-fast processing speeds and low latency. This is driving the adoption of high-speed networks and edge computing, enabling data processing closer to the source and reducing response times. AI-driven automation is also streamlining infrastructure management, automating tasks like network provisioning, security monitoring, and capacity planning. This not only reduces operational overhead but also improves efficiency and frees up valuable resources.
Ecosystm analysts Darian Bird, Peter Carr, Simona Dimovski, and Tim Sheedy present the key trends shaping the tech infrastructure market in 2025.
Click here to download ‘Building the AI Future: Top 5 Infra Trends for 2025’ as a PDF
1. The AI Buildout Will Accelerate; China Will Emerge as a Winner
In 2025, the race for AI dominance will intensify, with Nvidia emerging as the big winner despite an impending AI crash. Many over-invested companies will fold, flooding the market with high-quality gear at bargain prices. Meanwhile, surging demand for AI infrastructure – spanning storage, servers, GPUs, networking, and software like observability, hybrid cloud tools, and cybersecurity – will make it a strong year for the tech infrastructure sector.
Ironically, China’s exclusion from US tech deals has spurred its rise as a global tech giant. Forced to develop its own solutions, China is now exporting its technologies to friendly nations worldwide.
By 2025, Chinese chipmakers are expected to rival international peers, with some reaching parity.

2. AI-Optimised Cloud Platforms Will Dominate Infrastructure Investments
AI-optimised cloud platforms will become the go-to infrastructure for organisations, enabling seamless integration of machine learning capabilities, scalable compute power, and efficient deployment tools.
As regulatory demands grow and AI workloads become more complex, these platforms will provide localised, compliant solutions that meet data privacy laws while delivering superior performance.
This shift will allow businesses to overcome the limitations of traditional infrastructure, democratising access to high-performance AI resources and lowering entry barriers for smaller organisations. AI-optimised cloud platforms will drive operational efficiencies, foster innovation, and help businesses maintain compliance, particularly in highly regulated industries.

3. PaaS Architecture, Not Data Cleanup, Will Define AI Success
By 2025, as AI adoption reaches new heights, organisations will face an urgent need for AI-ready data, spurring significant investments in data infrastructure. However, the approach taken will be pivotal.
A stark divide will arise between businesses fixated on isolated data-cleaning initiatives and those embracing a Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) architecture.
The former will struggle, often unintentionally creating more fragmented systems that increase complexity and cybersecurity risks. While data cleansing is important, focusing exclusively on it without a broader architectural vision leads to diminishing returns. On the other hand, organisations adopting PaaS architectures from the start will gain a distinct advantage through seamless integration, centralised data management, and large-scale automation, all critical for AI.

4. Small Language Models Will Push AI to the Edge
While LLMs have captured most of the headlines, small language models (SLMs) will soon help to drive AI use at the edge. These compact but powerful models are designed to operate efficiently on limited hardware, like AI PCs, wearables, vehicles, and robots. Their small size translates into energy efficiency, making them particularly useful in mobile applications. They also help to mitigate the alarming electricity consumption forecasts that could make widespread AI adoption unsustainable.
Self-contained SMLs can function independently of the cloud, allowing them to perform tasks that require low latency or without Internet access.
Connected machines in factories, warehouses, and other industrial environments will have the benefit of AI without the burden of a continuous link to the cloud.

5. The Impact of AI PCs Will Remain Limited
AI PCs have been a key trend in 2024, with most brands launching AI-enabled laptops. However, enterprise feedback has been tepid as user experiences remain unchanged. Most AI use cases still rely on the public cloud, and applications have yet to be re-architected to fully leverage NPUs. Where optimisation exists, it mainly improves graphics efficiency, not smarter capabilities. Currently, the main benefit is extended battery life, explaining the absence of AI in desktop PCs, which don’t rely on batteries.
The market for AI PCs will grow as organisations and consumers adopt them, creating incentives for developers to re-architect software to leverage NPUs.
This evolution will enable better data access, storage, security, and new user-centric capabilities. However, meaningful AI benefits from these devices are still several years away.


Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on the Retail industry.
Click here to download ‘AI in Retail: Success Stories & Insights’ as a PDF
From personalised product recommendations to predictive analytics, AI is helping retailers deliver exceptional customer experiences and optimise their operations. However, many retailers are still grappling with the complexities of AI implementation. Those who can successfully navigate this challenge and harness the power of AI will emerge as industry leaders, driving innovation and shaping the future of retail.
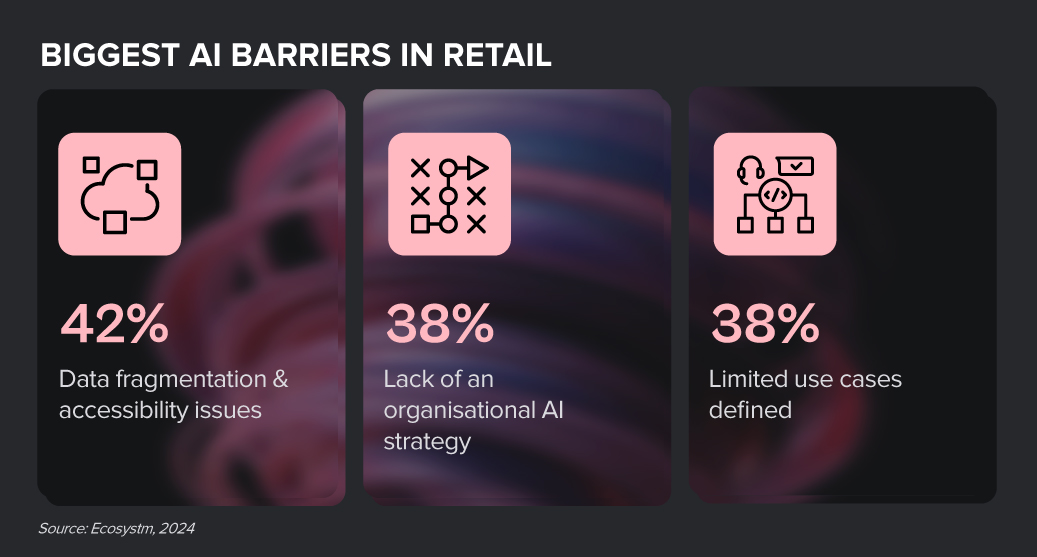
Despite the challenges, Retail organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Customer Experience & Engagement
- 2. Supply Chain Optimisation
- 3. Fraud & Risk Analysis
Customer Experience & Engagement
- Conversational AI. Providing real-time customer support and answering queries
- Personalisation. Offering tailored product suggestions based on customer preferences and behaviour
- Virtual Try-On. Allowing customers to visualise products in different settings using AR
“AI has helped us to refine our customer chatbots to allow for more self-service. We’ve experienced faster customer order processing and quicker resolution of issues, putting control directly in the hands of our customers.” – CX LEADER
Supply Chain Optimisation
- Inventory Management. Automating inventory management processes to ensure optimal stock levels
- Supply Chain Visibility. Monitoring and optimising supply chain operations, including logistics and distribution
- Demand Forecasting. Predicting sales and demand trends to optimise inventory and production planning
“We use AI to optimise the supply chain, saving operational costs. Digital supply chains and cloud-based tracking systems streamline operations and enhance efficiency.” – CFO
Fraud & Risk Analysis
- Fraud Detection. Identify and prevent fraudulent activities, such as online fraud and chargebacks
- Risk Assessment. Assessing risk factors associated with customer transactions and preventing losses
- Customer & Market Insights. Understanding customer behaviour, market trends, and growth opportunities
“With eCommerce as a key market force, understanding customer habits is crucial to ensuring we have the right products in stock and optimising our pricing strategy.” – COO

Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme.
Here are some insights from our research.
Click here to download ‘AI in BFSI: Success Stories & Insights’ as a PDF
From personalised recommendations to streamlined operations, AI is transforming the products, services and processes in the BFSI industries. While leaders realise that AI holds significant potential, turning that potential into reality is often tough. Many BFSI organisations struggle to move beyond AI pilots because of some key barriers.
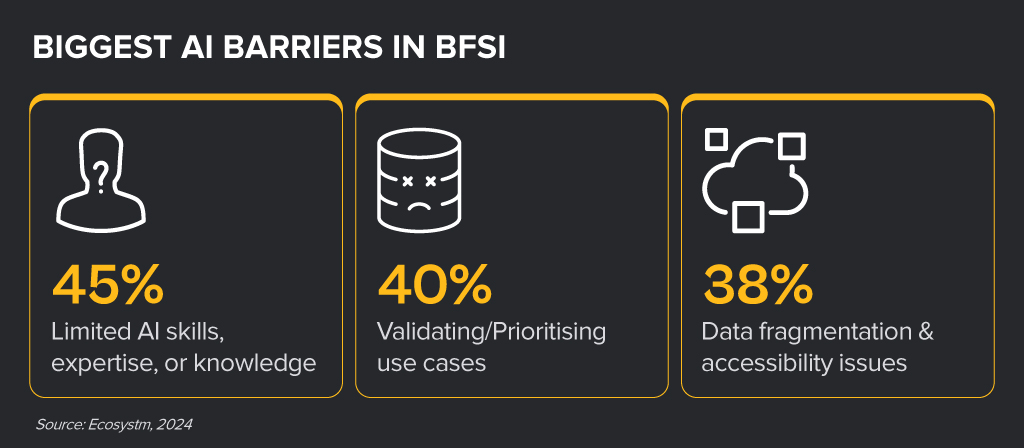
Despite the challenges, BFSI organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Customer Service & Engagement
- 2. Risk Management & Fraud Detection
- 3. Process Automation & Efficiency
Customer Service & Engagement Use Cases
- Virtual Assistants and Chatbots. Delivering real-time product information and customer support
- Customer Experience Analysis. Analysing data to uncover trends and improve user experiences
- Personalised Recommendations. Providing tailored financial products based on user behaviour and preferences
“While we remain cautious about customer-facing applications, many of our AI use cases provide valuable customer insights to our employees. Human-in-the-loop is still a critical consideration.” – INSURANCE CX LEADER
Risk Management & Fraud Detection Use Cases
- Enhanced Credit Scoring. Improved assessment of creditworthiness and risks
- Advanced Fraud Detection. Easier detection and prevention of fraudulent activities
- Comprehensive Risk Strategy. Assessment of risk factors to develop effective strategies
“We deployed enterprise-grade AI models that are making a significant impact in specialised areas like credit decisioning and risk modelling.” – BANKING DATA LEADER
Process Automation and Efficiency
- Backend Process Streamlining. Automating workflows and processes to boost efficiency
- Loan & Claims Processing. Speeding up application and approval processes
- Invoice Processing. Automating invoice management to minimise errors
“Our focus is on creating a mindset where employees see AI as a tool that can augment their capabilities rather than replace them.” – BANKING COO

In my last Ecosystm Insights, I outlined various database options available to you. The challenge lies in selecting the right one. Selecting the right database is crucial for the success of any application or project. It involves understanding your data, the operations you’ll perform, scalability requirements, and more. Here is a guide that will walk you through key considerations and steps to choose the most suitable database from the list I shared last week.
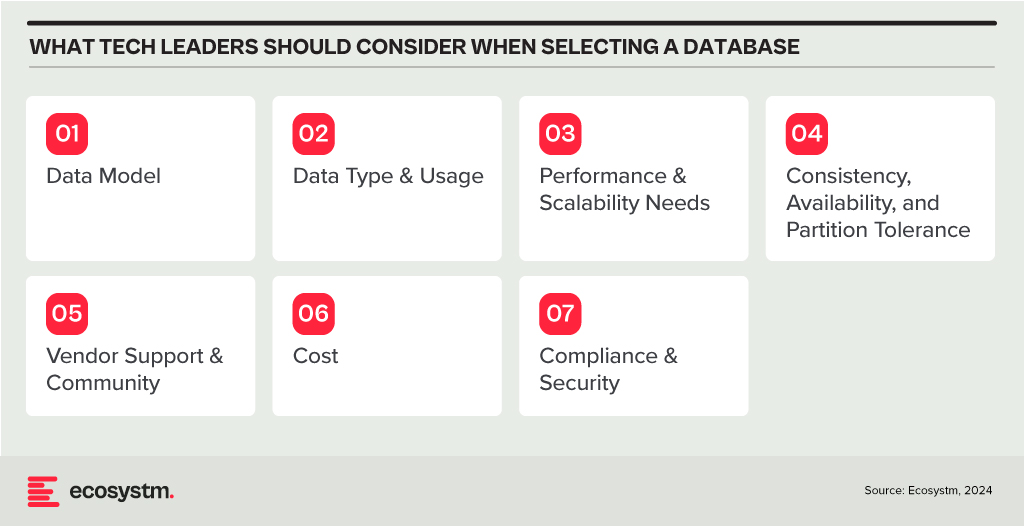
Understand Your Data Model
Relational (RDBMS) vs. NoSQL. Choose RDBMS if your data is structured and relational, requiring complex queries and transactions with ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties. Opt for NoSQL if you have unstructured or semi-structured data, need to scale horizontally, or require flexibility in your schema design.
Consider the Data Type and Usage
Document Databases are ideal for storing, retrieving, and managing document-oriented information. They’re great for content management systems, ecommerce applications, and handling semi-structured data like JSON, XML.
Key-Value Stores shine in scenarios where quick access to data is needed through a key. They’re perfect for caching and storing user sessions, configurations, or any scenario where the lookup is based on a unique key.
Wide-Column Stores offer flexibility and scalability for storing and querying large volumes of data across many servers, suitable for big data applications, real-time analytics, and high-speed transactions.
Graph Databases are designed for data intensely connected through relationships, ideal for social networks, recommendation engines, and fraud detection systems where relationships between data points are key.
Time-Series Databases are optimised for storing and querying sequential data points indexed in time order. Use them for monitoring systems, IoT applications, and financial trading systems where time-stamped data is critical.
Spatial Databases support spatial data types and queries, making them suitable for geographic information systems (GIS), location-based services, and applications requiring spatial indexing and querying capabilities.
Assess Performance and Scalability Needs
In-Memory Databases like Redis offer high throughput and low latency for scenarios requiring rapid access to data, such as caching, session storage, and real-time analytics.
Distributed Databases like Cassandra or CouchDB are designed to run across multiple machines, offering high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability for applications with global reach and massive scale.
Evaluate Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance (CAP Theorem)
Understand the trade-offs between consistency, availability, and partition tolerance. For example, if your application requires strong consistency, consider databases that prioritise consistency and partition tolerance (CP) like MongoDB or relational databases. If availability is paramount, look towards databases that offer availability and partition tolerance (AP) like Cassandra or CouchDB.
Other Considerations
Check for Vendor Support and Community. Evaluate the support and stability offered by vendors or open-source communities. Established products like Oracle Database, Microsoft SQL Server, and open-source options like PostgreSQL and MongoDB have robust support and active communities.
Cost. Consider both initial and long-term costs, including licenses, hardware, maintenance, and scalability. Open-source databases can reduce upfront costs, but ensure you account for support and operational expenses.
Compliance and Security. Ensure the database complies with relevant regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.) and offers robust security features to protect sensitive data.
Try Before You Decide. Prototype your application with shortlisted databases to evaluate their performance, ease of use, and compatibility with your application’s requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting the right database is a strategic decision that impacts your application’s functionality, performance, and scalability. By carefully considering your data model, type of data, performance needs, and other factors like cost, support, and security, you can identify the database that best fits your project’s needs. Always stay informed about the latest developments in database technologies to make educated decisions as your requirements evolve.

AI has become a business necessity today, catalysing innovation, efficiency, and growth by transforming extensive data into actionable insights, automating tasks, improving decision-making, boosting productivity, and enabling the creation of new products and services.
Generative AI stole the limelight in 2023 given its remarkable advancements and potential to automate various cognitive processes. However, now the real opportunity lies in leveraging this increased focus and attention to shine the AI lens on all business processes and capabilities. As organisations grasp the potential for productivity enhancements, accelerated operations, improved customer outcomes, and enhanced business performance, investment in AI capabilities is expected to surge.
In this eBook, Ecosystm VP Research Tim Sheedy and Vinod Bijlani and Aman Deep from HPE APAC share their insights on why it is crucial to establish tailored AI capabilities within the organisation.

The AI landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, moving from traditional predictive AI use cases towards Generative AI (GenAI). Currently, most GenAI use cases promise an improvement in employee productivity, without focusing on how to leverage this into new or additional revenue generating streams. This raises concerns about the long-term return on investment (ROI) if this is not adequately addressed.
The Rise of Generative AI Over Predictive AI
Traditionally, predictive AI has been integral to business strategies, leveraging data to forecast future outcomes with remarkable accuracy. Industries across the board have used predictive models for a range of applications, from demand forecasting in retail to fraud detection in finance. However, the tide is changing with the emergence of GenAI technologies. GenAI, capable of creating content, designing products, and even coding, holds the promise to revolutionise how businesses operate, innovate, and compete.
The appeal of GenAI lies in its versatility and creativity, offering solutions that go beyond the capabilities of predictive models. For example, in the area of content creation, GenAI can produce written content, images, and videos at scale, potentially transforming marketing, entertainment, and education sectors. However, the current enthusiasm for GenAI’s productivity enhancements overshadows a critical aspect of technology adoption: monetisation.
The Productivity Paradox
While the emphasis on productivity improvements through GenAI applications is undoubtedly beneficial, there is a notable gap in exploring use cases that directly contribute to creating new revenue streams. This productivity paradox – prioritising operational efficiency and cost reduction – may not guarantee the sustained growth and ROI necessary from AI investments.
True innovation in AI should not only aim at making existing processes more efficient but also at uncovering opportunities for monetisation. This involves leveraging GenAI to develop new products, services, or business models to access untapped markets or enhance customer value in ways that directly impact the bottom line.
The Imperative for Strategic Reorientation
Ignoring the monetisation aspect of GenAI applications poses a significant risk to the anticipated ROI from AI investments. As businesses allocate resources to AI adoption and integration, it’s also important to consider how these technologies can generate revenue, not just save costs. Without a clear path to monetisation, the investments in AI, particularly in the cutting-edge domain of GenAI, may not prove viable in the next financial year and beyond.
To mitigate this risk, companies need to adopt a dual approach. First, they must continue to explore and exploit the productivity gains offered by GenAI, which are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving operational excellence. At the same time, businesses must strategically explore and invest in GenAI-driven opportunities for monetisation. This could mean innovating in product design, personalised customer experiences, or entirely new business models that were previously unfeasible.
Conclusion
The excitement around GenAI’s potential to transform industries is well-founded, but it must be tempered with strategic planning to ensure long-term viability and ROI. Businesses that recognise and act on the opportunity to not only improve productivity but also to monetise GenAI innovations will lead the next wave of growth in their respective sectors. The challenge lies in balancing the drive for efficiency with the pursuit of new revenue streams, ensuring that investments in AI deliver sustainable returns. As the AI landscape evolves, the ability to innovate in monetisation as much as in technology will distinguish the leaders from the followers.






















































