Organisations across the globe, are facing disruption on a scale never seen before, and are urgently seeking ways of remaining viable. Predictably, cybersecurity is a secondary concern and is often handled reactively. To make matters worse, a chronic cybersecurity skills shortage is being made much more severe by the crisis.
Remote working has reached unprecedented levels as organisations try hard to keep going. This is massively expanding the attack surface for cyber criminals, weakening security and leading to a cybercrime pandemic. Hacking activity and phishing, inspired by the COVID-19 crisis, are growing rapidly. Containing and suppressing this cybercrime pandemic is proving to be almost impossible.
Remote working intensifies known threats posed by phishing and ransomware. More alarming are the distinctive cybersecurity vulnerabilities associated with home working including reliance on home Wi-Fi, increased use of unpatched VPNs and devices, and the exponential growth of network access points. These vulnerabilities increase the likelihood of a breach enormously.
Corporate IT is in a very challenging position. It needs to ensure that organisations can operate in a way that they have never operated before, while ensuring that their assets are secure – a very difficult, if not an impossible task for which there is no precedent.
Some important cybersecurity considerations, during and after the COVID-19 pandemic include:
Re-enforce Basic Cyber Hygiene
As massive numbers of people work from home, basic cyber hygiene becomes more critical than ever before. Organisations must maintain awareness of security threats among employees, ensure security policies are being followed and be certain that corporate software is being updated and patched on time. With a dispersed workforce, these basic practices are more challenging, and training becomes more critical. Phishing attacks are often the primary attack vector for malicious actors, so employees must be able to identify these attacks. They increasingly exploit shortages of goods such as protective equipment and sometimes claim to offer official information relating to COVID-19.
Remote employees often access sensitive business data through home Wi-Fi networks that will not have the same security controls – such as firewalls – that are used in offices. There is more connectivity from remote locations, which requires greater focus on data privacy, and hunting for intrusions from a much larger number of entry points.
Place More Focus on Endpoint Security
The unprecedented switch to remote working is radically increasing the number of vulnerable endpoints. Given that endpoints are located at a distance from corporate premises, it is frequently difficult for IT departments to configure endpoint systems and install necessary security software.
It is vital to assess the security posture of all endpoints connecting to the corporate network. This practice enables an organisation to determine whether or not an endpoint requesting to access internal resources meets security policy requirements. It requires the ability to monitor and enforce policy across all devices, while making onboarding and offboarding seamless.
It is essential that endpoint solutions can be rapidly deployed for remote workers, as needed on both personal and corporate devices. Devices used for remote work need much more than the basic antivirus and antispyware protection. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and on-board endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities are crucial.
Be More Selective About How and When Video Conferencing and Collaboration Platforms are Used
Since lockdowns spread around the world, the use of video conferencing and collaboration tools has grown beyond the wildest expectations of suppliers of these tools. The extraordinary growth of Zoom has made it a target for attackers. Many security vulnerabilities have been discovered with Zoom such as, a vulnerability to UNC path injection in the client chat feature, which allows hackers to steal Windows credentials, keeping decryption keys in the cloud which can potentially be accessed by hackers and gives the ability for trolls to ‘Zoombomb’ open and unprotected meetings. Zoom has so far managed to augment its security features in part by its recent acquisition of Keybase, a secure messaging service.
Switching to an alternative video conferencing platform will not necessarily offer greater levels of security as privacy is typically not a strength of any collaboration platform. Collaboration platforms tend to tread a fine line between a great experience and security. Too much security can cause performance and usability to be impacted negatively. Too little security, as we have seen, allows hackers to find vulnerabilities. If data privacy is critical for a meeting, then perhaps collaboration platforms should not be used, or organisations should not share critical information on them.
Protect all Cloud Workloads
In today’s remote working paradigm, cloud computing is being used more than ever. This frequently exposes organisations to risks that are not adequately mitigated.
Organisations typically need to manage a mix of on-premises technology together with multiple clouds, which are often poorly integrated. These complexities are compounded by the increasing risk from cyberattacks associated with cloud migration and hybrid cloud implementations. In cloud environments, the leading cybersecurity risks include insecure interfaces and APIs, data breaches and data loss, unauthorised access, DDoS attacks, and a lack of a unified view of assets.
Protection requirements for securing hybrid multicloud environments are evolving rapidly. In addition to tightening up endpoint security, organisations must also place greater emphasis on cloud workload protection. Cloud security solutions need to offer a unified and consistent view across all physical machines, virtual machines, serverless workloads and containers, used by an organisation.
Amend Incident Response Plans
It is the containment of breaches that often determines the success of security policies and procedures. Basic cyber hygiene as well as changes to IT architecture, such as micro segmentation, play an essential role in breach containment. But incident response plans also need to be made relevant to the current pandemic scenario.
Employees and IT teams are now working in a completely different environment than envisaged by most incident response plans. Existing plans may now be obsolete. At the very least, they will need to be modified. Usually, incident response plans are designed to respond to threats when most employees are operating in a corporate environment. This clearly needs to change. Employees need to be trained in the updated plan and know how to reach support if they believe that a security breach has occurred in their remote location.
Critically, new alert and warning systems need to be established, which can be used by employees to warn of threats as well as to receive information on threats and best practices.
Organisations are struggling to keep the lights on. In this battle to remain operational, cybersecurity has been taking a back seat. This cannot last for long as the deluge of new vulnerabilities is creating easy pickings for attackers. Cyber hygiene, endpoint security, cloud security, security policies and incident response plans must be continually reviewed.
Click here to download the full report ?

What used to be commonly known by names such as computer security or IT security is now most commonly referred to as cybersecurity. The techniques of securing computers, applications, networks, programs and data have evolved and so has the terminology. The change in the jargon reflects the progression from discrete to interconnected devices and networks. It is only when the computers and devices became connected with each other – and with the Internet – that the issues and attempts of unauthorised access became prominent.
Simply put, cybersecurity is the protection of computer systems from cyber-attacks. This is made possible with multiple layers of security across the system, individual devices, enterprises and even nations against unauthorised access and exploitation.
Cybersecurity is a constant battle
Preventing cyberattacks is a challenging task for security professionals and to accomplish that, cybersecurity experts should stay ahead of cyber attackers and cybercriminals. A range of effective methods and technologies have been devised to strengthen cybersecurity. One important aspect of cybersecurity is identity and access management (IDAM). IDAM allows various defined levels of access on the basis of individual roles, administrator levels and even at a system level. The common IDAM methods include single sign-on systems, multi-factor authentication, privileged access management (PAM), biometrics, voice or facial recognition, and other distinctive physical attributes to verify and identify individuals. IDAM procedures are being implemented at all levels of businesses, enterprises and even for national-level security with the growth of eGovernment systems.
Another common security measure is Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software and services. The term combines security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM) and is provided by vendors as software or appliance. SIEM works by collecting log data and delivering real-time insights and generates security alerts using a range of techniques. SIEM is used by enterprises where compliance to a set, or sets, of rules is a strong factor. In addition, it also prevents interferences from individual attackers, organised crime groups, or other actors.
SIEM systems comprise three major components:
- Data collection. SIEM system collects logs and data from system activity, access, firewalls, application monitors, operating system layers and network traffic and generates an event every time activity happens.
- Data analysis. The SIEM system is tasked with correlating and analysing data in a format. The analysis is performed in various ways: log management and retention, event correlation, user activity monitoring, and predictive and forensic analysis.
- Another major step is reporting in the form of real-time alerts, dashboards, email and SMS notifications of events, analytical reporting, auditing and governance, and compliance.
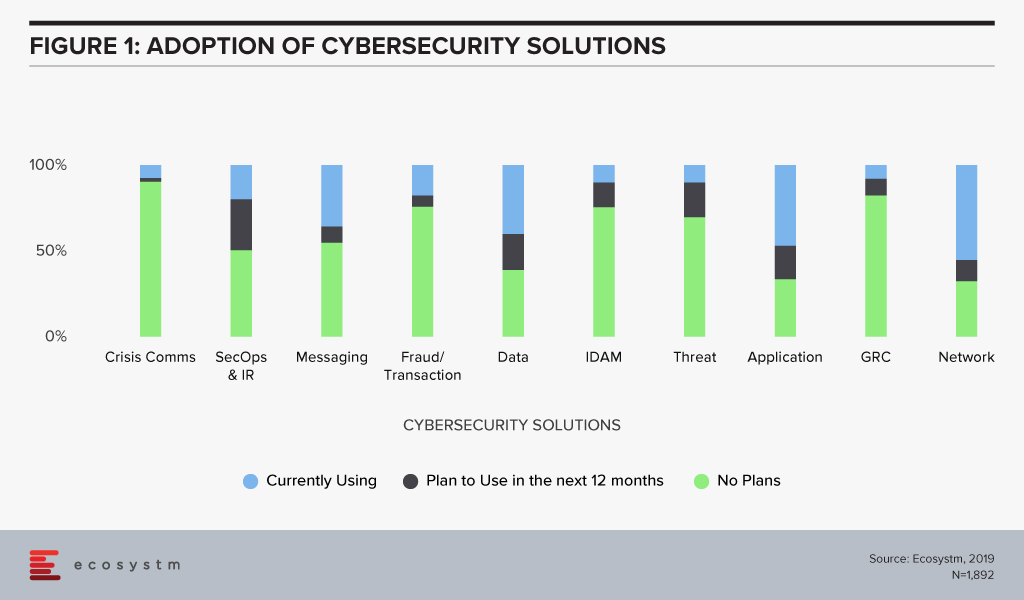
The global Ecosystm Cybersecurity Study covers various cybersecurity solutions such as Crisis Communication solutions; Security Operations & Incident Response, IDAM and more. The study shows that organisations are primarily focusing more on Application, Data and Network level security, whereas, the other cybersecurity fields such as Crisis communication, Fraud transaction, IDAM, Threat Analysis and Reporting are looked down.
National Cybersecurity and Safety
Countries across the globe are accelerating their cybersecurity efforts to address risks, enhance public safety, protect communications, safeguard mission-critical applications and prevent threats. Cybersecurity is important to governments, where it is increasingly seen as an area of international conflict. Most countries have now setup their dedicated national cybersecurity centres, drawing on the capabilities of private industry, government and academic specialists in the area.
As cybersecurity threats have proliferated and computer technology has advanced, government data security compliance has become increasingly complex. The governments of various nations have set up compliances with a wave of new privacy regulations.
Security is an ongoing and constant effort which should be adopted at an individual, business, organisation, enterprise and national level. To strengthen cybersecurity there are many excellent solutions, a range of comprehensive suites and products. However, malicious parties and criminals are constantly employing new techniques and technologies. It is a new arms race, and there is no one size fits all solution.



