Consider the sheer volume of information flowing through today’s financial systems: every QR payment, e-KYC onboarding, credit card swipe, and cross-border transfer captures a data point. With digital banking and Open Banking, financial institutions are sitting on a goldmine of insights. But this isn’t just about data collection; it’s about converting that data into strategic advantage in a fast-moving, customer-driven landscape.
With digital banks gaining traction and regulators around the world pushing bold reforms, the industry is entering a new phase of financial innovation powered by data and accelerated by AI.
Ecosystm gathered insights and identified key challenges from senior banking leaders during a series of roundtables we moderated across Asia Pacific. The conversations revealed a clear picture of where momentum is building – and where obstacles continue to slow progress. From these discussions, several key themes emerged that highlight both opportunities and ongoing barriers in the Banking sector.
1. AI is Leading to End-to-End Transformation
Banks are moving beyond generic digital offerings to deliver hyper-personalised, data-driven experiences that build loyalty and drive engagement. AI is driving this shift by helping institutions anticipate customer needs through real-time analysis of behavioural, transactional, and demographic data. From pre-approved credit offers and contextual investment nudges to app interfaces that adapt to individual financial habits, personalisation is becoming a core strategy, not just a feature. This is a huge departure from reactive service models, positioning data as a long-term strategic asset.
But the impact of AI isn’t limited to customer-facing experiences. It’s also driving innovation deep within the banking stack, from fraud detection and SME loan processing to intelligent chatbots that scale customer support. On the infrastructure side, banks are investing in agile, AI-ready platforms to support automation, model training, and advanced analytics at scale. These shifts are redefining how banks operate, make decisions, and deliver value. Institutions that integrate AI across both front-end journeys and back-end processes are setting a new benchmark for agility, efficiency, and competitiveness in a fast-changing financial landscape.

2. Regulatory Shifts are Redrawing the Competitive Landscape
Regulators are moving quickly in Asia Pacific by introducing frameworks for Open Banking, real-time payments, and even AI-specific standards like Singapore’s AI Verify. But the challenge for banks isn’t just keeping up with evolving external mandates. Internally, many are navigating a complicated mix of overlapping policies, built up over years of compliance with local, regional, and global rules. This often slows down innovation and makes it harder to implement AI and automation consistently across the organisation.
As banks double down on AI, it is clear that governance can’t be an afterthought. Many are still dealing with fragmented ownership of AI systems, inconsistent oversight, and unclear rules around things like model fairness and explainability. The more progressive ones are starting to fix this by setting up centralised governance frameworks, investing in risk-based controls, and putting processes in place to monitor things like bias and model drift from day one. They are not just trying to stay compliant; they are preparing for what’s coming next. In this landscape, the ability to manage regulatory complexity with speed and clarity, both internally and externally, is quickly becoming a competitive edge.

3. Success Depends on Strategy, Not Just Tech
While enthusiasm for AI is high, sustainable success hinges on a clear, aligned strategy that connects technology to business outcomes. Many banks struggle with fragmented initiatives because they lack a unified roadmap that prioritises high-impact use cases. Without clear goals, AI projects often fail to deliver meaningful value, becoming isolated pilots with limited scalability.
To avoid this, banks need to develop robust return-on-investment (ROI) models tailored to their context — measuring benefits like faster credit decisioning, reduced fraud losses, or increased cross-selling effectiveness. These models must consider not only the upfront costs of infrastructure and talent, but also ongoing expenses such as model retraining, governance, and integration with existing systems.
Ethical AI governance is another essential pillar. With growing regulatory scrutiny and public concern about opaque “black box” models, banks must embed transparency, fairness, and accountability into their AI frameworks from the outset. This goes beyond compliance; strong governance builds trust and is key to responsible, long-term use of AI in sensitive, high-stakes financial environments.

4. Legacy Challenges Still Hold Banks Back
Despite strong momentum, many banks face foundational barriers that hinder effective AI deployment. Chief among these is data fragmentation. Core customer, transaction, compliance, and risk data are often scattered across legacy systems and third-party platforms, making it difficult to access the integrated, high-quality data that AI models require.
This limits the development of comprehensive solutions and makes AI implementations slower, costlier, and less effective. Instead of waiting for full system replacements, banks need to invest in integration layers and modern data platforms that unify data sources and make them AI-ready. These platforms can connect siloed systems – such as CRM, payments, and core banking – to deliver a consolidated view, which is crucial for accurate credit scoring, personalised offers, and effective risk management.
Banks must also address talent gaps. The shortage of in-house AI expertise means many institutions rely on external consultants, which increases costs and reduces knowledge transfer. Without building internal capabilities and adjusting existing processes to accommodate AI, even sophisticated models may end up underused or misapplied.

5. Collaboration and Capability Building are Key Enablers
AI transformation isn’t just a technology project – it’s an organisation-wide shift that requires new capabilities, ways of working, and strategic partnerships. Success depends on more than just hiring data scientists. Relationship managers, credit officers, compliance teams, and frontline staff all need to be trained to understand and act on AI-driven insights. Processes such as loan approvals, fraud escalations, and customer engagement must be redesigned to integrate AI outputs seamlessly.
To drive continuous innovation, banks should establish internal Centres of Excellence for AI. These hubs can lead experimentation with high-value use cases like predictive credit scoring or real-time fraud detection, while ensuring that learnings are shared across business units. They also help avoid duplication and promote strategic alignment.
Partnerships with fintechs, technology providers, and academic institutions play a vital role as well. These collaborations offer access to cutting-edge tools, niche expertise, and locally relevant AI models that reflect the regulatory, cultural, and linguistic contexts banks operate in. In a fast-moving and increasingly competitive space, this combination of internal capability building and external collaboration gives banks the agility and foresight to lead.


Customer Success leaders are keenly aware of AI’s burgeoning potential, and our latest research confirms it. AI is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a present-day reality, already shaping content strategies for 55% of organisations and poised to expand its influence across a multitude of use cases.
Over the past two years, Ecosystm’s research – including surveys and deep dives with business and tech leaders – has consistently pointed to AI as the dominant theme.
Here are some insights for Customer Success Leaders from our research.
Click here to download “AI Stakeholders: The Customer Success Perspective” as a PDF.
AI in Action: Real-World Applications
The data speaks for itself. We’re seeing a significant uptake of AI in automating sales processes (69%), location-based marketing (63%), and delivering personalised product/service recommendations (61%). But beyond the numbers, what does this look like in practice?
In Marketing, AI tailors campaigns in real time based on customer behaviour, ensuring content and offers resonate. For e.g. in the Travel industry, AI analyses customer preferences to create customised itineraries, boosting satisfaction and repeat bookings. In Sales, AI-driven analysis of buying patterns helps teams stay ahead of trends, equipping them with the right products to meet demand. In Customer Experience, AI-powered feedback analysis identifies pain points before they escalate, leading to proactive problem-solving. We have already seen organisations using conversational AI to enable 24/7 customer engagement, instantly resolving issues while reducing team workload and enhancing CX.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the AI Landscape
However, the path to AI adoption isn’t without its hurdles. Customer Success leaders face significant challenges, including the lack of an organisation-wide AI strategy, data complexity and access issues, and the cost of implementation.
Despite these challenges, the focus on AI to enhance Customer Success is evident, with nearly 40% of AI initiatives geared towards this goal. This requires a more active role for these leaders in shaping AI strategies and roadmaps.
Our research reveals that there lies a critical gap: Customer Success leaders have limited involvement in AI initiatives. Only 19% are involved in identifying and prioritising use cases, and a mere 10% have input into data ownership and governance. This lack of participation is a missed opportunity.
The 2025 Vision: AI-Driven Customer Success
Looking ahead, Customer Success leaders expect AI to deliver significant benefits, including improved customer experience (56%), increased productivity (50%), and enhanced innovation (44%). These expectations underscore AI’s pivotal role in shaping the future of customer success.
To fully harness AI’s potential and advancements like Agentic AI, leaders must take a more active role. This means driving a clear AI strategy, tackling data challenges, and working closely with IT and data science teams to ensure AI solutions address real customer pain points and business gaps.

Operations leaders are on the front lines of the AI revolution. They see the transformative potential of AI and are actively driving its adoption to streamline processes, boost efficiency, and unlock new levels of performance. The value is clear: AI is no longer a futuristic concept, but a present-day necessity.
Over the past two years, Ecosystm’s research – including surveys and deep dives with business and tech leaders has confirmed this: AI is the dominant theme.
Here are some insights for Operations Leaders from our research.
Click here to download “AI Stakeholders: The Operations Perspective” as a PDF
From Streamlined Workflows to Smarter Decisions
AI is already making a tangible difference in operations. A significant 60% of operations leaders are currently leveraging AI for intelligent document processing, freeing up valuable time and resources. But this is just the beginning. The vision extends far beyond, with plans to expand AI’s reach into crucial areas like workflow analysis, fraud detection, and streamlining risk and compliance processes. Imagine AI optimising transportation routes in real-time, predicting equipment maintenance needs before they arise, or automating complex scheduling tasks. This is the operational reality AI is creating.
Real-World Impact, Real-World Examples
The impact of AI is not just theoretical. Operations leaders are witnessing firsthand how AI is driving tangible improvements. “With AI-powered vision and sensors, we’ve boosted efficiency, accuracy, and safety in our manufacturing processes,” shares one leader. Others highlight the security benefits: “From fraud detection to claims processing, AI is safeguarding our transactions and improving trust in our services.” Even complex logistical challenges are being conquered: “Our AI-driven logistics solution has cut costs, saved time, and turned complex operations into seamless processes.” These real-world examples showcase the power of AI to deliver concrete results across diverse operational functions.
Operations Takes a Seat at the AI Strategy Table (But Faces Challenges)
With 54% of organisations prioritising cost savings from AI, operations leaders are rightfully taking a seat at the AI strategy table, shaping use cases and driving adoption. A remarkable 56% of operations leaders are actively involved in defining high-value AI applications. However, a disconnect exists. Despite their influence on AI strategy, only a small fraction (7%) of operations leaders have direct data governance responsibilities. This lack of control over the very fuel that powers AI – data – creates a significant hurdle.
Further challenges include data access across siloed systems, limiting the ability to gain a holistic view, difficulty in identifying and prioritising the most impactful AI use cases, and persistent skills shortages. These barriers, while significant, are not deterring operations leaders.
The Future is AI-Driven
Despite these challenges, operations leaders are doubling down on AI. A striking 7 out of 10 plan to prioritise AI investments in 2025, driven by the pursuit of greater cost savings. And the biggest data effort on the horizon? Identifying and prioritising better use cases for AI. This focus on practical applications demonstrates a clear understanding: the future of operations is inextricably linked to the power of AI. By addressing the challenges they face and focusing on strategic implementation, operations leaders are poised to unlock the full potential of AI and transform their organisations.

AI has broken free from the IT department. It’s no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day reality transforming every facet of business. Departments across the enterprise are now empowered to harness AI directly, fuelling innovation and efficiency without waiting for IT’s stamp of approval. The result? A more agile, data-driven organisation where AI unlocks value and drives competitive advantage.
Ecosystm’s research over the past two years, including surveys and in-depth conversations with business and technology leaders, confirms this trend: AI is the dominant theme. And while the potential is clear, the journey is just beginning.
Here are key AI insights for HR Leaders from our research.
Click here to download “AI Stakeholders: The HR Perspective” as a PDF.
HR: Leading the Charge (or Should Be)
Our research reveals a fascinating dynamic in HR. While 54% of HR leaders currently use AI for recruitment (scanning resumes, etc.), their vision extends far beyond. A striking majority plan to expand AI’s reach into crucial areas: 74% for workforce planning, 68% for talent development and training, and 62% for streamlining employee onboarding.
The impact is tangible, with organisations already seeing significant benefits. GenAI has streamlined presentation creation for bank employees, allowing them to focus on content rather than formatting and improving efficiency. Integrating GenAI into knowledge bases has simplified access to internal information, making it quicker and easier for employees to find answers. AI-driven recruitment screening is accelerating hiring in the insurance sector by analysing resumes and applications to identify top candidates efficiently. Meanwhile, AI-powered workforce management systems are transforming field worker management by optimising job assignments, enabling real-time tracking, and ensuring quick responses to changes.
The Roadblocks and the Opportunity
Despite this promising outlook, HR leaders face significant hurdles. Limited exploration of use cases, the absence of a unified organisational AI strategy, and ethical concerns are among the key barriers to wider AI deployments.
Perhaps most concerning is the limited role HR plays in shaping AI strategy. While 57% of tech and business leaders cite increased productivity as the main driver for AI investments, HR’s influence is surprisingly weak. Only 20% of HR leaders define AI use cases, manage implementation, or are involved in governance and ownership. A mere 8% primarily manage AI solutions.
This disconnect represents a massive opportunity.
2025 and Beyond: A Call to Action for HR
Despite these challenges, our research indicates HR leaders are prioritising AI for 2025. Increased productivity is the top expected outcome, while three in ten will focus on identifying better HR use cases as part of a broader data-centric approach.
The message is clear: HR needs to step up and claim its seat at the AI table. By proactively defining use cases, championing ethical considerations, and collaborating closely with tech teams, HR can transform itself into a strategic driver of AI adoption, unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology for the entire organisation. The future of HR is intelligent, and it’s time for HR leaders to embrace it.

Over the past year, Ecosystm has conducted extensive research, including surveys and in-depth conversations with industry leaders, to uncover the most pressing topics and trends. And unsurprisingly, AI emerged as the dominant theme. Here are some insights from our research on the Manufacturing industry.
Click here to download “AI in Manufacturing: Success Stories & Insights” as a PDF
AI is revolutionising production lines, supply chains, and product development in the manufacturing sector. Yet, many manufacturers find themselves stuck between ambition and execution. Those who bridge this gap will gain a competitive edge, driving innovation and leading the industry forward.
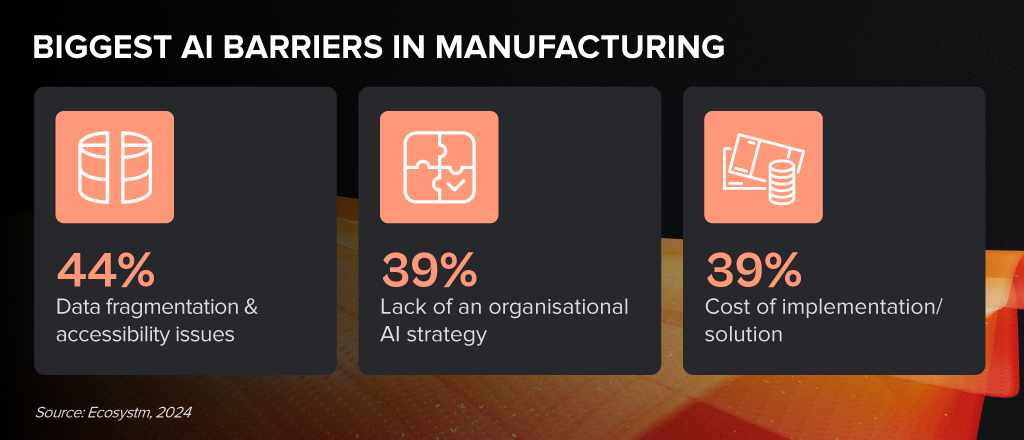
Despite the challenges, Manufacturing organisations are witnessing early AI success in these 3 areas:
- 1. Quality Control & Assurance
- 2. Supply Chain Management & Optimisation
- 3. Process Automation & Efficiency
Quality Control & Assurance
- Defect Detection. Identifying defects in products and improving quality
- Product Inspection. Implementing AI-powered vision systems to inspect products and ensure they meet quality standards
- Data Analysis. Analysing operational data and customer feedback to identify operations and product issues
“AI is the future of design. It streamlines the design process, leading to faster time-to-market and superior products.” – OPERATIONS LEADER
Supply Chain Management & Optimisation
- Inventory Management. Optimising inventory levels and reducing costs
- Supply Chain Visibility. Gaining real-time visibility into supply chain operations
- Demand Forecasting. Predicting demand for products to improve production planning and inventory management
“By leveraging AI, we’re not just optimising our supply chain; we’re pioneering sustainable practices to reduce our carbon footprint.” – CIO
Process Automation and Efficiency
- Process Optimisation. Identifying areas for improvement and potential operational bottlenecks
- Predictive Maintenance. Predicting equipment failures and preventing downtime
- Customer Feedback Analysis. Analysing customer feedback to improve design processes, products, and services
“Our goal is to build intelligent manufacturing plants. By proactively monitoring equipment health, we minimise downtime and maximise productivity – we have set a new internal standard for operational efficiency in the last two years.” – HEAD OF PRODUCTION

As AI adoption continues to surge, the tech infrastructure market is undergoing a significant transformation. Traditional IT infrastructure providers are facing increasing pressure to innovate and adapt to the evolving demands of AI-powered applications. This shift is driving the development of new technologies and solutions that can support the intensive computational requirements and data-intensive nature of AI workloads.
At Lenovo’s recently held Asia Pacific summit in Shanghai they detailed their ‘AI for All’ strategy as they prepare for the next computing era. Building on their history as a major force in the hardware market, new AI-ready offerings will be prominent in their enhanced portfolio.
At the same time, Lenovo is adding software and services, both homegrown and with partners, to leverage their already well-established relationships with client IT teams. Sustainability is also a crucial message as it seeks to address the need for power efficiency and zero waste lifecycle management in their products.
Ecosystm Advisor Darian Bird comment on Lenovo’s recent announcements and messaging.
Click here to download Lenovo’s Innovation Roadmap: Takeaways from the APAC Analyst Summit as a PDF
1. Lenovo’s AI Strategy
Lenovo’s AI strategy focuses on launching AI PCs that leverage their computing legacy.
As the adoption of GenAI increases, there’s a growing need for edge processing to enhance privacy and performance. Lenovo, along with Microsoft, is introducing AI PCs with specialised components like CPUs, GPUs, and AI accelerators (NPUs) optimised for AI workloads.
Energy efficiency is vital for AI applications, opening doors for mobile-chip makers like Qualcomm. Lenovo’s latest ThinkPads, featuring Qualcomm’s Snapdragon X Elite processors, support Microsoft’s Copilot+ features while maximising battery life during AI tasks.
Lenovo is also investing in small language models (SLMs) that run directly on laptops, offering GenAI capabilities with lower resource demands. This allows users to interact with PCs using natural language for tasks like file searches, tech support, and personal management.
2. Lenovo’s Computer Vision Solutions
Lenovo stands out as one of the few computing hardware vendors that manufactures its own systems.
Leveraging precision engineering, Lenovo has developed solutions to automate production lines. By embedding computer vision in processes like quality inspection, equipment monitoring, and safety supervision, Lenovo customises ML algorithms using customer-specific data. Clients like McLaren Automotive use this technology to detect flaws beyond human capability, enhancing product quality and speeding up production.
Lenovo extends their computer vision expertise to retail, partnering with Sensormatic and Everseen to digitise branch operations. By analysing camera feeds, Lenovo’s solutions optimise merchandising, staffing, and design, while their checkout monitoring system detects theft and scanning errors in real-time. Australian customers have seen significant reductions in retail shrinkage after implementation.
3. AI in Action: Autonomous Robots
Like other hardware companies, Lenovo is experimenting with new devices to futureproof their portfolio.
Earlier this year, Lenovo unveiled the Daystar Bot GS, a six-legged robotic dog and an upgrade from their previous wheeled model. Resembling Boston Dynamics’ Spot but with added legs inspired by insects for enhanced stability, the bot is designed for challenging environments. Lenovo is positioning it as an automated monitoring assistant for equipment inspection and surveillance, reducing the need for additional staff. Power stations in China are already using the robot to read meters, detect temperature anomalies, and identify defective equipment.
Although it is likely to remain a niche product in the short term, the robot is an avenue for Lenovo to showcase their AI wares on a physical device, incorporating computer vision and self-guided movement.
Considerations for Lenovo’s Future Growth
Lenovo outlined an AI vision leveraging their expertise in end user computing, manufacturing, and retail. While the strategy aligns with Lenovo’s background, they should consider the following:
Hybrid AI. Initially, AI on PCs will address performance and privacy issues, but hybrid AI – integrating data across devices, clouds, and APIs – will eventually dominate.
Data Transparency & Control. The balance between convenience and privacy in AI is still unclear. Evolving transparency and control will be crucial as users adapt to new AI tools.
AI Ecosystem. AI’s value lies in data, applications, and integration, not just hardware. Hardware vendors must form deeper partnerships in these areas, as Lenovo’s focus on industry-specific solutions demonstrates.
Enhanced Experience. AI enhances operational efficiency and customer experience. Offloading level one support to AI not only cuts costs but also resolves issues faster than live agents.

As AI evolves, the supporting infrastructure has become a crucial consideration for organisations and technology companies alike. AI demands massive processing power and efficient data handling, making high-performance computing clusters and advanced data management systems essential. Scalability, efficiency, security, and reliability are key to ensuring AI systems handle increasing demands and sensitive data responsibly.
Data centres must evolve to meet the increasing demands of AI and growing data requirements.
Equinix recently hosted technology analysts at their offices and data centre facilities in Singapore and Sydney to showcase how they are evolving to maintain their leadership in the colocation and interconnection space.
Equinix is expanding in Latin America, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia Pacific. In Asia Pacific, they recently opened data centres in Kuala Lumpur and Johor Bahru, with capacity additions in Mumbai, Sydney, Melbourne, Tokyo, and Seoul. Plans for the next 12 months include expanding in existing cities and entering new ones, such as Chennai and Jakarta.
Ecosystm analysts comment on Equinix’s growth potential and opportunities in Asia Pacific.
Small Details, Big Impact
TIM SHEEDY. The tour of the new Equinix data centre in Sydney revealed the complexity of modern facilities. For instance, the liquid cooling system, essential for new Nvidia chipsets, includes backup cold water tanks for redundancy. Every system and process is designed with built-in redundancy.
As power needs grow, so do operational and capital costs. The diesel generators at the data centre, comparable to a small power plant, are supported by multiple fuel suppliers from several regions in Sydney to ensure reliability during disasters.
Security is critical, with some areas surrounded by concrete walls extending from the ceiling to the floor, even restricting access to Equinix staff.
By focusing on these details, Equinix enables customers to quickly set up and manage their environments through a self-service portal, delivering a cloud-like experience for on-premises solutions.
Equinix’s Commitment to the Environment
ACHIM GRANZEN. Compute-intensive AI applications challenge data centres’ “100% green energy” pledges, prompting providers to seek additional green measures. Equinix addresses this through sustainable design and green energy investments, including liquid cooling and improved traditional cooling. In Singapore, one of Equinix’s top 3 hubs, the company partnered with the government and Sembcorp to procure solar power from panels on public buildings. This improves Equinix’s power mix and supports Singapore’s renewable energy sector.
TIM SHEEDY Building and operating data centres sustainably is challenging. While the basics – real estate, cooling, and communications – remain, adding proximity to clients, affordability, and 100% renewable energy complicates matters. In Australia, reliant on a mixed-energy grid, Equinix has secured 151 MW of renewable energy from Victoria’s Golden Plains Wind Farm, aiming for 100% renewable by 2029.
Equinix leads with AIA-rated data centres that operate in warmer conditions, reducing cooling needs and boosting energy efficiency. Focusing on efficient buildings, sustainable water management, and a circular economy, Equinix aims for climate neutrality by 2030, demonstrating strong environmental responsibility.
Equinix’s Private AI Value Proposition
ACHIM GRANZEN. Most AI efforts, especially GenAI, have occurred in the public cloud, but there’s rising demand for Private AI due to concerns about data availability, privacy, governance, cost, and location. Technology providers in a position to offer alternative AI stacks (usually built on top of a GPU-as-a-service model) to the hyperscalers find themselves in high interest. Equinix, in partnership with providers such as Nvidia, offers Private AI solutions on a global turnkey AI infrastructure. These solutions are ideal for industries with large-scale operations and connectivity challenges, such as Manufacturing, or those slow to adopt public cloud.
SASH MUKHERJEE. Equinix’s Private AI value proposition will appeal to many organisations, especially as discussions on AI cost efficiency and ROI evolve. AI unites IT and business teams, and Equinix understands the need for conversations at multiple levels. Infrastructure leaders focus on data strategy capacity planning; CISOs on networking and security; business lines on application performance, and the C-suite on revenue, risk, and cost considerations. Each has a stake in the AI strategy. For success, Equinix must reshape its go-to-market message to be industry-specific (that’s how AI conversations are shaping) and reskill its salesforce for broader conversations beyond infrastructure.
Equinix’s Growth Potential
ACHIM GRANZEN. In Southeast Asia, Malaysia and Indonesia provide growth opportunities for Equinix. Indonesia holds massive potential as a digital-savvy G20 country. In Malaysia, the company’s data centres can play a vital part in the ongoing Mydigital initiative, having a presence in the country before the hyperscalers. Also, the proximity of the Johor Bahru data centre to Singapore opens additional business opportunities.
TIM SHEEDY. Equinix is evolving beyond being just a data centre real estate provider. By developing their own platforms and services, along with partner-provided solutions, they enable customers to optimise application placement, manage smaller points of presence, enhance cloud interconnectivity, move data closer to hyperscalers for backup and performance, and provide multi-cloud networking. Composable services – such as cloud routers, load balancers, internet access, bare metal, virtual machines, and virtual routing and forwarding – allow seamless integration with partner solutions.
Equinix’s focus over the last 12 months on automating and simplifying the data centre management and interconnection services is certainly paying dividends, and revenue is expected to grow above tech market growth rates.
2024 has started cautiously for organisations, with many choosing to continue with tech projects that have already initiated, while waiting for clearer market conditions before starting newer transformation projects. This means that tech providers must continue to refine their market messaging and enhance their service/product offerings to strengthen their market presence in the latter part of the year. Ecosystm analysts present five key considerations for tech providers as they navigate evolving market and customer trends, this year.
Navigating Market Dynamics

Continuing Economic Uncertainties. Organisations will focus on ongoing projects and consider expanding initiatives in the latter part of the year. This means that tech providers should maintain visibility and trust with existing clients. They also need to help their customers meet multiple KPIs.
Popularity of Generative AI. For organisations, this will be the time to go beyond the novelty factor and assess practical business outcomes, allied costs, and change management. Tech providers need to include ROI discussions for short-term and mid-term perspectives as organisations move beyond pilots.
Infrastructure Market Disruption. Tech leaders will keep an eye out for advancements and disruptions in the market (likely to originate from the semiconductor sector). The disruptions might require tech vendors to re-assess the infrastructure partner ecosystem.
Need for New Tech Skills. Tech leaders will evaluate Generative AI’s impact on AIOps and IT Architecture; invest in upskilling for talent retention. Tech providers must prioritise creating user-friendly experiences to make technology accessible to business users. Training and partner enablement will also need a higher focus.
Increased Focus on Governance. Tech leaders will consult tech vendors on how to implement safeguards for data usage, sharing, and cybersecurity. This opens up opportunities in offering governance-related services.
5 Key Considerations for Tech Vendors
#1 Get Ready for the Year of the AI Startup

While many AI companies have been around for years, this will be the year that many of them make a significant play into enterprises in Asia Pacific. This comes at a time when many organisations are attempting to reduce tech debt and simplify their tech architecture.
For these AI startups to succeed, they will need to create watertight business cases, and do a lot of the hard work in pre-integrating their solutions with the larger platforms to reduce the time to value and simplify the systems integration work.
To respond to these emerging threats, existing tech providers will need to not only accelerate their own use of AI in their platforms, but also ramp up the education and promotion of these capabilities.
#2 Lead With Data, Not AI Capabilities

Organisations recognise the need for AI to enhance their workforce, improve customer experience, and automate processes. However, the initial challenge lies in improving data quality, as trust in early AI models hinges on high-quality training data for long-term success.
Tech vendors that can help with data source discovery, metadata analysis, and seamless data pipeline creation will emerge as trusted AI partners. Transformation tools that automate deduplication and quality assurance tasks empower data scientists to focus on high-value work. Automation models like Segment Anything enhance unstructured data labeling, particularly for images. Finally synthetic data will gain importance as quality sources become scarce.
Tech vendors will be tempted to capitalise on the Generative AI hype but for sake of positive early experiences, they should begin with data quality.
#3 Prepare Thoroughly for AI-driven Business Demand

Besides pureplay AI opportunities, AI will drive a renewed and increased interest in data and data management. Tech and service providers can capitalise on this by understanding the larger picture around their clients’ data maturity and governance. Initial conversations around AI can be door openers to bigger, transformational engagements.
Tech vendors should avoid the pitfall of downplaying AI risks. Instead, they should make all efforts to own and drive the conversation with their clients. They need to be forthcoming about their in-house responsible AI guidelines and understand what is happening in AI legislation world-wide (hint: a lot!)
Tech providers must establish strong client partnerships for AI initiatives to succeed. They must address risk and benefit equally to reap the benefits of larger AI-driven transformation engagements.
#4 Converge Network & Security Capabilities

Networking and security vendors will need to develop converged offerings as these two technologies increasingly overlap in the hybrid working era. Organisations are now entering a new phase of maturity as they evolve their remote working policies and invest in tools to regain control. They will require simplified management, increased visibility, and to provide a consistent user experience, wherever employees are located.
There has already been a widespread adoption of SD-WAN and now organisations are starting to explore next generation SSE technologies. Procuring these capabilities from a single provider will help to remove complexity from networks as the number of endpoints continue to grow.
Tech providers should take a land and expand approach, getting a foothold with SASE modules that offer rapid ROI. They should focus on SWG and ZTNA deals with an eye to expanding in CASB and FWaaS, as customers gain experience.
#5 Double Down on Your Partner Ecosystem

The IT services market, particularly in Asia Pacific, is poised for significant growth. Factors, including the imperative to cut IT operational costs, the growing complexity of cloud migrations and transformations, change management for Generative AI capabilities, and rising security and data governance needs, will drive increased spending on IT services.
Tech services providers – consultants, SIs, managed services providers, and VARs – will help drive organisations’ tech spend and strategy. This is a good time to review partners, evaluating whether they can take the business forward, or whether there is a need to expand or change the partner mix.
Partner reviews should start with an evaluation of processes and incentives to ensure they foster desired behaviour from customers and partners. Tech vendors should develop a 21st century partner program to improve chances of success.

The process of developing advertising campaigns is evolving with the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI). Advertisers want to optimise the amount of data at their disposal to craft better campaigns and drive more impact. Since early 2020, there has been a real push to integrate AI to help measure the effectiveness of campaigns and where to allocate ad spend. This now goes beyond media targeting and includes planning, analytics and creative. AI can assist in pattern matching, tailoring messages through AI-enabled hyper-personalisation, and analysing traffic to communicate through pattern identification of best times and means of communication. AI is being used to create ad copy; and social media and online advertising platforms are starting to roll out tools that help advertisers create better ads.
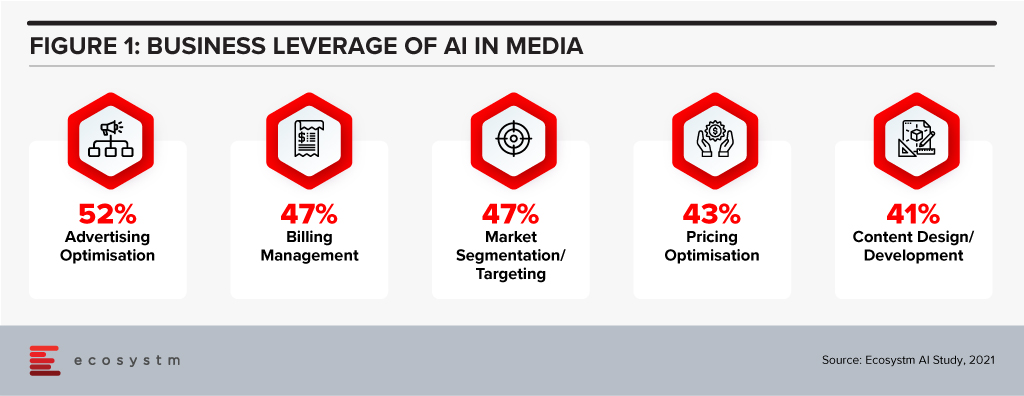
Ecosystm research shows that Media companies report optimisation, targeting and administrative functions such as billing are aided by AI use (Figure 1). However, the trend of Media companies leveraging AI for content design and media analysis is growing.
WPP Strengthening Tech Capabilities
This week, WPP announced the acquisition of Satalia, a UK-based company, who will consult with all WPP agencies globally to promote AI capabilities across the company and help shape the company’s AI strategy, including research and development, AI ethics, partnerships, talent and products.
It was announced that Satalia, whose clients include BT, DFS, DS Smith, PwC, Gigaclear, Tesco and Unilever, will join Wunderman Thompson Commerce to work on the technology division of their global eCommerce consultancy. Prior to the acquisition, Satalia had launched tools such as Satalia Workforce to automate work assignments; and Satalia Delivery, for automated delivery routes and schedules. The tools have been adopted by companies including PwC, DFS, Selecta and Australian supermarket chain Woolworths.
Like other global advertising organisations, WPP has been focused on expanding the experience, commerce and technology parts of the business, most recently acquiring Brazilian software engineering company DTI Digital in February. WPP also launched their own global data consultancy, Choreograph, in April. Choreograph is WPP’s newly formed global data products and technology company focused on helping brands activate new customer experiences by turning data into intelligence. This article from last year from the WPP CTO is an interesting read on their technology strategy, especially their move to cloud to enable their strategy.
Ethics & AI – The Right Focus
The acquisition of Satalia will give WPP and opportunity to evaluate important areas such as AI ethics, partnerships and talent which will be significantly important in the medium term. AI ethics in advertising is also a longer-term discussion. With AI and machine learning, the system learns patterns that help steer targeting towards audiences that are more likely to convert and identify the best places to get your message in front of these buyers. If done responsibly it should provide consumers with the ability to learn about and purchase relevant products and services. However, as we have recently discussed, AI has two main forms of bias – underrepresented data and developer bias – that also needs to be looked into.
Summary
The role of AI in the orchestration of the advertising process is developing rapidly. Media firms are adopting cloud platforms, making IP investments, and developing partnerships to build the support they can offer with their advertising services. The use of AI in advertising will help mature and season the process to be even more tailored to customer preferences.







































































