Automation and AI hold immense promise for accelerating productivity, reducing errors, and streamlining tasks across virtually every industry. From manufacturing plants that operate robotic arms to software-driven solutions that analyse millions of data points in seconds, these technological advancements are revolutionising how we work. However, AI has already led to, and will continue to bring about, many unintended consequences.
One that has been discussed for nearly a decade but is starting to impact employees and brand experiences is the “automation paradox”. As AI and automation take on more routine tasks, employees find themselves tackling the complex exceptions and making high-stakes decisions.
What is the Automation Paradox?
1. The Shifting Burden from Low to High Value Tasks
When AI systems handle mundane or repetitive tasks, ‘human’ employees can direct their efforts toward higher-value activities. At first glance, this shift seems purely beneficial. AI helps filter out extraneous work, enabling humans to focus on the tasks that require creativity, empathy, or nuanced judgment. However, by design, these remaining tasks often carry greater responsibility. For instance, in a retail environment with automated checkout systems, a human staff member is more likely to deal with complex refund disputes or tense customer interactions. Or in a warehouse, as many processes are automated by AI and robots, humans are left with the oversight of, and responsibility for entire processes. Over time, handling primarily high-pressure situations can become mentally exhausting, contributing to job stress and potential burnout.
2. Increased Reliance on Human Judgment in Edge Cases
AI excels at pattern recognition and data processing at scale, but unusual or unprecedented scenarios can stump even the best-trained models. The human workforce is left to solve these complex, context-dependent challenges. Take self-driving cars as an example. While most day-to-day driving can be safely automated, human oversight is essential for unpredictable events – like sudden weather changes or unexpected road hazards.
Human intervention can be a critical, life-or-death matter, amplifying the pressure and stakes for those still in the loop.
3. The Fallibility Factor of AI
Ironically, as AI becomes more capable, humans may trust it too much. When systems make mistakes, it is the human operator who must detect and rectify them. But the further removed people are from the routine checks and balances – since “the system” seems to handle things so competently – the greater the chance that an error goes unnoticed until it has grown into a major problem. For instance, in the aviation industry, pilots who rely heavily on autopilot systems must remain vigilant for rare but critical emergency scenarios, which can be more taxing due to limited practice in handling manual controls.
Add to These the Known Challenges of AI!
Bias in Data and Algorithms. AI systems learn from historical data, which can carry societal and organisational biases. If left unchecked, these algorithms can perpetuate or even amplify unfairness. For instance, an AI-driven hiring platform trained on past decisions might favour candidates from certain backgrounds, unintentionally excluding qualified applicants from underrepresented groups.
Privacy and Data Security Concerns. The power of AI often comes from massive data collection, whether for predicting consumer trends or personalising user experiences. This accumulation of personal and sensitive information raises complex legal and ethical questions. Leaks, hacks, or improper data sharing can cause reputational damage and legal repercussions.
Skills Gap and Workforce Displacement. While AI can eliminate the need for certain manual tasks, it creates a demand for specialised skills, such as data science, machine learning operations, and AI ethics oversight. If an organisation fails to provide employees with retraining opportunities, it risks exacerbating skill gaps and losing valuable institutional knowledge.
Ethical and Social Implications. AI-driven decision-making can have profound impacts on communities. For example, a predictive policing system might inadvertently target specific neighbourhoods based on historical arrest data. When these systems lack transparency or accountability, public trust erodes, and social unrest can follow.
How Can We Mitigate the Known and Unknown Consequences of AI?
While some of the unintended consequences of AI and automation won’t be known until systems are deployed and processes are in practice, there are some basic hygiene approaches that technology leaders and their organisational peers can take to minimise these impacts.
- Human-Centric Design. Incorporate user feedback into AI system development. Tools should be designed to complement human skills, not overshadow them.
- Comprehensive Training. Provide ongoing education for employees expected to handle advanced AI or edge-case scenarios, ensuring they remain engaged and confident when high-stakes decisions arise.
- Robust Governance. Develop clear policies and frameworks that address bias, privacy, and security. Assign accountability to leaders who understand both technology and organisational ethics.
- Transparent Communication. Maintain clear channels of communication regarding what AI can and cannot do. Openness fosters trust, both internally and externally.
- Increase your organisational AIQ (AI Quotient). Most employees are not fully aware of the potential of AI and its opportunity to improve – or change – their roles. Conduct regular upskilling and knowledge sharing activities to improve the AIQ of your employees so they start to understand how people, plus data and technology, will drive their organisation forward.
Let me know your thoughts on the Automation Paradox, and stay tuned for my next blog on redefining employee skill pathways to tackle its challenges.

At the Nutanix .NEXT 2024 event in Barcelona, it became clear that the discourse around cloud computing has evolved significantly. The debate that once polarised organisations over whether on-prem/co-located data centres or public cloud was better has been decisively settled. Both cloud providers and on-prem equipment providers are thriving, as evident from their earnings reports.
Hybrid cloud has emerged as the clear victor, offering the flexibility and control that organisations demand. This shift is particularly relevant for tech buyers in the Asia Pacific region, where diverse market maturities and unique business challenges require a more adaptable approach to IT infrastructure.
The Hybrid Cloud Advantage
Hybrid cloud architecture combines the best of both worlds. It provides the scalability and agility of public cloud services while retaining the control and security of on-prem systems. For Asia Pacific organisations, that often operate across various regulatory environments and face unique data sovereignty issues, this dual capability is invaluable. The ability to seamlessly move workloads between on-prem, private cloud, and public cloud environments enables enterprises to optimise their IT strategies, balancing cost, performance, and compliance.
Market Maturity and Adoption in Asia Pacific
The region shows a wide spectrum of technological maturity among its markets. Countries like Australia, Japan, and Singapore lead with advanced cloud adoption and robust IT infrastructures, while emerging markets such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines are still in the nascent stages of cloud integration.
However, regardless of their current maturity levels, organisations in Asia Pacific are recognising the benefits of a hybrid cloud approach. Mature markets are leveraging hybrid cloud to refine their IT strategies, focusing on enhancing business agility and driving innovation.
Ecosystm research shows that 75% of organisations in Australia have a hybrid, multi-cloud strategy. Over 30% of organisations have repatriated workloads from the public cloud, and only 22% employ a “cloud first” strategy when deploying new services.

Meanwhile, emerging markets see hybrid cloud as a pathway to accelerate their digital transformation journeys without the need for extensive upfront investments in on-prem infrastructure. Again, Ecosystm data shows that when it comes to training large AI models and applications, organisations across Southeast Asia use a mix of public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud environments.
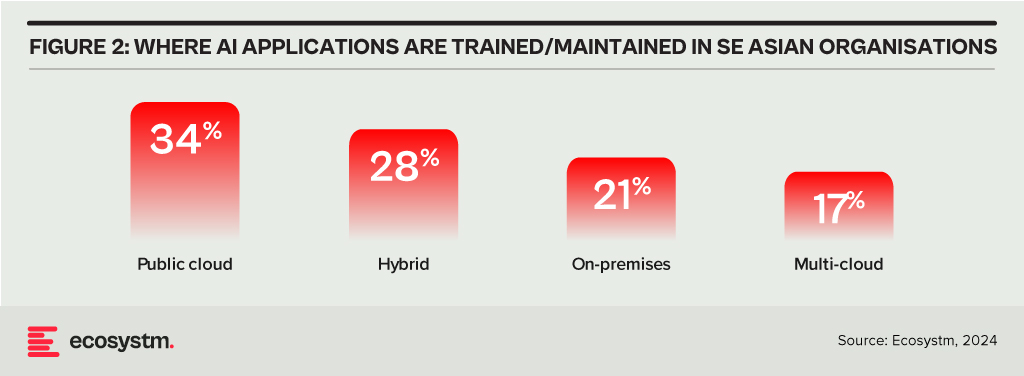
Strategic Flexibility Without Compromise
One of the most compelling messages from the Nutanix .NEXT 2024 event is that hybrid cloud eliminates the need for compromise when deciding where to place workloads – and that is what the data above represents. The location of the workload is no longer a limiting factor. Being “cloud first” locks organisations into a tech provider, whereas agility was once exclusively in favour of public cloud providers. Whether it’s for performance optimisation, cost efficiency, or regulatory compliance, tech leaders can now choose the best environment for every workload without being constrained by location.
For example, an organisation might keep sensitive customer data within a private cloud to comply with local data protection laws while leveraging public cloud resources for less sensitive applications to take advantage of its scalability and cost benefits. I recently spoke to an organisation in the gaming space that had 5 different regulatory bodies to appease – which required data to be stored in 5 different locations! This strategic flexibility ensures that IT investments are fully aligned with business objectives, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Moving Forward: Actionable Insights for Asia Pacific Tech Leaders
To fully capitalise on the hybrid cloud revolution, APAC tech leaders should:
- Assess Workload Requirements. Evaluate the specific needs of each workload to determine the optimal environment, considering factors like latency, security, and compliance.
- Invest in Integration Tools. Ensure seamless interoperability between on-premises and cloud environments by investing in advanced integration and management tools.
- Focus on Skill Development. Equip IT teams with the necessary skills to manage hybrid cloud infrastructures, emphasising continuous learning and certification.
- Embrace a Multi-Cloud Strategy. Consider a multi-cloud approach within the hybrid model to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance resilience.
Conclusion
The hybrid cloud has definitively won the battle for enterprise IT infrastructure, particularly in the diverse Asia Pacific region. By enabling organisations to place their workloads wherever they make the most sense without compromising on performance, security, or compliance, hybrid cloud empowers tech leaders to drive their digital transformation agendas forward with confidence. Based on everything we know today*, the future of cloud is hybrid. Reform your sourcing practices to put business needs, not cloud service providers or data centres, at the centre of your data decisions.
*In this fast-changing world, it seems naïve to make sweeping statements about the future of technology!
In my earlier post this week, I referred to the need for a grown-up conversation on AI. Here, I will focus on what conversations we need to have and what the solutions to AI disruption might be.
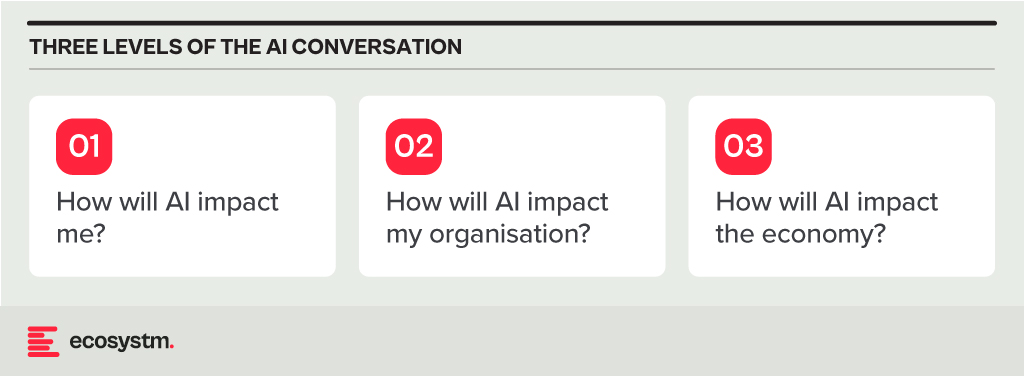
The Impact of AI on Individuals
AI is likely to impact people a lot! You might lose your job to AI. Even if it is not that extreme, it’s likely AI will do a lot of your job. And it might not be the “boring bits” – and sometimes the boring bits make a job manageable! IT helpdesk professionals, for instance, are already reporting that AIOps means they only deal with the difficult challenges. While that might be fun to start with, some personality types find this draining, knowing that every problem that ends up in the queue might take hours or days to resolve.
Your job will change. You will need new skills. Many organisations don’t invest in their employees, so you’ll need to upskill yourself in your own time and at your own cost. Look for employers who put new skill acquisition at the core of their employee offering. They are likelier to be more successful in the medium-to-long term and will also be the better employers with a happier workforce.
The Impact of AI on Organisations
Again – the impact on organisations will be huge. It will change the shape and size of organisations. We have already seen the impact in many industries. The legal sector is a major example where AI can do much of the job of a paralegal. Even in the IT helpdesk example shared earlier, where organisations with a mature tech environment will employ higher skilled professionals in most roles. These sectors need to think where their next generation of senior employees will come from, if junior roles go to AI. Software developers and coders are seeing greater demand for their skills now, even as AI tools increasingly augment their work. However, these skills are at an inflection point, as solutions like TuringBots have already started performing developer roles and are likely to take over the job of many developers and even designers in the near future.
Some industries will find that AI helps junior roles act more like senior employees, while others will use AI to perform the junior roles. AI will also create new roles (such as “prompt engineers”), but even those jobs will be done by AI in the future (and we are starting to see that).
HR teams, senior leadership, and investors need to work together to understand what the future might look like for their organisations. They need to start planning today for that future. Hint: invest in skills development and acquisition – that’s what will help you to succeed in the future.
The Impact of AI on the Economy
Assuming the individual and organisational impacts play out as described, the economic impacts of widespread AI adoption will be significant, similar to the “Great Depression”. If organisations lay off 30% of their employees, that means 30% of the economy is impacted, potentially leading to drying up of some government and an increase in government spend on welfare etc. – basically leading to major societal disruption.
The “AI won’t displace workers” narrative strikes me as the technological equivalent of climate change denial. Just like ignoring environmental warnings, dismissing the potential for AI to significantly impact the workforce is a recipe for disaster. Let’s not fall into the same trap and be an “AI denier”.
What is the Solution?
The solutions revolve around two ideas, and these need to be adopted at an industry level and driven by governments, unions, and businesses:
- Pay a living salary (for all citizens). Some countries already do this, with the Nordic nations leading the charge. And it is no surprise that some of these countries have had the most consistent long-term economic growth. The challenge today is that many governments cannot afford this – and it will become even less affordable as unemployment grows. The solution? Changing tax structures, taxing organisational earnings in-country (to stop them recognising local earnings in low-tax locations), and taxing wealth (not incomes). Also, paying essential workers who will not be replaced by AI (nurses, police, teachers etc.) better salaries will also help keep economies afloat. Easier said than done, of course!
- Move to a shorter work week (but pay full salaries). It is in the economic interest of every organisation that people stay gainfully employed. We have already discussed the ripple effect of job cuts. But if employees are given more flexibility, and working 3-day weeks, this not only spreads the work around more workers, but means that these workers have more time to spend money – ensuring continuing economic growth. Can every company do this? Probably not. But many can and they might have to. The concept of a 5-day work week isn’t that old (less than 100 years in fact – a 40-hour work week was only legislated in the US in the 1930s, and many companies had as little as 6-hour working days even in the 1950s). Just because we have worked this way for 80 years doesn’t mean that we will always have to. There is already a move towards 4-day work weeks. Tech.co surveyed over 1,000 US business leaders and found that 29% of companies with 4-day workweeks use AI extensively. In contrast, only 8% of organisations with a 5-day workweek use AI to the same degree.
AI Changes Everything
We are only at the beginning of the AI era. We have had a glimpse into the future, and it is both frightening and exciting. The opportunities for organisations to benefit from AI are already significant and will become even more as the technology improves and businesses learn to better adopt AI in areas where it can make an impact. But there will be consequences to this adoption. We already know what many of those consequences will be, so let’s start having those grown-up conversations today.

If you have seen me present recently – or even spoken to me for more than a few minutes, you’ve probably heard me go on about how the AI discussions need to change! At the moment, most senior executives, board rooms, governments, think tanks and tech evangelists are running around screaming with their hands on their ears when it comes to the impact of AI on jobs and society.
We are constantly being bombarded with the message that AI will help make knowledge workers more productive. AI won’t take people’s jobs – in fact it will help to create new jobs – you get the drift; you’ve been part of these conversations!
I was at an event recently where a leading cloud provider had a huge slide with the words: “Humans + AI Together” in large font across the screen. They then went on to demonstrate an opportunity for AI. In a live demo, they had the customer of a retailer call a store to check for stock of a dress. The call was handled by an AI solution, which engaged in a natural conversation with the customer. It verified their identity, checked dress stock at the store, processed the order, and even confirmed the customer’s intent to use their stored credit card.
So, in effect, on one slide, the tech provider emphasised that AI was not going to take our jobs, and two minutes later they showed how current AI capabilities could replace humans – today!
At an analyst event last week, representatives from three different tech providers told analysts how Microsoft Copilot is freeing up 10-15 hours a week. For a 40-hour work week, that’s a 25-38 time saving. In France (where the work week is 35 hours), that’s up to 43% of their time saved. So, by using a single AI platform, we can save 25-43% of our time – giving us the ability to work on other things.
What are the Real Benefits of AI?
The critical question is: What will we do with this saved time? Will it improve revenue or profit for businesses? AI might make us more agile, faster, more innovative but unless that translates to benefits on the bottom line, it is pointless. For example, adopting AI might mean we can create three times as many products. However, if we don’t make any more revenue and/or profit by having three times as many products, then any productivity benefit is worthless. UNLESS it is delivered through decreased costs.
We won’t need as many humans in our contact centres if AI is taking calls. Ideally, AI will lead to more personalised customer experiences – which will drive less calls to the contact centre in the first place! Even sales-related calls may disappear as personal AI bots will find deals and automatically sign us up. Of course, AI also costs money, particularly in terms of computing power. Some of the productivity uplift will be offset by the extra cost of the AI tools and platforms.
Many benefits that AI delivers will become table stakes. For example, if your competitor is updating their product four times a year and you are updating it annually, you might lose market share – so the benefits of AI might be just “keeping up with the competition”. But there are many areas where additional activity won’t deliver benefits. Organisations are unlikely to benefit from three times more promotional SMSs or EDMs and design work or brand redesigns.
I also believe that AI will create new roles. But you know what? AI will eventually do those jobs too. When automation came to agriculture, workers moved to factories. When automation came to factories, workers moved to offices. The (literally) trillion-dollar question is where workers go when automation comes to the office.
The Wider Impact of AI
The issue is that very few senior people in businesses or governments are planning for a future where maybe 30% of jobs done by knowledge workers go to AI. This could lead to the failure of economies. Government income will fall off a cliff. It will be unemployment on levels not seen since the great depression – or worse. And if we have not acknowledged these possible outcomes, how can we plan for it?
This is what I call the “grown up conversation about AI”. This is acknowledging the opportunity for AI and its impacts on companies, industries, governments and societies. Once we acknowledge these likely outcomes we can plan for it.
And that’s what I’ll discuss shortly – look out for my next Ecosystm Insight: The Three Possible Solutions for AI-driven Mass Unemployment.

Banks, insurers, and other financial services organisations in Asia Pacific have plenty of tech challenges and opportunities including cybersecurity and data privacy management; adapting to tech and customer demands, AI and ML integration; use of big data for personalisation; and regulatory compliance across business functions and transformation journeys.
Modernisation Projects are Back on the Table
An emerging tech challenge lies in modernising, replacing, or retiring legacy platforms and systems. Many banks still rely on outdated core systems, hindering agility, innovation, and personalised customer experiences. Migrating to modern, cloud-based systems presents challenges due to complexity, cost, and potential disruptions. Insurers are evaluating key platforms amid evolving customer needs and business models; ERP and HCM systems are up for renewal; data warehouses are transforming for the AI era; even CRM and other CX platforms are being modernised as older customer data stores and models become obsolete.
For the past five years, many financial services organisations in the region have sidelined large legacy modernisation projects, opting instead to make incremental transformations around their core systems. However, it is becoming critical for them to take action to secure their long-term survival and success.
Benefits of legacy modernisation include:
- Improved operational efficiency and agility
- Enhanced customer experience and satisfaction
- Increased innovation and competitive advantage
- Reduced security risks and compliance costs
- Preparation for future technologies
However, legacy modernisation and migration initiatives carry significant risks. For instance, TSB faced a USD 62M fine due to a failed mainframe migration, resulting in severe disruptions to branch operations and core banking functions like telephone, online, and mobile banking. The migration failure led to 225,492 complaints between 2018 and 2019, affecting all 550 branches and required TSB to pay more than USD 25M to customers through a redress program.
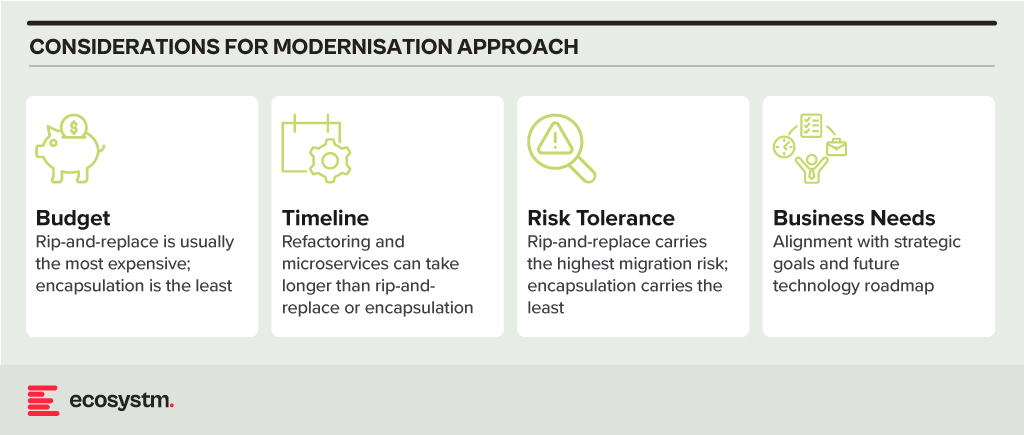
Modernisation Options
- Rip and Replace. Replacing the entire legacy system with a modern, cloud-based solution. While offering a clean slate and faster time to value, it’s expensive, disruptive, and carries migration risks.
- Refactoring. Rewriting key components of the legacy system with modern languages and architectures. It’s less disruptive than rip-and-replace but requires skilled developers and can still be time-consuming.
- Encapsulation. Wrapping the legacy system with a modern API layer, allowing integration with newer applications and tools. It’s quicker and cheaper than other options but doesn’t fully address underlying limitations.
- Microservices-based Modernisation. Breaking down the legacy system into smaller, independent services that can be individually modernised over time. It offers flexibility and agility but requires careful planning and execution.
Financial Systems on the Block for Legacy Modernisation
Data Analytics Platforms. Harnessing customer data for insights and targeted offerings is vital. Legacy data warehouses often struggle with real-time data processing and advanced analytics.
CRM Systems. Effective customer interactions require integrated CRM platforms. Outdated systems might hinder communication, personalisation, and cross-selling opportunities.

Payment Processing Systems. Legacy systems might lack support for real-time secure transactions, mobile payments, and cross-border transactions.

Core Banking Systems (CBS). The central nervous system of any bank, handling account management, transactions, and loan processing. Many Asia Pacific banks rely on aging, monolithic CBS with limited digital capabilities.
Digital Banking Platforms. While several Asia Pacific banks provide basic online banking, genuine digital transformation requires mobile-first apps with features such as instant payments, personalised financial management tools, and seamless third-party service integration.
Modernising Technical Approaches and Architectures
Numerous technical factors need to be addressed during modernisation, with decisions needing to be made upfront. Questions around data migration, testing and QA, change management, data security and development methodology (agile, waterfall or hybrid) need consideration.
Best practices in legacy migration have taught some lessons.
Adopt a data fabric platform. Many organisations find that centralising all data into a single warehouse or platform rarely justifies the time and effort invested. Businesses continually generate new data, adding sources, and updating systems. Managing data where it resides might seem complex initially. However, in the mid to longer term, this approach offers clearer benefits as it reduces the likelihood of data discrepancies, obsolescence, and governance challenges.
Focus modernisation on the customer metrics and journeys that matter. Legacy modernisation need not be an all-or-nothing initiative. While systems like mainframes may require complete replacement, even some mainframe-based software can be partially modernised to enable services for external applications and processes. Assess the potential of modernising components of existing systems rather than opting for a complete overhaul of legacy applications.
Embrace the cloud and SaaS. With the growing network of hyperscaler cloud locations and data centres, there’s likely to be a solution that enables organisations to operate in the cloud while meeting data residency requirements. Even if not available now, it could align with the timeline of a multi-year legacy modernisation project. Whenever feasible, prioritise SaaS over cloud-hosted applications to streamline management, reduce overhead, and mitigate risk.
Build for customisation for local and regional needs. Many legacy applications are highly customised, leading to inflexibility, high management costs, and complexity in integration. Today, software providers advocate minimising configuration and customisation, opting for “out-of-the-box” solutions with room for localisation. The operations in different countries may require reconfiguration due to varying regulations and competitive pressures. Architecting applications to isolate these configurations simplifies system management, facilitating continuous improvement as new services are introduced by platform providers or ISV partners.
Explore the opportunity for emerging technologies. Emerging technologies, notably AI, can significantly enhance the speed and value of new systems. In the near future, AI will automate much of the work in data migration and systems integration, reducing the need for human involvement. When humans are required, low-code or no-code tools can expedite development. Private 5G services may eliminate the need for new network builds in branches or offices. AIOps and Observability can improve system uptime at lower costs. Considering these capabilities in platform decisions and understanding the ecosystem of partners and providers can accelerate modernisation journeys and deliver value faster.
Don’t Let Analysis Paralysis Slow Down Your Journey!
Yes, there are a lot of decisions that need to be made; and yes, there is much at stake if things go wrong! However, there’s a greater risk in not taking action. Maintaining a laser-focus on the customer and business outcomes that need to be achieved will help align many decisions. Keeping the customer experience as the guiding light ensures organisations are always moving in the right direction.

“AI Guardrails” are often used as a method to not only get AI programs on track, but also as a way to accelerate AI investments. Projects and programs that fall within the guardrails should be easy to approve, govern, and manage – whereas those outside of the guardrails require further review by a governance team or approval body. The concept of guardrails is familiar to many tech businesses and are often applied in areas such as cybersecurity, digital initiatives, data analytics, governance, and management.
While guidance on implementing guardrails is common, organisations often leave the task of defining their specifics, including their components and functionalities, to their AI and data teams. To assist with this, Ecosystm has surveyed some leading AI users among our customers to get their insights on the guardrails that can provide added value.
Data Security, Governance, and Bias
- Data Assurance. Has the organisation implemented robust data collection and processing procedures to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and relevance for the purpose of the AI model? This includes addressing issues like missing values, inconsistencies, and outliers.
- Bias Analysis. Does the organisation analyse training data for potential biases – demographic, cultural and so on – that could lead to unfair or discriminatory outputs?
- Bias Mitigation. Is the organisation implementing techniques like debiasing algorithms and diverse data augmentation to mitigate bias in model training?
- Data Security. Does the organisation use strong data security measures to protect sensitive information used in training and running AI models?
- Privacy Compliance. Is the AI opportunity compliant with relevant data privacy regulations (country and industry-specific as well as international standards) when collecting, storing, and utilising data?
Model Development and Explainability
- Explainable AI. Does the model use explainable AI (XAI) techniques to understand and explain how AI models reach their decisions, fostering trust and transparency?
- Fair Algorithms. Are algorithms and models designed with fairness in mind, considering factors like equal opportunity and non-discrimination?
- Rigorous Testing. Does the organisation conduct thorough testing and validation of AI models before deployment, ensuring they perform as intended, are robust to unexpected inputs, and avoid generating harmful outputs?
AI Deployment and Monitoring
- Oversight Accountability. Has the organisation established clear roles and responsibilities for human oversight throughout the AI lifecycle, ensuring human control over critical decisions and mitigation of potential harm?
- Continuous Monitoring. Are there mechanisms to continuously monitor AI systems for performance, bias drift, and unintended consequences, addressing any issues promptly?
- Robust Safety. Can the organisation ensure AI systems are robust and safe, able to handle errors or unexpected situations without causing harm? This includes thorough testing and validation of AI models under diverse conditions before deployment.
- Transparency Disclosure. Is the organisation transparent with stakeholders about AI use, including its limitations, potential risks, and how decisions made by the system are reached?
Other AI Considerations
- Ethical Guidelines. Has the organisation developed and adhered to ethical principles for AI development and use, considering areas like privacy, fairness, accountability, and transparency?
- Legal Compliance. Has the organisation created mechanisms to stay updated on and compliant with relevant legal and regulatory frameworks governing AI development and deployment?
- Public Engagement. What mechanisms are there in place to encourage open discussion and engage with the public regarding the use of AI, addressing concerns and building trust?
- Social Responsibility. Has the organisation considered the environmental and social impact of AI systems, including energy consumption, ecological footprint, and potential societal consequences?
Implementing these guardrails requires a comprehensive approach that includes policy formulation, technical measures, and ongoing oversight. It might take a little longer to set up this capability, but in the mid to longer term, it will allow organisations to accelerate AI implementations and drive a culture of responsible AI use and deployment.

2024 and 2025 are looking good for IT services providers – particularly in Asia Pacific. All types of providers – from IT consultants to managed services VARs and systems integrators – will benefit from a few converging events.
However, amidst increasing demand, service providers are also challenged with cost control measures imposed in organisations – and this is heightened by the challenge of finding and retaining their best people as competition for skills intensifies. Providers that service mid-market clients might find it hard to compete and grow without significant process automation to compensate for the higher employee costs.
Why Organisations are Opting for IT Service
- Organisations are seeking further cost reductions. Managed services providers will see more opportunities to take cost and complexity out of organisation’s IT functions. The focus in 2024 will be less on “managing” services and more on “transforming” them using ML, AI, and automation to reduce cost and improve value.
- Big app upgrades are back on the agenda. SAP is going above and beyond to incentivise their customers and partners to migrate their on-premises and hyperscale hosted instances to true cloud ERP. Initiatives such as Rise with SAP have been further expanded and improved to accelerate the transition. Salesforce customers are also looking to streamline their deployments while also taking advantage of the new AI and data capabilities. But many of these projects will still be complex and time-consuming.
- Cloud deployments are getting more complex. For many organisations, the simple cloud migrations are done. This is the stage of replatforming, retiring, and refactoring applications to take advantage of public and hybrid cloud capabilities. These are not simple lift and shift – or switch to SaaS – engagements.
- AI will drive a greater need for process improvement and transformation. This will happen along with associated change management and training programs. While it is still early days for GenAI, before the end of 2024, many organisations will move beyond experimentation to department or enterprise wide GenAI initiatives.
- Increasing cybersecurity and data governance demands will prolong the security skill shortage. More organisations will turn to managed security services providers and cybersecurity consultants to help them develop their strategy and response to the rising threat levels.
Choosing the Right Cost Model for IT Services
Buyers of IT services must implement strict cost-control measures and consider various approaches to align costs with business and customer outcomes, including different cost models:
Fixed-Price Contracts. These contracts set a firm price for the entire project or specific deliverables. Ideal when project scope is clear, they offer budget certainty upfront but demand detailed specifications, potentially leading to higher initial quotes due to the provider assuming more risk.
Time and Materials (T&M) Contracts with Caps. Payment is based on actual time and materials used, with negotiated caps to prevent budget overruns. Combining flexibility with cost predictability, this model offers some control over total expenses.
Performance-Based Pricing. Fees are tied to service provider performance, incentivising achievement of specific KPIs or milestones. This aligns provider interests with client goals, potentially resulting in cost savings and improved service quality.
Retainer Agreements with Scope Limits. Recurring fees are paid for ongoing services, with defined limits on work scope or hours within a given period. This arrangement ensures resource availability while containing expenses, particularly suitable for ongoing support services.
Other Strategies for Cost Efficiency and Effective Management
Technology leaders should also consider implementing some of the following strategies:
Phased Payments. Structuring payments in phases, tied to the completion of project milestones, helps manage cash flow and provides a financial incentive for the service provider to meet deadlines and deliverables. It also allows for regular financial reviews and adjustments if the project scope changes.
Cost Transparency and Itemisation. Detailed billing that itemises the costs of labour, materials, and other expenses provides transparency to verify charges, track spending against the budget, and identify areas for potential savings.
Volume Discounts and Negotiated Rates. Negotiating volume discounts or preferential rates for long-term or large-scale engagements, makes providers to offer reduced rates for a commitment to a certain volume of work or an extended contract duration.
Utilisation of Shared Services or Cloud Solutions. Opting for shared or cloud-based solutions where feasible, offers economies of scale and reduces the need for expensive, dedicated infrastructure and resources.
Regular Review and Adjustment. Conducting regular reviews of the services and expenses with the provider to ensure alignment with the budget and objectives, prepares organisations to adjust the scope, renegotiate terms, or implement cost-saving measures as needed.
Exit Strategy. Planning an exit strategy that include provisions for contract termination, transition services, protects an organisation in case the partnership needs to be dissolved.
Conclusion
Many businesses swing between insourcing and outsourcing technology capabilities – with the recent trend moving towards insourcing development and outsourcing infrastructure to the public cloud. But 2024 will see demand for all types of IT services across nearly every geography and industry. Tech services providers can bring significant value to your business – but improved management, monitoring, and governance will ensure that this value is delivered at a fair cost.

The tech industry tends to move in waves, driven by the significant, disruptive changes in technology, such as cloud and smartphones. Sometimes, it is driven by external events that bring tech buyers into sync – such as Y2K and the more recent pandemic. Some tech providers, such as SAP and Microsoft, are big enough to create their own industry waves. The two primary factors shaping the current tech landscape are AI and the consequential layoffs triggered by AI advancements.
While many of the AI startups have been around for over five years, this will be the year they emerge as legitimate solutions providers to organisations. Amidst the acceleration of AI-driven layoffs, individuals from these startups will go on to start new companies, creating the next round of startups that will add value to businesses in the future.
Tech Sourcing Strategies Need to Change
The increase in startups implies a change in the way businesses manage and source their tech solutions. Many organisations are trying to reduce tech debt, by typically consolidating the number of providers and tech platforms. However, leveraging the numerous AI capabilities may mean looking beyond current providers towards some of the many AI startups that are emerging in the region and globally.
The ripple effect of these decisions is significant. If organisations opt to enhance the complexity of their technology architecture and increase the number of vendors under management, the business case must be watertight. There will be less of the trial-and-error approach towards AI from 2023, with a heightened emphasis on clear and measurable value.
AI Startups Worth Monitoring
Here is a selection of AI startups that are already starting to make waves across Asia Pacific and the globe.
- ADVANCE.AI provides digital transformation, fraud prevention, and process automation solutions for enterprise clients. The company offers services in security and compliance, digital identity verification, and biometric solutions. They partner with over 1,000 enterprise clients across Southeast Asia and India across sectors, such as Banking, Fintech, Retail, and eCommerce.
- Megvii is a technology company based in China that specialises in AI, particularly deep learning. The company offers full-stack solutions integrating algorithms, software, hardware, and AI-empowered IoT devices. Products include facial recognition software, image recognition, and deep learning technology for applications such as consumer IoT, city IoT, and supply chain IoT.
- I’mCloud is based in South Korea and specialises in AI, big data, and cloud storage solutions. The company has become a significant player in the AI and big data industry in South Korea. They offer high-quality AI-powered chatbots, including for call centres and interactive educational services.
- H2O.ai provides an AI platform, the H2O AI Cloud, to help businesses, government entities, non-profits, and academic institutions create, deploy, monitor, and share data models or AI applications for various use cases. The platform offers automated machine learning capabilities powered by H2O-3, H2O Hydrogen Torch, and Driverless AI, and is designed to help organisations work more efficiently on their AI projects.
- Frame AI provides an AI-powered customer intelligence platform. The software analyses human interactions and uses AI to understand the driving factors of business outcomes within customer service. It aims to assist executives in making real-time decisions about the customer experience by combining data about customer interactions across various platforms, such as helpdesks, contact centres, and CRM transcripts.
- Uizard offers a rapid, AI-powered UI design tool for designing wireframes, mockups, and prototypes in minutes. The company’s mission is to democratise design and empower non-designers to build digital, interactive products. Uizard’s AI features allow users to generate UI designs from text prompts, convert hand-drawn sketches into wireframes, and transform screenshots into editable designs.
- Moveworks provides an AI platform that is designed to automate employee support. The platform helps employees to automate tasks, find information, query data, receive notifications, and create content across multiple business applications.
- Tome develops a storytelling tool designed to reduce the time required for creating slides. The company’s online platform creates or emphasises points with narration or adds interactive embeds with live data or content from anywhere on the web, 3D renderings, and prototypes.
- Jasper is an AI writing tool designed to assist in generating marketing copy, such as blog posts, product descriptions, company bios, ad copy, and social media captions. It offers features such as text and image AI generation, integration with Grammarly and other Chrome extensions, revision history, auto-save, document sharing, multi-user login, and a plagiarism checker.
- Eightfold AI provides an AI-powered Talent Intelligence Platform to help organisations recruit, retain, and grow a diverse global workforce. The platform uses AI to match the right people to the right projects, based on their skills, potential, and learning ability, enabling organisations to make informed talent decisions. They also offer solutions for diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI), skills intelligence, and governance, among others.
- Arthur provides a centralised platform for model monitoring. The company’s platform is model and platform agnostic, and monitors machine learning models to ensure they deliver accurate, transparent, and fair results. They also offer services for explainability and bias mitigation.
- DNSFilter is a cloud-based, AI-driven content filtering and threat protection service, that can be deployed and configured within minutes, requiring no software installation.
- Spot AI specialises in building a modern AI Camera System to create safer workplaces and smarter operations for every organisation. The company’s AI Camera System combines cloud and edge computing to make video footage actionable, allowing customers to instantly surface and resolve problems. They offer intelligent video recorders, IP cameras, cloud dashboards, and advanced AI alerts to proactively deliver insights without the need to manually review video footage.
- People.ai is an AI-powered revenue intelligence platform that helps customers win more revenue by providing sales, RevOps, marketing, enablement, and customer success teams with valuable insights. The company’s platform is designed to speed up complex enterprise sales cycles by engaging the right people in the right accounts, ultimately helping teams to sell more and faster with the same headcount.
These examples highlight a few startups worth considering, but the landscape is rich with innovative options for organisations to explore. Similar to other emerging tech sectors, the AI startup market will undergo consolidation over time, and incumbent providers will continue to improve and innovate their own AI capabilities. Till then, these startups will continue to influence enterprise technology adoption and challenge established providers in the market.

Earlier in the year, Microsoft unveiled its vision for Copilot, a digital companion that aims to provide a unified user experience across Bing, Edge, Microsoft 365, and Windows. This vision includes a consistent user experience. The rollout began with Windows in September and expanded to Microsoft 365 Copilot for enterprise customers this month.
Many organisations across Asia Pacific will soon face the question on whether to invest in Microsoft 365 Copilot – despite its current limitations in supporting all regional languages. Copilot is currently supported in English (US, GB, AU, CA, IN), Japanese, and Chinese Simplified. Microsoft plans to support more languages such as Arabic, Chinese Traditional, Korean and Thai over the first half of 2024. There are still several languages used across Asia Pacific that will not be supported until at least the second half of 2024 or later.
Access to Microsoft 365 Copilot comes with certain prerequisites. Organisations need to have either a Microsoft 365 E3 or E5 license and an Azure Active Directory account. F3 licenses do not currently have access to 365 Copilot. For E3 license holders the cost per user for adding Copilot would nearly double – so it is a significant extra spend and will need to deliver measurable and tangible benefits and a strong business case. It is doubtful whether most organisations will be able to justify this extra spend.
However, Copilot has the potential to significantly enhance the productivity of knowledge workers, saving them many hours each week, with hundreds of use cases already emerging for different industries and user profiles. Microsoft is offering a plethora of information on how to best adopt, deploy, and use Copilot. The key focus when building a business case should revolve around how knowledge workers will use this extra time.
Maximising Copilot Integration: Steps to Drive Adoption and Enhance Productivity
Identifying use cases, building the business proposal, and securing funding for Copilot is only half the battle. Driving the change and ensuring all relevant employees use the new processes will be significantly harder. Consider how employees currently use their productivity tools compared to 15 years ago, with many still relying on the same features and capabilities in their Office suites as they did in earlier versions. In cases where new features were embraced, it typically occurred because knowledge workers didn’t have to make any additional efforts to incorporate them, such as the auto-type ahead functions in email or the seamless integration of Teams calls.
The ability of your organisation to seamlessly integrate Copilot into daily workflows, optimising productivity and efficiency while harnessing AI-generated data and insights for decision-making will be of paramount importance. It will be equally important to be watchful to mitigate potential risks associated with an over-reliance on AI without sufficient oversight.
Implementing Copilot will require some essential steps:
- Training and onboarding. Provide comprehensive training to employees on how to use Copilot’s features within Microsoft 365 applications.
- Integration into daily tasks. Encourage employees to use Copilot for drafting emails, documents, and generating meeting notes to familiarise them with its capabilities.
- Customisation. Tailor Copilot’s settings and suggestions to align with company-specific needs and workflows.
- Automation. Create bots, templates, integrations, and other automation functions for multiple use cases. For example, when users first log onto their PC, they could get a summary of missed emails, chats – without the need to request it.
- Feedback loop. Implement a feedback mechanism to monitor how Copilot is used and to make adjustments based on user experiences.
- Evaluating effectiveness. Gauge how Copilot’s features are enhancing productivity regularly and adjust usage strategies accordingly. Focus on the increased productivity – what knowledge workers now achieve with the time made available by Copilot.
Changing the behaviours of knowledge workers can be challenging – particularly for basic processes that they have been using for years or even decades. Knowledge of use cases and opportunities for Copilot will not just filter across the organisation. Implementing formal training and educational programs and backing them up with refresher courses is important to ensure compliance and productivity gains.