In my previous Ecosystm Insights, I covered how to choose the right database for the success of any application or project. Often organisations select cloud-based databases for the scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Here’s a look at some prominent cloud-based databases and guidance on the right cloud-based database for your organisational needs.
Click here to download ‘Databases Demystified. Cloud-Based Databases’ as a PDF.
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
Pros.
Managed Service. Automates database setup, maintenance, and scaling, allowing you to focus on application development.
Scalability. Easily scales database’s compute and storage resources with minimal downtime.
Variety of DB Engines. Supports multiple database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, and SQL Server.
Cons.
Cost. Can be expensive for larger databases or high-throughput applications.
Complex Pricing. The pricing model can be complex to understand, with costs for storage, I/O, and data transfer.
Google Cloud SQL
Pros.
Fully Managed. Takes care of database management tasks like replication, patch management, and backups.
Integration. Seamlessly integrates with other GCP services, enhancing data analytics and machine learning capabilities.
Security. Offers robust security features, including data encryption at rest and in transit.
Cons.
Limited Customisation. Compared to managing your own database, there are limitations on configurations and fine-tuning.
Egress Costs. Data transfer costs (especially egress) can add up if you have high data movement needs.
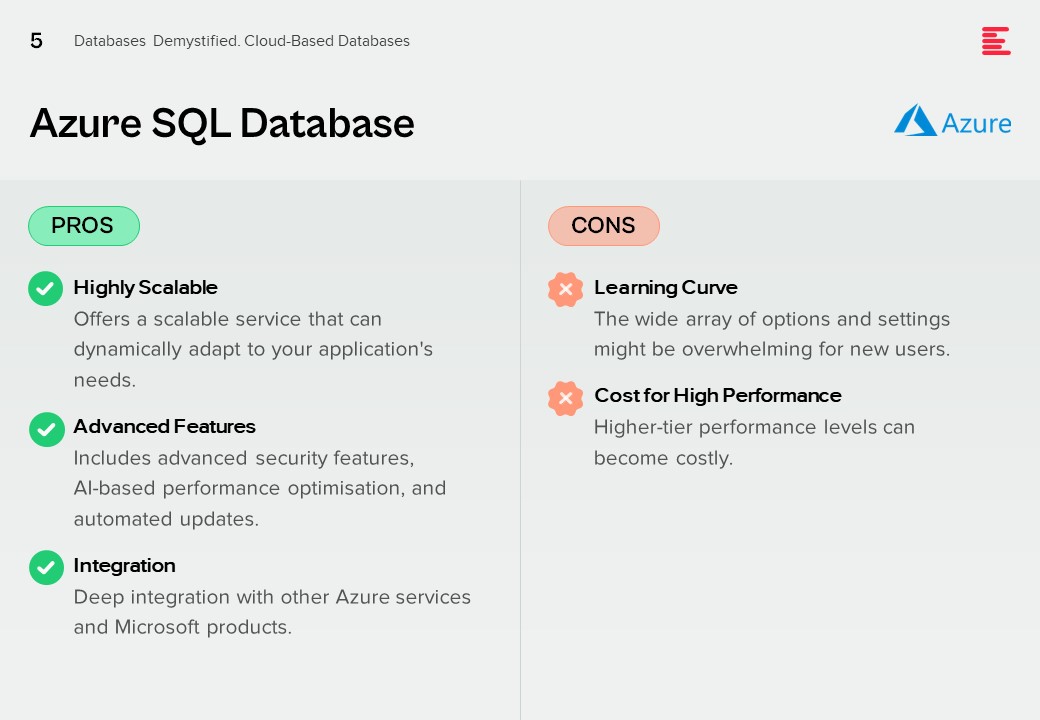
Azure SQL Database
Pros.
Highly Scalable. Offers a scalable service that can dynamically adapt to your application’s needs.
Advanced Features. Includes advanced security features, AI-based performance optimisation, and automated updates.
Integration. Deep integration with other Azure services and Microsoft products.
Cons.
Learning Curve. The wide array of options and settings might be overwhelming for new users.
Cost for High Performance. Higher-tier performance levels can become costly.
MongoDB Atlas
Pros.
Flexibility. Offers a flexible document database that is ideal for unstructured data.
Global Clusters. Supports global clusters to improve access speeds for distributed applications.
Fully Managed. Provides a fully managed service, including automated backups, patches, and security.
Cons.
Cost at Scale. While it offers a free tier, costs can grow significantly with larger deployments and higher performance requirements.
Indexing Limitations. Efficient querying requires proper indexing, which can become complex as your dataset grows.
Amazon DynamoDB
Pros.
Serverless. Offers a serverless NoSQL database that scales automatically with your application’s demands.
Performance. Delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale.
Durability and Availability. Provides built-in security, backup, restore, and in-memory caching for internet-scale applications.
Cons.
Pricing Model. Pricing can be complex and expensive, especially for read/write throughput and storage.
Learning Curve. Different from traditional SQL databases, requiring time to learn best practices for data modeling and querying.
Selection Considerations
Data Model Compatibility. Ensure the database supports the data model you plan to use (relational, document, key-value, etc.).
Scalability and Performance Needs. Assess whether the database can meet your application’s scalability and performance requirements.
Cost. Understand the pricing model and estimate monthly costs based on your expected usage.
Security and Compliance. Check for security features and compliance with regulations relevant to your industry.
Integration with Existing Tools. Consider how well the database integrates with your current application ecosystem and development tools.
Vendor Lock-in. Be aware of the potential for vendor lock-in and consider the ease of migrating data to other services if needed.
Choosing the right cloud-based database involves balancing these factors to find the best fit for your application’s requirements and your organisation’s budget and skills.