Many opinions exist on how automation and machine learning will help our return to the office environment. Removing physical touchpoints and leveraging machine learning to trace employee behaviour can help with the transition back to the workplace. But will people trust the office’s automated suggestions on where to work in the building, or help themselves to alternative workspaces?
Processes & Trust for People Engagement
Organisations such as Disney and Amazon understand what kinds of processes and trust it takes to engage people. These organisations took their time to create a vision of the contactless trusted experience before developing an implementation plan. The RFID wristbands at Disney that open hotel doors and get you on to rides involve many elements of trust and privacy. The automated order and delivery tracking of Amazon, along with suggestions and buying patterns, require the person to opt-in and share information to make happen.
So for your company, once employees re-enter the workplace, how will your company create those processes, that level of trust and faith, that would allow movements and health status to be tracked by office automation? For example, how often should employees overtly be aware of their temperature being scanned?
Abilities of Buildings to Manage
Facilities management is trending towards intelligent building management systems (iBMS) which know about room occupancy, room hygiene and are tracking who has been where and with whom. Elevators will limit occupancy and direct users to the correct lift going to the correct location. I have already seen this in our city hospital where you get directed to the correct lift once you have entered information on your destination. This combines user interface devices such as touchless pads, system hardware, and access control management software.
The building can also possibly direct you via a building app to request a place to work. You could swipe your personnel card and then be shown several options based on your personal profile and job role, including private quiet rooms, communal areas, and outside meeting tables. Previous occupants can be noted to share hygiene tracing if necessary. Intelligent buildings already offer direct support to the employees who interact with them for HVAC, lighting control, and occupation sensor. They have the ability to reduce user friction while raising workplace experience metrics to create a measured environment.
User Trust & Participation
Users should be willing to participate to get access. To create the trust that is required for employees to be willing to participate in the process, companies need to share policies and demonstrate stewardship of the data accessed. Who is holding my locational data, for how long, and for what purpose?
Trust facilitates successful data sharing, which in turn reinforces trust. Trust is built when the purpose of data sharing is made clear, and when those involved in the process know each other, understand each other’s expectations, and carry out their commitments as agreed. Trust increases the likelihood of further collaboration and improves core surveillance capacity by supporting surveillance networks.
Conclusion
Will we put our trust in buildings and facilities management on our return to the office? If communication is clear and policy well articulated, the building can play a role in engaging users to return to some standards of in-office participation. But if communication is muddy and policy not made clear, people will make their own way to safety – potentially impacting the environment of others.
Transform and be better prepared for future disruption, and the ever-changing competitive environment and customer, employee or partner demands in 2021. Download Ecosystm Predicts: The top 5 Future of Work Trends For 2021.

Public sector organisations are looking at 2021 as the year where they either hobble back to normalcy or implement their successful pilots (that were honed under tremendous pressure). Ecosystm research finds that 60% of government agencies are looking at 2021 as the year they make a recovery to normal – or the normal that finally emerges. The path to recovery will be technology-driven, and this time they will look at scalability and data-driven intelligence.
Ecosystm Advisors Alan Hesketh, Mike Zamora and Sash Mukherjee present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Cities of the Future in 2021. This is a summary of our Cities of the Future predictions – the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform here.
The Top 5 Cities of the Future Trends for 2021
#1 Cities Will Re-start Their Transformation Journey by Taking Stock
In 2021 the first thing that cities will do is introspect and reassess. There have been a lot of abrupt policy shifts, people changes, and technology deployments. Most have been ad-hoc, without the benefit of strategy planning, but many of the services that cities provide have been transformed completely. Government agencies in cities have seen rapid tech adoption, changes in their business processes and in the mindset of how their employees – many who were at the frontline of the crisis – provide citizen services.
Technology investments, in most cases, took on an unexpected trajectory and agencies will find that they have digressed from their technology and transformation roadmap. This also provides an opportunity, as many solutions would have gone through an initial ‘proof-of-concept’ without the formal rigours and protocols. Many of these will be adopted for longer term applications. In 2021, they will retain the same technology priorities as 2020, but consolidate and strengthen on their spend.
#2 Cities Will be Instrumented Using Intelligent Edge Devices
The capabilities of edge devices continue to increase dramatically, while costs decline. This reduces the barriers to entry for cities to collect and analyse significantly more data about the city and its people. Edge devices move computational power and data storage as close to the point of usage as possible to provide good performance. Devices range from battery powered IoT devices for data collection through to devices such as smart CCTV cameras with embedded pattern recognition software.
Cities will develop many use cases for intelligent edge devices. These uses will range from enhancing old assets using newer approaches to data collection – through to accelerating the speed and quality of the build of a new asset. The move to data-driven maintenance and decision-making will improve outcomes.
#3 COVID-19 Will Impact City Design
The world has received a powerful reminder of the vulnerability of densely populated cities, and the importance of planning and regulating public health. COVID-19 will continue to have an impact on city design in 2021.
A critical activity in controlling the pandemic in this environment is the test-and-trace capabilities of the local public health authorities. Technology to provide automated, accurate, contact tracing to replace manual efforts is now available. Scanning of QR codes at locations visited is proving to be the most widely adopted approach. The willingness of citizens to track their travels will be a crucial aid in managing the spread of COVID-19.
Early detection of new disease outbreaks, or other high-risk environmental events, is essential to minimise harm. Intelligent edge devices that detect the presence of viruses will become crucial tools in a city’s defence.
Intelligent edge devices will also play a role in managing building ventilation. Well-ventilated spaces are an important factor in controlling virus transmission. But a limited number of buildings have ventilation systems that are capable of meeting those requirements. Property owners will begin to refit their facilities to provide better air movement.
#4 Technology Vendors Will Emerge as the Conductors of Cities of the Future
The built environment comprises not only of the physical building, but also the space around the buildings and building operations. The real estate developer/investor owns the building – the urban fabric, the relationship of buildings to each other, the common space and the common services provided to the city, is owned by the City. The question is who will coordinate the players, e.g. business, citizens, government and the built environment. Ideally the government should be the conductor. However, they may not have sufficient experience or knowledge to properly implement this role. This means a capable and knowledgeable neutral consultant will at least initially fill this role. There is an opportunity for a technology vendor to fill that consulting role and impact the city fabric. This enhanced city environment will be requested by the Citizen, driven by the City, and guided by Technology Vendors. 2021 will see leading technology vendors working very closely with cities.
#5 Compliance Will be at the Core of Citizen Engagement Initiatives
Many Smart Cities have long focused on online services – over the last couple of years mobile apps have further improved citizen services. In 2020, the pandemic challenged government agencies to continue to provide services to citizens who were housebound and had become more digital savvy almost overnight. And many cities were able to scale up to fulfill citizen expectations.
However, in 2021 there will be a need to re-evaluate measures that were implemented this year – and one area that will be top priority for public sector agencies is compliance, security and privacy.
The key drivers for this renewed focus on security and privacy are:
- The need to temper the focus of ‘service delivery at any cost’ and further remind agencies and employees that security and privacy must comply with standard to allow the use of government data.
- The rise of cyberattacks that target not only essential infrastructure, but also individual citizens and small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
- The rise of app adoption by city agencies – many that have been developed by third parties. It will become essential to evaluate their compliance to security and privacy requirements.

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Mike Zamora
There have been a few articles recently about investment companies looking to buy large national US retail companies, for example, JC Penney and Dillards. Their historical approach was to purchase the land and develop the sites as a retail centre and operate their stores. They then lease the remaining retail space to other retailers. It is a business model which has been in use for many decades.
Historically a long and deep negative economic cycle has caused some retail operators/developers to sell part of their operations. This happened in the US in 1995 with Sears. The real estate development and investment companies’ interest is in exploring if there is a higher and better use for the properties. That is the essence of land economics, going from a lower economic use to a higher income/value use.
A key difference this time is the use of advanced technology. We see this in many dimensions: building systems and operations; retail management, social media, entertainment and food and beverage (F&B) operations.
The Smart Building revolution in Retail is about changing the management philosophy of buildings and using technology to aid in the process. The defining characteristic of building smarter is not the application of technology or a function of outcomes on energy use or maintenance. Instead, it is a commitment to leveraging the overall footprint to achieve the goals that perhaps inspired the building in the first place.
Evolution of Space for Retail Activities
The old axiom of real estate is location, location, location. This means that every retail centre will have to be assessed for its best purpose for its locations and surrounding environment. Retail has been morphing in the past few years from a traditional purpose of picking something up to an intersection of shopping and entertainment. This combines on-premise activities with a buying transaction which can be handled either onsite or online. Technology infrastructure investment opportunities are driven by optimising the customer retail experience.
Retail centres are seeking new functionality, including the adaptation of both design and use. Below are four approaches we believe can be used to assess each retail centre.
Reuse: Retail Lifecycle – Consumption to Redemption
There is a shift from consumers discovering and experiencing products in a physical retail space to retailers delivering on-demand. Many smaller retailers have capitalised on this by becoming pick-up points for online orders. They hope to increase footfall by drawing the customer into their own premises when retrieving their online delivery.
Retail centres need to expand on this trend to become a fulfilment location rather than a retail shopping space. Consumers could pick up online orders, recycle used goods, get products maintained and repaired, have appointments for personal services (dental, eye, hair, dry cleaning, etc.), try and test goods in mini-showrooms and collect points and benefits from gamification activities. By having a centralised exchange facility with multiple functionalities, consumer data can be leveraged to create marketing pull activities such as exclusive shopping events, and personalised customer service based on preferences and purchase history.
The current square meterage can be reallocated for distribution including the use of dark stores, green recycling centres for 3D printed product disposal and retail pick-up and exchange points. Staff will not be salespeople, but customer delivery service managers. The technology opportunities in this area would be re-allocation of network resources; focus on efficiency in delivery and customer satisfaction; and automation tools for customer service staff.
Redesign: Blended – Community Environment and Retail Experience
An alternative and more involved development approach would be to redesign the retail centre with deeper use cases to get more customers to come and stay longer. If a consumer stays onsite longer, there is a higher probability they will spend more at the retail centre. The future retail centre (Figure 1) would include additional space usages for a community space, a distribution centre for pick-ups, expanded F&B and remote working.
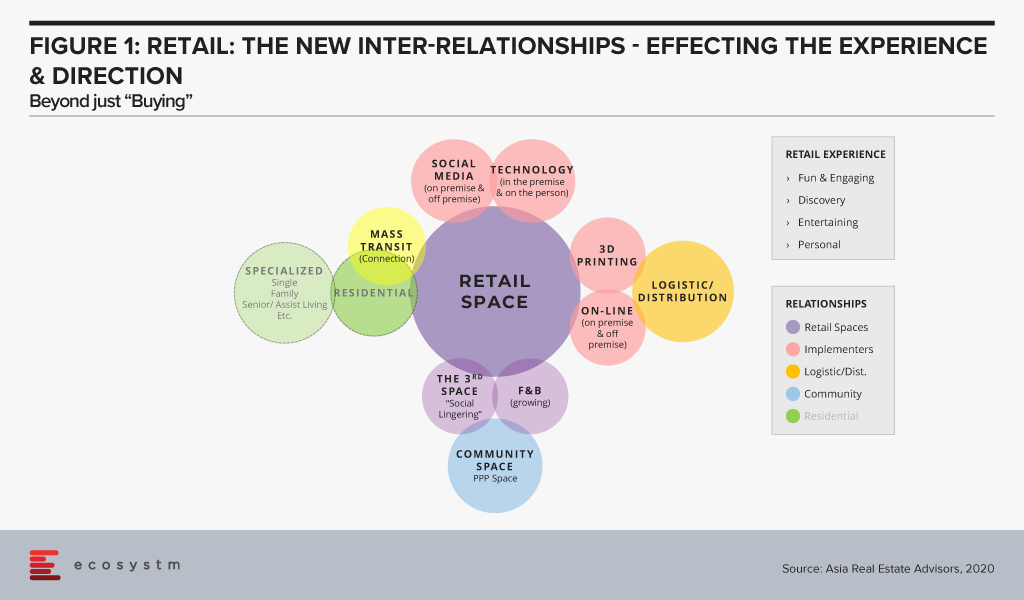
The technology opportunities are in two areas: customer experience and building operations. From a customer perspective, some technology examples would include entertainment and gaming in the F&B area, digital signage and mobile device technology to further engage people. For building operations examples could include technologies to control climate, lighting, security, energy management and building management.
Redevelop – Living Space for a Quality of Life
In some locations, the retail environment could have an oversupply of newly development retail centres. This means the optimal use for the centre would be to change it to a ‘Village Community’ – a community where people can live, work, learn and play. It would encompass multiple uses – multi-family residential units, a community centre, learning centres for younger children and a co-working area. The technology opportunies would be identical to a connected Smart City – at a lesser scale. Smart residential solutions would make the living environmental more user friendly. Retail could include digital media, mobile push features, enhanced and operational technology, energy management, climate control and security. Schools could include interactive and collaborative tools. Parks would have Wi-Fi and enhanced security. Connected Services (eg utilities, fire life safety, security and communications) could include operational technology systems for utilities, audio and video security systems and communication.
Repurpose: Knowledge & Learning Environment
For some retail centres a redevelopment may not be required, but would instead need a major repurposing of the space. The repurpose could be as a learning or healthcare centre. Learning environments require large open spaces with high ceilings for auditoriums or class rooms; common areas for gathering in between classes; onsite housing for students; food courts; and adequate parking for commuters. A healthcare environment would require patient reception, examination rooms, inpatient rooms, surgical units, and administrative offices. It could also include a medical learning centre.
The technology opportunities would be to develop a 24×7 site, with technologies to support the key purpose of the centre. The learning environment could include collaborative audio/video tools for Smart Classrooms. The social areas could including advanced food ordering and delivery systems and multiple player gaming centres for entertainment. The living areas would include systems and technology for smart living. The parking area could include enhanced security and surveillance systems, and smart parking systems. Behind the scenes, the building operations would need to upgrade energy management, building maintenance and management, digital food court operations, and a wellness air quality system.
The Future of Sustainable Retail Space
The decline of a retail centre is not necessarily a bad thing for a community. It is just the “Circle of Life” as an area evolves. Locations morph over the long-term. This has been seen in all the large cities around the world which have stood the test of time, eg. London, Paris, Amsterdam, New York, Tokyo and Beijing. The transformation also breathes fresh air into the surrounding environment. There are multiple layers of technology available to provide for an incredible Sustainable and Smart Community. It is large opportunity, not only for real estate developers, but also for technology vendors who understand the transformation process into the multiple variations of smart environments. Large real estate players and REITs will buy these retail portfolios and begin to transform older, low revenue, semi-vacant shopping centres into vibrant destination centres. Technology vendors should bring their ideas and systems to the attention of retail real estate owners early on in the the process. This will increase their chances of having their systems incorporated into the overall design concept and operational approach. It is a physical and digital transformation which improves neighborhoods, businesses and the city. It is a win for all.

Smarter buildings and public facilities have long been of interest to architects and developers. Innovators can see that the promise of intelligent data used for spatial design can transform how we work, live and play.
How can Big Data be used for intelligent building design? There are a consortia of companies trying to figure this out together. I will discuss the Building 4.0 Co-operative Research Centre (CRC) in Australia.
I have already been examining the new approaches to using big data in facilities management. This is done by developing smarter office spaces, embedded with devices employing Ambient Intelligence (AmI). Research looked at how the intelligent use of big data contributed to building an environment with greater energy efficiency, optimised space utilisation, enhanced workplace experience and occupants’ comfort. This includes sound masking, the use of lighting for enhance environments, and sensors for occupancy for hygiene controls.
Ambient Intelligence (AmI)
AmI refers to electronic environments that are sensitive and responsive to the presence of employees, residents or visitors. These environments can have ecosystems (pun intended) of different IoT devices communicating with each other.
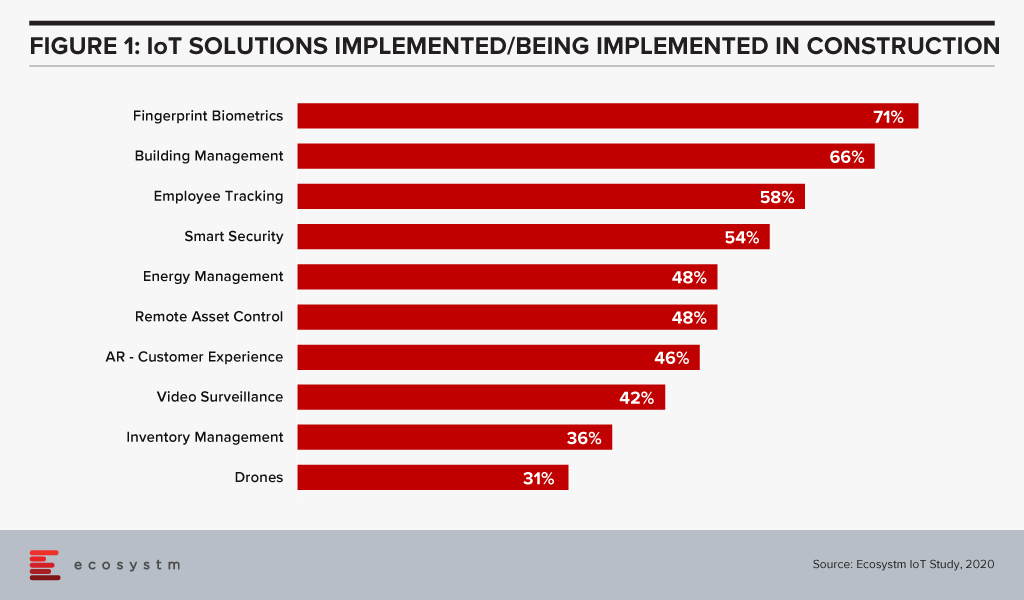
There is a real emphasis here on edge computing, sensors and other IoT devices, and building intelligence into the edge for near real-time decision making closer to where the problem may sit. Ecosystm research finds that construction firms focus a significant amount of IoT investment for building management and energy management (Figure 1).
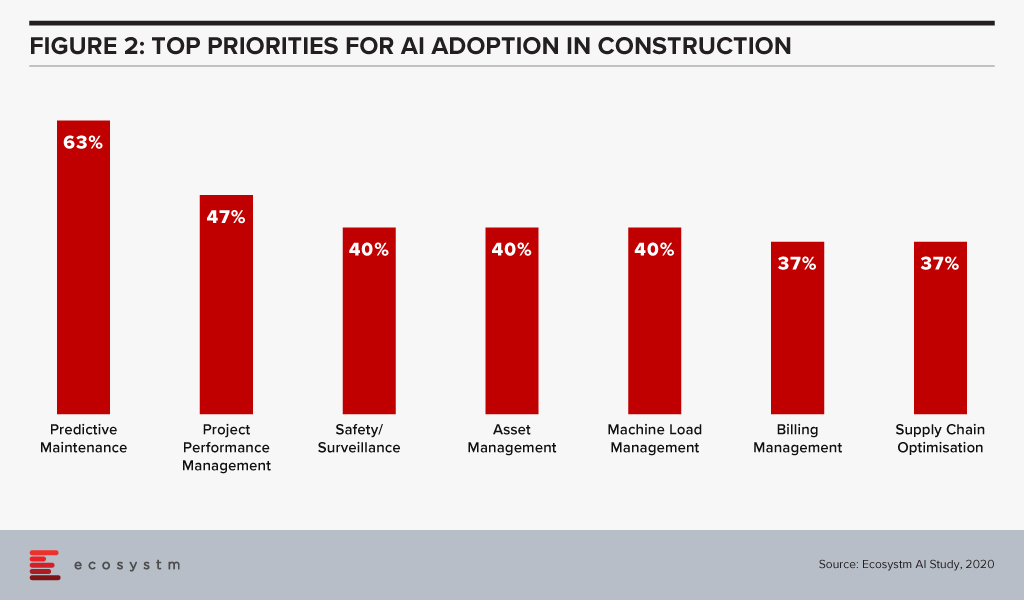
For example, if an HVAC system is on the verge of malfunction, the system could send a message for a repair intervention. When it comes to AI, predictive maintenance and surveillance are two of the leading use cases in the construction industry (Figure 2).
Building 4.0 Co-operative Research Centre (CRC)
In Australia, this push for sustainable and smarter building development is being driven by a consortium of companies looking at Big Data and infrastructure development for buildings. This year, the Building 4.0 Co-operative Research Centre (CRC) has been awarded a USD 19.5 million grant to focus on medium to long-term industry-led collaborations that can assist in driving the growth of new industries. The Australian building and construction industry is a major economic engine that contributes 13% of GDP and employs over 1.4 million Australians. Development of the Building 4.0 CRC makes sense and is timely given the current pandemic and economic conditions.
Part of its research program focus on develop new building processes and techniques through leveraging the latest technologies, data science and AI to ultimately improve all aspects of the key building phases. Their overall ecosystem is designed for enablement of several use cases (Figure 3).
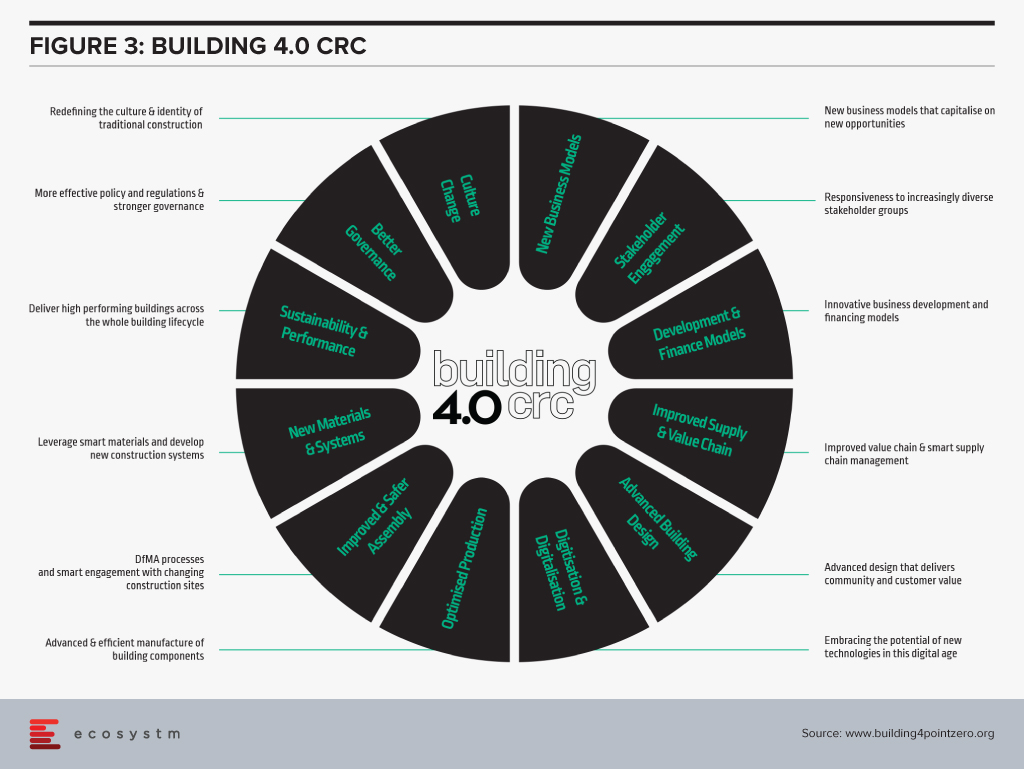
The Building 4.0 CRC’s principle aims are “to decrease waste; create buildings that are faster, cheaper, and smarter; and capture new opportunities by facilitating collaborative work between stakeholders across the whole value chain in cooperation with government and research organisations.”
Green Star, the rating system which was created by Green Building Council of Australia (GBCA) in 2003, rates the sustainability of buildings, fit outs and communities through Australia’s largest national, voluntary, holistic rating system. The GBCA is a partner organisation in the Building 4.0 CRC – as are many other major organisations in construction and trade, all pulling together here, for innovative efforts for the industry.
Where might the Building 4.0 CRC effort make an impact? Its collaborative structure of industry, academia, vocational trade organisation and governmental bodies harness innovative ideas to transmit them to transformative practices of industry and construction partners.
To be smarter, one must work smarter and more efficiently. A consortia such as this pulls the best minds together to try to accelerate industry efforts for intelligent design with data.

COVID-19 is accelerating digital transformation activities across industries. Remote working is now standard practice and digital engagement is replacing face-to-face interaction. Cloud technology has become essential rather than an option, and rollouts of new technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and intelligent automation are being expedited.
One of the industries that offer great potential for technology-driven transformation is the property sector.
Many activities within the property ecosystem have remained unchanged for decades. There are several opportunities for digital engagement and automation in this sector, ranging from the use of robots in construction to the ‘uberisation’ of the residential property customer journey.
The processes associated with buying or renting property remain cumbersome and complex for customers. Indeed, customers engage with many different organisations throughout their residential property lifecycles. When compared to some other industries, the customer experience can be poor. Components of the journey – such as property search – offer some great experiences but other parts such as exchanging contracts can rarely be described as positive customer experiences.
Although AR and virtual reality (VR) technologies can facilitate property inspection, most inspections are still undertaken on-premise, together with a real estate agent. Contract exchanges often involve interactions with legal professionals in-person. Securing a mortgage or a rental agreement also typically requires face-to-face interaction. Deposits commonly necessitate the physical presentation of a cheque.
The Uberisation of the Property Sector
So, in the residential sector, there are clear opportunities for start-ups and property search platforms to offer greatly enhanced customer experiences. The COVID-19 crisis will speed up the rate at which digital technologies are used to automate activities throughout the residential property customer journey and to engage customers digitally.
Property search platforms such as Singapore-based PropertyGuru, have been creating innovative ways of engaging customers and extending their range of services, for many years. For PropertyGuru, its news features, mortgage calculator, and ability to search for investment properties overseas, have enabled it to offer customers more value from its platform. Its PropertyGuru Lens feature uses AR and artificial intelligence (AI) to give customers a more immersive and improved experience. In common with other real estate platforms, it offers AR and VR tools for inspections.
Today’s crisis creates opportunities for platforms such as ProperyGuru to engage customers throughout their journey. It can potentially transform the residential property business, by becoming an Uber-style platform for agents, movers, shippers, storage companies, interior designers, renovation firms and all other stakeholders within the residential property ecosystem. Subject to regulation, it could also act as a mortgage broker and an agency for the exchange of contracts. In other words, it could ‘own’ the customer journey and act as a platform for all services associated with residential property. From the customer perspective, such a platform would be a welcome way of enhancing the experience associated with buying, renting, maintaining, improving, managing, and selling residential property.
IoT and the Commercial Property Sector
From a commercial property perspective, the COVID-19 crisis can also be expected to accelerate the digitalisation of many activities associated with the construction, maintenance, and management of buildings.
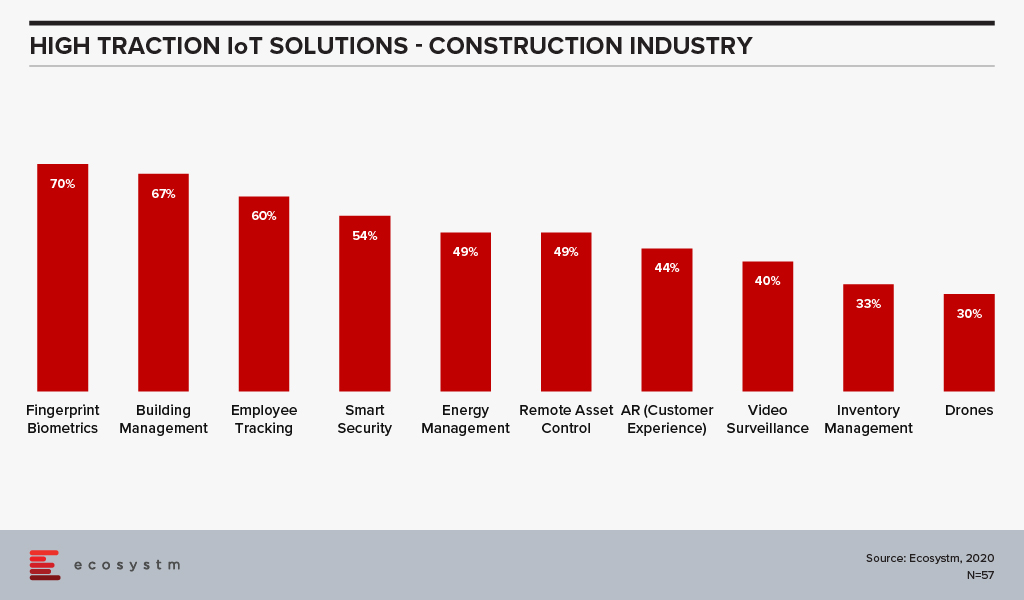
According to the findings of the Ecosystm IoT Study, the Construction industry is evaluating several technology solutions that are expected to benefit the industry (Figure 1).
While the industry views these solutions as beneficial, the adoption has so far been low. This will change. Drones have been used to inspect the outside of tall buildings for several years, but this is not yet standard practice. Structural inspections and maintenance of buildings will be automated at a much faster rate post COVID-19. IoT technology will be used for building management. Using IoT technology for the predictive maintenance and management of lighting, climate control, elevators, security, windows and doors will become standard as firms seek to reduce human interactions. Technology that measures footfall, manages safe distancing, takes peoples’ temperatures and identifies those who enter and leave buildings will be introduced, as organisations guard against disease clusters developing within or around their premises.
In essence, the COVID-19 crisis will act as a catalyst for the digital transformation of the property sector. There is a huge opportunity to create new business models not least by offering customers a digital platform on which all of their property-related needs can be addressed. For the commercial property sector, a similar platform can be offered. Additionally, many core activities ranging from construction to building management will be automated, fully leveraging robot, AI and IoT technologies.







