The increasing alignment between IT and business functions, while crucial for organisational success, complicates the management of enterprise systems. Tech leaders must balance rapidly evolving business needs with maintaining system stability and efficiency. This dynamic adds pressure to deliver agility while ensuring long-term ERP health, making management increasingly complex.

As tech providers such as SAP enhance their capabilities and products, they will impact business processes, technology skills, and the tech landscape.
At SAP NOW Southeast Asia in Singapore, SAP presented their future roadmap, with a focus on empowering their customers to transform with agility. Ecosystm Advisors Sash Mukherjee and Tim Sheedy provide insights on SAP’s recent announcements and messaging.

Click here to download SAP NOW Southeast Asia: Highlights
What was your key takeaway from the event?
TIM SHEEDY. SAP is making a strong comeback in Asia Pacific, ramping up their RISE with SAP program after years of incremental progress. The focus is on transitioning customers from complex, highly customised legacy systems to cloud ERP, aligning with the region’s appetite for simplifying core processes, reducing customisations, and leveraging cloud benefits. Many on-prem SAP users have fallen behind on updates due to over-customisation, turning even minor upgrades into major projects – and SAP’s offerings aim to solve for these challenges.
SASH MUKHERJEE. A standout feature of the session was the compelling customer case studies. Unlike many industry events where customer stories can be generic, the stories shared were examples of SAP’s impact. From Mitr Phol’s use of SAP RISE to enhance farm-to-table transparency to CP Group’s ambitious sustainability goals aligned with the SBTi, and Standard Chartered Bank’s focus on empowering data analytics teams, these testimonials offered concrete illustrations of SAP’s value proposition.
How is SAP integrating AI into their offerings?
TIM SHEEDY. SAP, like other tech platforms, is ramping up their AI capabilities – but with a twist.
They are not only highlighting GenAI but also emphasising their predictive AI features. SAP’s approach focuses on embedded AI, integrating it directly into systems and processes to offer low-risk, user-friendly solutions.
Joule, their AI copilot, is enterprise-ready, providing seamless integration with SAP backend systems and meeting strict compliance standards like GDPR and SOC-II. By also integrating with Microsoft 365, Joule extends its reach to daily tools like Outlook, Teams, Word, and Excel.
While SAP AI may lack the flash of other platforms, it is designed for SAP users – managers and board members – who prioritise consistency, reliability, and auditability alongside business value.
What is the value proposition of SAP’s Clean Core?
SASH MUKHERJEE. SAP’s Clean Core marks a strategic shift in ERP management.
Traditionally, businesses heavily customised SAP to meet specific needs, resulting in complex and costly IT landscapes. Clean Core advocates for a standardised system with minimal customisations, offering benefits like increased agility, lower costs, and reduced risk during upgrades. However, necessary customisations can still be achieved using SAP’s BTP.
The move to the Clean Core is often driven by CEO mandates, as legacy SAP solutions have become too complex to fully leverage data. For example, an Australian mining company reduced customisations from 27,000 to 200, and Standard Chartered Bank used Clean Core data to launch a carbon program within four months.
However, the transition can be challenging and will require enhanced developer productivity, expansion of tooling, and clear migration paths.
How is SAP shifting their partner strategy?
As SAP customers face significant transformations, tech partners – cloud hyperscalers, systems integrators, consulting firms and managed services providers – will play a crucial role in executing these changes before SAP ECC loses support in 2027.
TIM SHEEDY. SAP has always relied on partners for implementations, but with fewer large-scale upgrade projects in recent years, many partner teams have shrunk. Recognising this, SAP is working to upskill partners on RISE with SAP. This effort aims to ensure they can effectively manage and optimise the modern Cloud ERP platform, utilise assets, templates, accelerators, and tools for rapid migration, and foster continuous innovation post-migration. The availability of these skills in the market will be essential for SAP customers to ensure successful transitions to the Cloud ERP platform.
SASH MUKHERJEE. SAP’s partner strategy emphasises business transformation over technology migration. This shift requires partners to focus on delivering measurable business outcomes rather than solely selling technology. Given the prevalence of partner-led sales in Southeast Asia, there is a need to empower partners with tools and resources to effectively communicate the value proposition to business decision-makers. While RISE certifications will be beneficial for larger partners, a significant portion of the market comprises SMEs that rely on smaller, local partners – and they will need support mechanisms too.
What strategies should SAP prioritise to maintain market leadership?
TIM SHEEDY. Any major platform change gives customers an opportunity to explore alternatives.
Established players like Oracle, Microsoft, and Salesforce are aggressively pursuing the ERP market. Meanwhile, industry-specific solutions, third-party support providers, and even emerging technologies like those offered by ServiceNow are challenging the traditional ERP landscape.
However, SAP has made significant strides in easing the transition from legacy platforms and is expected to continue innovating around RISE with SAP. By offering incentives and simplifying migration, SAP aims to retain their customer base. While SAP’s focus on renewal and migration could pose challenges for growth, the company’s commitment to execution suggests they will retain most of their customers. GROW with SAP is likely to be a key driver of new business, particularly in mid-sized organisations, especially if SAP can tailor offerings for the cost-sensitive markets in the region.

At the Nutanix .NEXT 2024 event in Barcelona, it became clear that the discourse around cloud computing has evolved significantly. The debate that once polarised organisations over whether on-prem/co-located data centres or public cloud was better has been decisively settled. Both cloud providers and on-prem equipment providers are thriving, as evident from their earnings reports.
Hybrid cloud has emerged as the clear victor, offering the flexibility and control that organisations demand. This shift is particularly relevant for tech buyers in the Asia Pacific region, where diverse market maturities and unique business challenges require a more adaptable approach to IT infrastructure.
The Hybrid Cloud Advantage
Hybrid cloud architecture combines the best of both worlds. It provides the scalability and agility of public cloud services while retaining the control and security of on-prem systems. For Asia Pacific organisations, that often operate across various regulatory environments and face unique data sovereignty issues, this dual capability is invaluable. The ability to seamlessly move workloads between on-prem, private cloud, and public cloud environments enables enterprises to optimise their IT strategies, balancing cost, performance, and compliance.
Market Maturity and Adoption in Asia Pacific
The region shows a wide spectrum of technological maturity among its markets. Countries like Australia, Japan, and Singapore lead with advanced cloud adoption and robust IT infrastructures, while emerging markets such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines are still in the nascent stages of cloud integration.
However, regardless of their current maturity levels, organisations in Asia Pacific are recognising the benefits of a hybrid cloud approach. Mature markets are leveraging hybrid cloud to refine their IT strategies, focusing on enhancing business agility and driving innovation.
Ecosystm research shows that 75% of organisations in Australia have a hybrid, multi-cloud strategy. Over 30% of organisations have repatriated workloads from the public cloud, and only 22% employ a “cloud first” strategy when deploying new services.

Meanwhile, emerging markets see hybrid cloud as a pathway to accelerate their digital transformation journeys without the need for extensive upfront investments in on-prem infrastructure. Again, Ecosystm data shows that when it comes to training large AI models and applications, organisations across Southeast Asia use a mix of public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments.
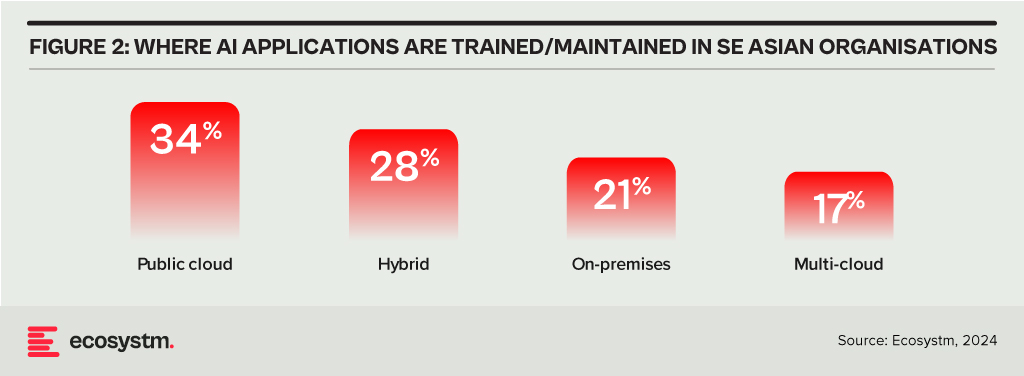
Strategic Flexibility Without Compromise
One of the most compelling messages from the Nutanix .NEXT 2024 event is that hybrid cloud eliminates the need for compromise when deciding where to place workloads – and that is what the data above represents. The location of the workload is no longer a limiting factor. Being “cloud first” locks organisations into a tech provider, whereas agility was once exclusively in favour of public cloud providers. Whether it’s for performance optimisation, cost efficiency, or regulatory compliance, tech leaders can now choose the best environment for every workload without being constrained by location.
For example, an organisation might keep sensitive customer data within a private cloud to comply with local data protection laws while leveraging public cloud resources for less sensitive applications to take advantage of its scalability and cost benefits. I recently spoke to an organisation in the gaming space that had 5 different regulatory bodies to appease – which required data to be stored in 5 different locations! This strategic flexibility ensures that IT investments are fully aligned with business objectives, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Moving Forward: Actionable Insights for Asia Pacific Tech Leaders
To fully capitalise on the hybrid cloud revolution, APAC tech leaders should:
- Assess Workload Requirements. Evaluate the specific needs of each workload to determine the optimal environment, considering factors like latency, security, and compliance.
- Invest in Integration Tools. Ensure seamless interoperability between on-premises and cloud environments by investing in advanced integration and management tools.
- Focus on Skill Development. Equip IT teams with the necessary skills to manage hybrid cloud infrastructures, emphasising continuous learning and certification.
- Embrace a Multi-Cloud Strategy. Consider a multi-cloud approach within the hybrid model to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance resilience.
Conclusion
The hybrid cloud has definitively won the battle for enterprise IT infrastructure, particularly in the diverse Asia Pacific region. By enabling organisations to place their workloads wherever they make the most sense without compromising on performance, security, or compliance, hybrid cloud empowers tech leaders to drive their digital transformation agendas forward with confidence. Based on everything we know today*, the future of cloud is hybrid. Reform your sourcing practices to put business needs, not cloud service providers or data centres, at the centre of your data decisions.
*In this fast-changing world, it seems naïve to make sweeping statements about the future of technology!
For many organisations migrating to cloud, the opportunity to run workloads from energy-efficient cloud data centres is a significant advantage. However, carbon emissions can vary from one country to another and if left unmonitored, will gradually increase over time as cloud use grows. This issue will become increasingly important as we move into the era of compute-intensive AI and the burden of cloud on natural resources will shift further into the spotlight.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that data centres are responsible for up to 1.5% of global electricity use and 1% of GHG emissions. Cloud providers have recognised this and are committed to change. Between 2025 and 2030, all hyperscalers – AWS, Azure, Google, and Oracle included – expect to power their global cloud operations entirely with renewable sources.
Chasing the Sun
Cloud providers are shifting their sights from simply matching electricity use with renewable power purchase agreements (PPA) to the more ambitious goal of operating 24/7 on carbon-free sources. A defining characteristic of renewables though is intermittency, with production levels fluctuating based on the availability of sunlight and wind. Leading cloud providers are using AI to dynamically distribute compute workloads throughout the day to regions with lower carbon intensity. Workloads that are processed with solar power during daylight can be shifted to nearby regions with abundant wind energy at night.
Addressing Water Scarcity
Many of the largest cloud data centres are situated in sunny locations to take advantage of solar power and proximity to population centres. Unfortunately, this often means that they are also in areas where water is scarce. While liquid-cooled facilities are energy efficient, local communities are concerned on the strain on water sources. Data centre operators are now committing to reduce consumption and restore water supplies. Simple measures, such as expanding humidity (below 20% RH) and temperature tolerances (above 30°C) in server rooms have helped companies like Meta to cut wastage. Similarly, Google has increased their reliance on non-potable sources, such as grey water and sea water.
From Waste to Worth
Data centre operators have identified innovative ways to reuse the excess heat generated by their computing equipment. Some have used it to heat adjacent swimming pools while others have warmed rooms that house vertical farms. Although these initiatives currently have little impact on the environmental impact of cloud, they suggest a future where waste is significantly reduced.
Greening the Grid
The giant facilities that cloud providers use to house their computing infrastructure are also set to change. Building materials and construction account for an astonishing 11% of global carbon emissions. The use of recycled materials in concrete and investing in greener methods of manufacturing steel are approaches the construction industry are attempting to lessen their impact. Smaller data centres have been 3D printed to accelerate construction and use recyclable printing concrete. While this approach may not be suitable for hyperscale facilities, it holds potential for smaller edge locations.
Rethinking Hardware Management
Cloud providers rely on their scale to provide fast, resilient, and cost-effective computing. In many cases, simply replacing malfunctioning or obsolete equipment would achieve these goals better than performing maintenance. However, the relentless growth of e-waste is putting pressure on cloud providers to participate in the circular economy. Microsoft, for example, has launched three Circular Centres to repurpose cloud equipment. During the pilot of their Amsterdam centre, it achieved 83% reuse and 17% recycling of critical parts. The lifecycle of equipment in the cloud is largely hidden but environmentally conscious users will start demanding greater transparency.
Recommendations
Organisations should be aware of their cloud-derived scope 3 emissions and consider broader environmental issues around water use and recycling. Here are the steps that can be taken immediately:
- Monitor GreenOps. Cloud providers are adding GreenOps tools, such as the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool, to help organisations measure the environmental impact of their cloud operations. Understanding the relationship between cloud use and emissions is the first step towards sustainable cloud operations.
- Adopt Cloud FinOps for Quick ROI. Eliminating wasted cloud resources not only cuts costs but also reduces electricity-related emissions. Tools such as CloudVerse provide visibility into cloud spend, identifies unused instances, and helps to optimise cloud operations.
- Take a Holistic View. Cloud providers are being forced to improve transparency and reduce their environmental impact by their biggest customers. Getting educated on the actions that cloud partners are taking to minimise emissions, water use, and waste to landfill is crucial. In most cases, dedicated cloud providers should reduce waste rather than offset it.
- Enable Remote Workforce. Cloud-enabled security and networking solutions, such as SASE, allow employees to work securely from remote locations and reduce their transportation emissions. With a SASE deployed in the cloud, routine management tasks can be performed by IT remotely rather than at the branch, further reducing transportation emissions.

While there has been much speculation about AI being a potential negative force on humanity, what we do know today is that the accelerated use of AI WILL mean an accelerated use of energy. And if that energy source is not renewable, AI will have a meaningful negative impact on CO2 emissions and will accelerate climate change. Even if the energy is renewable, GPUs and CPUs generate significant heat – and if that heat is not captured and used effectively then it too will have a negative impact on warming local environments near data centres.
Balancing Speed and Energy Efficiency
While GPUs use significantly more energy than CPUs, they run many AI algorithms faster than CPUs – so use less energy overall. But the process needs to run – and these are additional processes. Data needs to be discovered, moved, stored, analysed, cleansed. In many cases, algorithms need to be recreated, tweaked and improved. And then that algorithm itself will kick off new digital processes that are often more processor and energy-intensive – as now organisations might have a unique process for every customer or many customer groups, requiring more decisioning and hence more digitally intensive.
The GPUs, servers, storage, cabling, cooling systems, racks, and buildings have to be constructed – often built from raw materials – and these raw materials need to be mined, transported and transformed. With the use of AI exploding at the moment, so is the demand for AI infrastructure – all of which has an impact on the resources of the planet and ultimately on climate change.
Sustainable Sourcing
Some organisations understand this already and are beginning to use sustainable sourcing for their technology services. However, it is not a top priority with Ecosystm research showing only 15% of organisations focus on sustainable procurement.
Technology Providers Can Help
Leading technology providers are introducing initiatives that make it easier for organisations to procure sustainable IT solutions. The recently announced HPE GreenLake for Large Language Models will be based in a data centre built and run by Qscale in Canada that is not only sustainably built and sourced, but sits on a grid supplying 99.5% renewable electricity – and waste (warm) air from the data centre and cooling systems is funneled to nearby greenhouses that grow berries. I find the concept remarkable and this is one of the most impressive sustainable data centre stories to date.
The focus on sustainability needs to be universal – across all cloud and AI providers. AI usage IS exploding – and we are just at the tip of the iceberg today. It will continue to grow as it becomes easier to use and deploy, more readily available, and more relevant across all industries and organisations. But we are at a stage of climate warming where we cannot increase our greenhouse gas emissions – and offsetting these emissions just passes the buck.
We need more companies like HPE and Qscale to build this Sustainable Future – and we need to be thinking the same way in our own data centres and putting pressure on our own AI and overall technology value chain to think more sustainably and act in the interests of the planet and future generations. Cloud providers – like AWS – are committed to the NetZero goal (by 2040 in their case) – but this is meaningless if our requirement for computing capacity increases a hundred-fold in that period. Our businesses and our tech partners need to act today. It is time for organisations to demand it from their tech providers to influence change in the industry.

There is no doubt that 2023 is off to an uncertain start. However, despite the economic headwinds we expect that some areas of technology will see continued growth. In fact, from our conversations with business and technology leaders, it appears that many organisations will take the opportunity to right-size their businesses, remove excess fat and waste, and accelerate their transformation efforts. The plan is to emerge from a global slowdown – leaner, smarter and better.
Where there is an opportunity to automate organisations will take it – and technology spend will trump people spend in 2023.
But it won’t all be smooth sailing as technology buyers become more discerning than ever and manage costs closely.
Here is what tech providers should focus on to remain resilient in these uncertain times.
- Be prepared to work harder – especially cloud and SaaS providers
- Help customers optimise costs
- Accelerate innovation to stay ahead of M&A activity
- Employ security to manage risk
- Prepare for product-led growth
Read on to find out why.
Download Be Alert – Not Alarmed: Analyst Guidance for Tech Providers as a PDF

In 2023, organisations will continue to reinvent themselves to remain relevant to their customers, engage their employees and be efficient and profitable.
As per Ecosystm’s Digital Enterprise Study 2022, organisations will increase spend on digital workplace technologies, enterprise software upgrades, mobile applications, infrastructure and data centres, and hybrid cloud management.
Here are the top 5 trends for the Distributed Enterprise in 2023 according to Ecosystm analysts, Alea Fairchild, Darian Bird, Peter Carr, and Tim Sheedy.
- Deskless Workers Will Become Modern Professionals
- Need for Cost Efficiency Will Stimulate the Use of Waste Metrics in Public Cloud
- The Climate & Energy Crisis Will Change the Cloud Equation
- Industry Cloud Will Further Accelerate Business Innovation
- The SASE Piece Will Fall in Place
Read on for more details.
Download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for the Distributed Enterprise in 2023

2020 was a watershed year for the industry as they proved to be the backbone for the rapid changes in work practices, communication and entertainment. This has led telecom providers to embark on their won digital transformation journeys.
The challenges continue for the industry, especially as 5G has not yet delivered on the early promises. Telecom operators today are having to provide cutting-edge services and top-notch customer experience as they continue to be challenged by new market entrants and strong regulatory pressures.
In 2022, telecom providers will be driven by the need to innovate and improve their product and service lines; improve customer experience; comply with changing regulations; and to optimise costs.
Read on to find out what Ecosystm Analysts Darian Bird and Matt Walker think will be the key trends in the telecom industry in 2022.












































