India is undergoing a remarkable transformation across various industries, driven by rapid technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and a dynamic economic landscape. From the integration of new-age technologies like GenAI to the adoption of sustainable practices, industries in India are redefining their operations and strategies to stay competitive and relevant.
Here are some organisations that are leading the way.
Download ‘From Tradition to Innovation: Industry Transformation in India’ as a PDF
Redefining Customer Experience in the Financial Sector
Financial inclusion. India’s largest bank, the State Bank of India, is leading financial inclusion with its YONO app, to enhance accessibility. Initial offerings include five core banking services: cash withdrawals, cash deposits, fund transfers, balance inquiries, and mini statements, with plans to include account opening and social security scheme enrollments.
Customer Experience. ICICI Bank leverages RPA to streamline repetitive tasks, enhancing customer service with its virtual assistant, iPal, for handling queries and transactions. HDFC Bank customer preference insights to offer tailored financial solutions, while Axis Bank embraces a cloud-first strategy to digitise its platform and improve customer interfaces.
Indian banks are also collaborating with fintechs to harness new technologies for better customer experiences. YES Bank has partnered with Paisabazaar to simplify loan applications, and Canara HSBC Life Insurance has teamed up with Artivatic.AI to enhance its insurance processes via an AI-driven platform.
Improving Healthcare Access
Indian healthcare organisations are harnessing technology to enhance efficiency, improve patient experiences, and enable remote care.
Apollo Hospitals has launched an automated patient monitoring system that alerts experts to health deteriorations, enabling timely interventions through remote monitoring. Manipal Hospitals’ video consultation app reduces emergency department pressure by providing medical advice, lab report access, bill payments, appointment bookings, and home healthcare requests, as well as home medication delivery and Fitbit monitoring. Omni Hospitals has also implemented AI-based telemedicine for enhanced patient engagement and remote monitoring.
The government is also driving the improvement of healthcare access. eSanjeevani is the world’s largest government-owned telemedicine system, with the capacity to handle up to a million patients a day.
Driving Retail Agility & Consumer Engagement
India’s Retail sector, the fourth largest globally, contributes over 10% of the nation’s GDP. To stay competitive and meet evolving consumer demands, Indian retailers are rapidly adopting digital technologies, from eCommerce platforms to AI.
Omnichannel Strategies. Reliance Retail integrates physical stores with digital platforms like JioMart to boost sales and customer engagement. Tata CLiQ’s “phygital” approach merges online and offline shopping for greater convenience while Shoppers Stop uses RFID and data analytics for improved in-store experiences, online shopping, and targeted marketing.
Retail AI. Flipkart’s AI-powered shopping assistant, Flippi uses ML for conversational product discovery and intuitive guidance. BigBasket employs IoT-led AI to optimise supply chain and improve product quality.
Reshaping the Automotive Landscape
Tech innovation, from AI/ML to connected vehicle technologies, is revolutionising the Automotive sector. This shift towards software-defined vehicles and predictive supply chain management underscores the industry’s commitment to efficiency, transparency, safety, and environmental sustainability.
Maruti Suzuki’s multi-pronged approach includes collaborating with over 60 startups through its MAIL program and engaging Accenture to drive tech change. Maruti has digitised 24 out of 26 customer touchpoints, tracking every interaction to enhance customer service. In the Auto OEM space, they are shifting to software-defined vehicles and operating models.
Tata Motors is leveraging cloud, AI/ML, and IoT to enhancing efficiency, improving safety, and driving sustainability across its operations. Key initiatives include connected vehicles, automated driving, dealer management, cybersecurity, electric powertrains, sustainability, and supply chain optimisation.
Streamlining India’s Logistics Sector
India’s logistics industry is on the cusp of a digital revolution as it embraces cutting-edge technologies to streamline processes and reduce environmental impact.
Automation and Predictive Analytics. Automation is transforming warehousing operations in India, with DHL India automating sortation centres to handle 6,000 shipments per hour. Predictive analytics is reshaping logistics decision-making, with Delhivery optimising delivery routes to ensure timely service.
Sustainable Practices. The logistics sector contributes one-third of global carbon emissions. To combat this, Amazon India will convert its delivery fleet to 100% EVs by 2030 to reduce emissions and fuel costs. Blue Energy Motors is also producing 10,000 heavy-duty LNG trucks annually for zero-emission logistics.

The rapid adoption of technology in India is driving a surge in demand for AI solutions across sectors like finance, education, healthcare, and agriculture. AI is revolutionising these industries by making services more efficient, personalised, and accessible. This growing dependence on AI has created a fertile ground for innovation, propelling India’s emergence as a global hub for AI startups. With over 6,200 AI startups operating in the country, India offers a dynamic and challenging landscape for entrepreneurs seeking to make a meaningful impact.
Fuelling AI Innovation: India’s Strategic Investment
Earlier this year, the government allocated USD 1.3 billion for the India AI Mission, solidifying its commitment to AI. This comprehensive program is designed to catalyse the AI innovation ecosystem within the country. At the heart of this ecosystem’s development lies the expansion of compute infrastructure, a critical resource for AI startups. By providing access to powerful computing resources, the India AI Mission is empowering startups to scale their solutions and compete on a global level.
Beyond infrastructure, the initiative focuses on fostering collaborations between academia, industry, and startups to drive R&D. By creating a supportive environment that promotes knowledge sharing and resource accessibility, the India AI Mission aims to position India as a leader in the AI landscape.
A Spotlight on Indian Startups
Driving Industry Innovation
Healthcare. India’s vibrant AI startup ecosystem is driving innovation in healthcare, with companies leveraging AI to address critical challenges and improve patient outcomes.
- Cancer-Focused AI Startups. Several startups are revolutionising cancer care with AI-driven innovations. Niramai, globally recognised for its innovation, uses AI and thermal imaging for early breast cancer detection, particularly effective in younger women and dense breast tissue. Onward Assist provides predictive analytics for oncology, helping oncologists manage patient data and improve the accuracy of cancer care decisions. Similarly, Atom360 focuses on oral cancer screening with an AI-powered app that offers quick, affordable access to critical information, enhancing oral healthcare in underserved areas.
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Solutions. AI is significantly advancing diagnostics, enhancing accuracy, and reducing misdiagnosis. SigTuple develops AI-driven diagnostic solutions for medical imaging and pathology, improving accuracy and efficiency in disease detection. Endimension Technology, incubated at IIT Bombay, develops algorithms for detecting abnormalities in medical scans, aiming to reduce misdiagnosis and radiologist workload. Tricog Health delivers AI solutions for rapid heart attack diagnosis, reducing diagnosis time and improving outcomes, especially in underserved regions.
Financial Services. Fintechs have been at the forefront of AI-led innovations, offering innovative solutions for insurance, lending, and microfinance. Artivatic uses AI to transform traditional insurance systems into digital, personalised offerings, making coverage more accessible and affordable for a broader range of consumers. ZestMoney leverages AI for digital lending, providing credit to individuals without a credit history through easy EMI plans, and enhancing financial access. Meanwhile, mPokket offers instant micro-loans to students and young professionals, addressing short-term financial needs with flexible loan options and minimal documentation.
Other Industries. Beyond healthcare and financial services, AI startups are driving innovation across various industries, tackling critical challenges. Entropik uses AI to analyse human emotions and behaviour, helping businesses gain deeper insights into consumer preferences for market research and optimising user experiences. In agriculture, Intello Labs applies AI and computer vision to assess the quality of fresh produce, reducing food waste and improving supply chain efficiency. Similarly, AgNext enhances food value chains by offering AI-driven, real-time quality assessments through its SaaS platform, promoting safety and transparency in agribusiness.
Transforming Businesses
Technology for Security & Fraud. AI startups are offering innovative solutions tailored to organisations’ needs. SpoofSense combats deepfakes and identity fraud with advanced facial liveness detection, ensuring secure user verification by distinguishing between real users and spoofed images. Eagle Eye Networks provides cloud-based video surveillance solutions, using AI to offer real-time monitoring and analytics. In the e-commerce space, ThirdWatch uses AI to detect and prevent fraud in real-time by analysing user behaviour and transaction patterns, reducing financial losses for online retailers.
Tech Development. AI startups are empowering organisations to accelerate innovation and enhance productivity. Haptik helps businesses build intelligent virtual assistants, powering chatbots and voice bots across industries to improve customer engagement. DhiWise automates the development process, enabling faster app creation by converting designs into code. Additionally, Fluid AI provides advanced AI solutions like predictive analytics and natural language processing for sectors like finance, retail, and healthcare. Mihup enhances contact centre performance with its conversation intelligence platform, while Yellow.ai enables enterprises to automate customer engagement through its GenAI-powered platform, creating seamless and scalable customer service experiences.
Empowering People
AI startups are empowering individuals by providing personalised services that enhance learning, creativity, and financial management. SuperKalam and ZuAI offer students tailored learning experiences, using AI to create interactive lessons and assessments that adapt to individual learning styles, improving student engagement and outcomes. For creative professionals, Mugafi combines AI with human mentoring to assist writers in generating ideas and developing scripts, enabling them to create intellectual property with greater efficiency. Wright Research empowers individuals to make informed financial decisions through AI-powered investment advice, while Vahan simplifies job searches for blue-collar workers by using AI to match candidates with suitable employment opportunities via WhatsApp.
Promoting ESG
AI startups are driving meaningful change by optimising processes and creating economic opportunities. Ossus Biorenewables enhances biofuel production through AI, reducing waste and increasing efficiency in renewable energy generation, while Ishitva Robotic Systems promotes sustainability by automating waste sorting and recycling, contributing to a more efficient and circular economy. Karya connects rural workers with digital tasks, offering fair wages and skills development by matching them to tasks suited to their abilities using machine learning. In agriculture, KissanAI helps farmers improve crop yields and manage resources effectively through personalised, data-driven recommendations. ElasticRun improves last-mile delivery logistics in rural areas, enabling businesses to reach underserved markets.
Conclusion
Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang noted India’s potential to become the “largest exporter of AI,” signalling vast global opportunities. India’s AI startups are at the forefront of innovation but face hurdles such as fierce competition for skilled talent, navigating complex regulations, and securing funding. With strategic focus on these challenges and the backing of initiatives like Digital India and Startup India, India’s AI ecosystem can seize emerging market opportunities, accelerate tech advancements, and make a substantial impact on the global AI landscape.

Ecosystm research reveals that organisations in India are preparing to adopt emerging technologies driven by the Digital India movement. However, enterprise tech teams are grappling with challenges in their data and AI strategies, resource optimisation, and security threats.

India’s digital journey has been nothing short of remarkable, driven by a robust Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) framework known as the India Stack. Over the past decade, the government, in collaboration with public and private entities, has built this digital ecosystem to empower citizens, improve governance, and foster economic growth.
The India Stack is a set of open APIs and platforms that provide a foundation for large-scale public service delivery and innovation. It enables governments, businesses, startups, and developers to leverage technology to offer services to millions of Indians, especially those in underserved areas.
The India Stack is viewed as a layered infrastructure, addressing identity, payments, data, and services.
Click here to download The India Stack: A Foundation for Digital India as a PDF
Four Pillars of the Digital Stack
The four layers of India Stack include:
- Presenceless Layer. Aadhaar enables remote authentication, providing a digital ID that requires only a 12-digit number and a fingerprint or iris scan, eliminating the need for physical documents. It prevents duplicate and fake identities.
- Paperless Layer. Reliance on digital records, using Aadhaar eKYC, eSign, and Digital Locker. It enables secure digital storage and retrieval, creating a paperless system for verifying and accessing documents anytime, on any device.
- Cashless Layer. Led by NPCI, this aims to universalise digital payments. UPI enables instant, secure money transfers between bank accounts using a simple Virtual Payment Address (VPA), moving transactions into the digital age for transparency and ease of use.
- Consent Layer. Enables secure, user-controlled data sharing through electronic consent, allowing data to flow freely. The Account Aggregator ecosystem benefits most, with AA acting as a thin data aggregation layer between Financial Information Providers (FIPs) and Financial Information Users (FIUs).
The Impact of the India Stack
The India Stack has played a pivotal role in the country’s rapid digitalisation:
Financial Inclusion. Aadhaar-enabled payment systems (AePS) and UPI have significantly expanded financial access, increasing inclusion from 25% in 2008 to 80% in 2024, particularly benefiting rural and underserved communities.
Boost to Digital Payments. The India Stack has fuelled exponential growth in digital payments, with UPI processing 10 billion monthly transactions. This has driven the rise of digital wallets, fintech platforms, and digitisation of small businesses.
Better Government Services. Aadhaar authentication has improved the delivery of government schemes like Direct Benefit Transfers (DBTs), Public Distribution System (PDS), and pensions, ensuring transparency and reducing leakages.
The India Stack: A Catalyst for Startup Success
The India Stack is fuelling startup innovation by providing a robust digital infrastructure. It enables entrepreneurs to build services like digital payments, eCommerce, and financial solutions for underserved populations. Platforms such as Aadhaar and UPI have paved the way for businesses to offer secure, seamless transactions, allowing startups like Paytm and BharatPe to thrive. These innovations are driving financial inclusion, empowering rural entrepreneurs, and creating opportunities in sectors like lending and healthtech, supported by global and domestic investments.

From Local Success to Global Inspiration
The impact of the India Stack’s success is being felt worldwide. Global giants such as Google Pay, WhatsApp, and Amazon Pay are drawing inspiration from it to enhance their global payment systems. Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai plans to apply lessons from Google Pay’s Indian experience to other markets.
While India Stack has achieved significant success, there is still room for improvement. Strengthening data privacy and security is crucial as personal data collection continues to expand. The Digital Personal Data Protection Act aims to address these issues, but balancing innovation with privacy protection remains a challenge.
Bridging the digital divide by expanding Internet access and improving digital literacy, especially for rural and older populations, is key to ensuring that everyone can benefit from the India Stack’s advantages.

At a recently held Ecosystm roundtable, in partnership with Qlik and 121Connects, Ecosystm Principal Advisor Manoj Chugh, moderated a conversation where Indian tech and data leaders discussed building trust in data strategies. They explored ways to automate data pipelines and improve governance to drive better decisions and business outcomes. Here are the key takeaways from the session.

Data isn’t just a byproduct anymore; it’s the lifeblood of modern businesses, fuelling informed decisions and strategic growth. But with vast amounts of data, the challenge isn’t just managing it; it’s building trust. AI, once a beacon of hope, is now at risk without a reliable data foundation. Ecosystm research reveals that a staggering 66% of Indian tech leaders doubt their organisation’s data quality, and the problem of data silos is exacerbating this trust crisis.
At the Leaders Roundtable in Mumbai, I had the opportunity to moderate a discussion among data and digital leaders on the critical components of building trust in data and leveraging it to drive business value. The consensus was that building trust requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses the complexities of data management and positions the organisation for future success. Here are the key strategies that are essential for achieving these goals.
1. Adopting a Unified Data Approach
Organisations are facing a growing wave of complex workloads and business initiatives. To manage this expansion, IT teams are turning to multi-cloud, SaaS, and hybrid environments. However, this diverse landscape introduces new challenges, such as data silos, security vulnerabilities, and difficulties in ensuring interoperability between systems.

A unified data strategy is crucial to overcome these challenges. By ensuring platform consistency, robust security, and seamless data integration, organisations can simplify data management, enhance security, and align with business goals – driving informed decisions, innovation, and long-term success.
Real-time data integration is essential for timely data availability, enabling organisations to make data-driven decisions quickly and effectively. By integrating data from various sources in real-time, businesses can gain valuable insights into their operations, identify trends, and respond to changing market conditions.
Organisations that are able to integrate their IT and operational technology (OT) systems find their data accuracy increasing. By combining IT’s digital data management expertise with OT’s real-time operational insights, organisations can ensure more accurate, timely, and actionable data. This integration enables continuous monitoring and analysis of operational data, leading to faster identification of errors, more precise decision-making, and optimised processes.
2. Enhancing Data Quality with Automation and Collaboration
As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, ensuring high data quality is essential for organisations to make accurate decisions and to drive trust in data-driven solutions. Automated data quality tools are useful for cleansing and standardising data to eliminate errors and inconsistencies.

As mentioned earlier, integrating IT and OT systems can help organisations improve operational efficiency and resilience. By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can identify bottlenecks, optimise workflows, and proactively address potential issues before they escalate. This can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and improved customer satisfaction.
However, while automation technologies can help, organisations must also invest in training employees in data management, data visualisation, and data governance.
3. Modernising Data Infrastructure for Agility and Innovation
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, agility is paramount. Modernising data infrastructure is essential to remain competitive – the right digital infrastructure focuses on optimising costs, boosting capacity and agility, and maximising data leverage, all while safeguarding the organisation from cyber threats. This involves migrating data lakes and warehouses to cloud platforms and adopting advanced analytics tools. However, modernisation efforts must be aligned with specific business goals, such as enhancing customer experiences, optimising operations, or driving innovation. A well-modernised data environment not only improves agility but also lays the foundation for future innovations.

Technology leaders must assess whether their data architecture supports the organisation’s evolving data requirements, considering factors such as data flows, necessary management systems, processing operations, and AI applications. The ideal data architecture should be tailored to the organisation’s specific needs, considering current and future data demands, available skills, costs, and scalability.
4. Strengthening Data Governance with a Structured Approach
Data governance is crucial for establishing trust in data, and providing a framework to manage its quality, integrity, and security throughout its lifecycle. By setting clear policies and processes, organisations can build confidence in their data, support informed decision-making, and foster stakeholder trust.
A key component of data governance is data lineage – the ability to trace the history and transformation of data from its source to its final use. Understanding this journey helps organisations verify data accuracy and integrity, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies, improve data quality by proactively addressing issues, and enhance decision-making through context and transparency.
A tiered data governance structure, with strategic oversight at the executive level and operational tasks managed by dedicated data governance councils, ensures that data governance aligns with broader organisational goals and is implemented effectively.
Are You Ready for the Future of AI?
The ultimate goal of your data management and discovery mechanisms is to ensure that you are advancing at pace with the industry. The analytics landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, promising to revolutionise how organisations interact with data. A key innovation, the data fabric, is enabling organisations to analyse unstructured data, where the true value often lies, resulting in cleaner and more reliable data models.

GenAI has emerged as another game-changer, empowering employees across the organisation to become citizen data scientists. This democratisation of data analytics allows for a broader range of insights and fosters a more data-driven culture. Organisations can leverage GenAI to automate tasks, generate new ideas, and uncover hidden patterns in their data.
The shift from traditional dashboards to real-time conversational tools is also reshaping how data insights are delivered and acted upon. These tools enable users to ask questions in natural language, receiving immediate and relevant answers based on the underlying data. This conversational approach makes data more accessible and actionable, empowering employees to make data-driven decisions at all levels of the organisation.
To fully capitalise on these advancements, organisations need to reassess their AI/ML strategies. By ensuring that their tech initiatives align with their broader business objectives and deliver tangible returns on investment, organisations can unlock the full potential of data-driven insights and gain a competitive edge. It is equally important to build trust in AI initiatives, through a strong data foundation. This involves ensuring data quality, accuracy, and consistency, as well as implementing robust data governance practices. A solid data foundation provides the necessary groundwork for AI and GenAI models to deliver reliable and valuable insights.

India’s digital economy is on a meteoric rise, expected to reach USD 1 trillion by 2025. This surge in digital activity is fuelling the rapid expansion of its data centre market, positioning the country as a global player. With a projected market value of USD 4.5 billion by 2025, India’s data centre industry is set to surpass traditional regional hubs like Malaysia, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
This growth is driven by factors such as the proliferation of smartphones, internet connectivity, and digital services, generating massive amounts of data that need storage and processing. Government initiatives like Digital India and the National e-Governance Plan have promoted digitalisation, while favourable market conditions, including cost-effective infrastructure, skilled talent, and a large domestic market, make India an attractive destination for data centre investments.
As companies continue to invest, India is solidifying its role as a critical hub for Asia’s digital revolution, driving economic development and creating new opportunities for innovation and job creation.
What is Fuelling India’s Data Centre Growth?
India’s data centre industry is experiencing rapid growth in 2024, driven by a combination of strategic advantages and increasing demand. The country’s abundance of land and skilled workforce are key factors contributing to this boom.
- Digitisation push. The digital revolution is fueling the need for more sophisticated data centre infrastructure. The rise of social media, online gaming, and streaming apps has created a surge in demand for faster networks, better data storage options, and increased data centre services.
- Internet and mobile penetration. With 1.1 billion mobile phone subscribers, Indians use an average of 8.3 GB of data per month. As more people come online, businesses need to expand their data infrastructure to handle increased traffic, enhance service delivery, and support a growing digital economy.
- Increasing tech adoption. India’s AI market is projected to reach around USD 17 billion by 2027. As businesses integrate AI, IoT, cloud, and other technologies, data centres will become instrumental in supporting the vast computational and storage requirements.
- Government & regulatory measures. Apart from India being one of the world’s largest data consumption economies, government initiatives have also accelerated the ‘data based’ environment in the country. Additionally, states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu have implemented favourable real estate policies that reduce the costs of setting up data centres.
A Growing Network of Hubs
India’s data centre landscape is rapidly evolving, with major cities and emerging hotspots vying for a piece of the pie.
Mumbai-Navi Mumbai remains the undisputed leader, boasting a combined 39 data centres. Its strategic location with excellent submarine cable connectivity to Europe and Southeast Asia makes it a prime destination for global and domestic players.
Bangalore, India’s IT capital, is not far behind with 29 data centres. The city’s thriving tech ecosystem and skilled talent pool make it an attractive option for businesses looking to set up data centres.
Chennai, located on the east coast, has emerged as a crucial hub with 17 data centres. Its proximity to Southeast Asia and growing digital economy make it a strategic location. The Delhi-NCR region also plays a significant role, with 27 data centres serving the capital and surrounding areas.
Smaller cities like Pune, Jaipur, and Patna are rapidly emerging as data centre hotspots. As businesses seek to serve a growing but distributed user base across India, these cities offer more cost-effective options. Additionally, the rise of edge data centres in these smaller cities is further decentralising the data centre landscape.

A Competitive Market
India ranks 13th globally in the number of operational data centres, with 138 facilities in operation and an additional 45 expected to be completed by the end of 2025. Key initiatives include:
- AWS. AWS is investing USD 12.7 billion to establish four new data centres over the next two years.
- Meta. Meta is set to build a small data centre, potentially focused on cache with a 10-20 MW capacity.
- AdaniConnex. In partnership with EdgeConneX, AdaniConnex aims to develop a 1 GW network of hyperscale data centres over the next decade, all powered by 100% renewable energy.
- Google. Google is set to build an 80-storey data centre by 2025 and is in advanced talks to acquire a 22.5-acre land parcel for its first captive data centre.
- NTT. NTT is investing USD 241 million in a data campus, which will feature three data centres.
Data Centres: Driving Digital India’s Success
The Digital India initiative has transformed government services through improved online infrastructure and increased connectivity. Data centres play a pivotal role in supporting this vision by managing, storing, and processing the vast amounts of data that power essential services like Aadhaar and BharatNet.
Aadhaar, India’s biometric ID system, relies heavily on data centres to store and process biometric information, enabling seamless identification and authentication. BharatNet, the government’s ambitious project to connect rural areas with high-speed internet, also depends on data centres to provide the necessary infrastructure and support.
The impact of data centres on India’s digital transformation is far-reaching. Here are some key areas where data centres have made a significant contribution:
- Enabling Remote Work and Education. Data centres have been instrumental in supporting the surge in remote work and online learning during the pandemic. By providing the necessary infrastructure and connectivity, data centres have ensured business continuity and uninterrupted education.
- Fostering Start-Up Innovation. Data centres provide the essential infrastructure for start-ups to thrive. By offering reliable and scalable computing resources, data centres enable rapid growth and innovation, contributing to the expansion of India’s SaaS market.
- Supporting Government Services. Data centres underpin key government initiatives, including e-governance platforms and digital identity systems. They enhance the accessibility, transparency, and efficiency of government services, bridging the urban-rural divide and improving public service delivery.
Securing India’s Data Centre Future
Data centres are the backbone of India’s digital transformation, fuelling economic growth, government services, innovation, remote work, and technological progress. The Indian government’s ambitious plan to invest over USD 1 billion in hyperscale data centres over the next five years underscores the country’s commitment to building a robust digital infrastructure.
To secure the long-term success of India’s data centre industry, alignment with global standards and strategic investment are crucial. Prioritising reliability, efficiency, and sustainability will attract global providers and position India as a prime destination for digital infrastructure investments. Addressing challenges like legacy upgrades, modernisation, and cybersecurity risks will require collaboration across stakeholders, with government support and technological innovation playing key roles.
A unified effort from central and state governments is vital to enhance competitiveness. By fostering a favourable regulatory environment and offering incentives, the government can accelerate the development of world-class data centres. As India advances digitally, data centres will be instrumental in driving economic growth, improving quality of life, and solidifying India’s status as a global digital leader.

Chris White, Vice President, Marketing & Communities, Ecosystm and Anthony Johnston, Co-Founder and General Manager of CoVentured, discuss the exciting acquisition of CoVentured by Ecosystm in June 2024.
Learn how CoVentured’s AI-enabled technology discovery platform and managed services complement Ecosystm’s extensive tech ecosystem expertise to provide unparalleled insights and solutions for corporations, venture builders, and governments worldwide.
Discover how this strategic acquisition will enhance technology discovery, competitive analysis, lead generation, and decision-making processes across sectors and geographies.
Whether you’re a CTO, innovation leader, venture capitalist, or part of an R&D team, find out how Ecosystm and CoVentured can help you navigate the evolving tech landscape and drive growth for your organisation.
Topics Covered:
- Introduction to CoVentured and their Key Offerings
- Use cases for technology discovery and competitive analysis
- Synergies between Ecosystm and CoVentured
- Benefits for clients across various industries and roles
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 4:04 — 1.9MB)
Subscribe Spotify | Amazon Music | JioSaavn | Podchaser | RSS | More
Ecosystm’s Sustainability Technology Guide for Executives, created in partnership with IBM, addresses the pressing issues faced by leaders dedicated to advancing sustainability within their organisations.
The guide tackles crucial aspects such as:
- Identifying Effective Technology Solutions: Discover which technologies can turn sustainability from a concept into concrete achievements.
- Fostering Collaboration: Learn how executives and tech teams can work in unison to integrate sustainability deeply into the company’s ethos and operations.
Key insights include:
- The pivotal role of executive leadership in spearheading sustainability initiatives.
- Strategies for aligning business goals with technological objectives to drive sustainable outcomes.
- A detailed, three-tiered sustainability framework focusing on Strategy, Data, and Operationalisation.
- A practical checklist of sustainability technologies for collaborative review by executives and tech teams.
In an era where climate change demands urgent action, sustainability is no longer just about compliance or image—it’s integral to brand value, business performance, and responsible risk management. Technology is the key enabler in this transformation, allowing organisations to shift from theoretical sustainability to real, actionable results.
This whitepaper emphasises the importance of a strong synergy between executive leadership and technology teams, particularly in the Asia Pacific region. By collaborating effectively, these stakeholders can ensure that sustainability becomes an intrinsic part of their organisation’s identity and operations, driving a greener and more sustainable future with clear governance, measurable outcomes, and strategic action plans.
Download Whitepaper – Sustainability Technology Guide for Executives

(Clicking on this link will take you to the IBM website where you can download the whitepaper)

Over a century ago, the advent of commercial flights marked a pivotal moment in globalisation, shrinking the time-distance between cities and nations. Less than a century later, the first video call foreshadowed a future where conversations could span continents in real time, compressing the space-distance between people.
The world feels smaller, not literally, but in how we experience space and time. Messages that once took days to deliver arrive instantly. Distances between cities are now measured in hours, not miles. A product designed in New York is manufactured in Shenzhen and reaches London shelves within weeks. In essence, things traverse the world with far less friction than it once did.
Welcome to The Immediate Economy!
The gap between desire and fulfilment has narrowed, driven by technology’s speed and convenience. This time-space annihilation has ushered in what we now call The Immediate Economy.
Such transformations haven’t gone unnoticed, at the click of a button is now a native (sort of cliché) expression. Amidst all this innovation, a new type of consumer has emerged – one whose attention is fleeting and easy to lose. Modern consumers have compelled industries, especially retail and ecommerce, to evolve, creating experiences that not only capture but also hold their interest.
Beyond Usability: Crafting a Memorable User Experience
Selling a product is no longer about just the product itself; it’s about the lifestyle, the experience, and the rush of dopamine with every interaction. And it’s all because of technology.
In a podcast interview with the American Psychological Association, Professor Gloria Mark from the University of California, Irvine, revealed a significant decline in attention spans on screens, from 150 seconds in 2004 to 40 seconds in the last five years. Social media platforms have spoiled the modern consumer by curating content that caters instantly to desires. Influence spills into the retail sector, compelling retailers to create experiences matching the immediacy and personalisation people now expect.
Modern consumers require modern retail experiences. Take Whole Foods, and their recent partnership with Amazon’s Dash Cart, transforming the mundane act of grocery shopping into a seamless dance of efficiency. Shoppers can now glide through aisles with carts that tally selections and debit totals directly from their accounts, rendering checkout lines obsolete. It’s more than convenience; it reimagines retail – a choreography of consumerism where every step is both effortless and calculated.
Whole Foods can analyse data from their Dash Cart technology to gain valuable insights into shopping patterns. The Immediate Economy revolutionises retail, transforming it into a hyper-efficient, personalised experience.
Retail’s new Reality: The Rise of Experiential Shopping
Just as Netflix queues up a binge-worthy series; retailers create shopping experiences as engaging and addictive as your favourite shows.
It’s been a financially rough year for Nike, but that hasn’t stopped them from expanding their immersive retail experience. Nike’s “House of Innovation” leverages 3D holographic tech. Customers can inspect intricate details of sneakers, including the texture of the fabric, the design of the laces, and the construction of the sole. The holographic display can also adjust to different lighting conditions and present the sneaker in various colours, providing a truly immersive and personalised shopping experience.
Fashion commerce platforms like Farfetch are among many integrating Virtual Try-On (VTO) technology. Leveraging the camera and sensors of customer devices, their AR technology overlays a digital image of a handbag onto a live view of a customer, enabling them to see how different styles and sizes would look on you. This approach to ecommerce enhances experiences, elevating interaction.
The 3D holographic display and the AR tech, are unique and visually appealing ways to showcase products, allowing customers to interact with products in a way that is not possible with traditional displays. Each shopping trip feels like the next episode of retail therapy.
The Evolution of Shopptertainment
The bar for quick content consumption is higher than ever thanks to platforms like TikTok and Instagram.
A prime example of this trend is Styl, a tech startup from two Duke students, with their “Tinder for shopping” application. Styl offers a swipeable interface for discovering and purchasing fashion items, seamlessly integrating the convenience and engagement of social media into the retail experience.
Styl goes beyond a simple swipe. By leveraging AI algorithms, it learns your preferences and curates a personalised feed of clothing items that align with your taste. Streamlining the shopping process, they deliver a tailored experience that caters to the modern consumer’s desire for convenience and personalisation.
Interestingly, Styl isn’t even a retail company; it pools items from websites, redirecting the users with relevant interest. They combine ecommerce with AI, creating the ultimate shopping experience for today’s customer. It’s fast, customised, and changing the way we shop.
Styl is not the first ones to do this, Instagram and TikTok provide individualised suggestions within their marketplace. But they differ by selling an experience, a vibe. That’s what sets them apart.
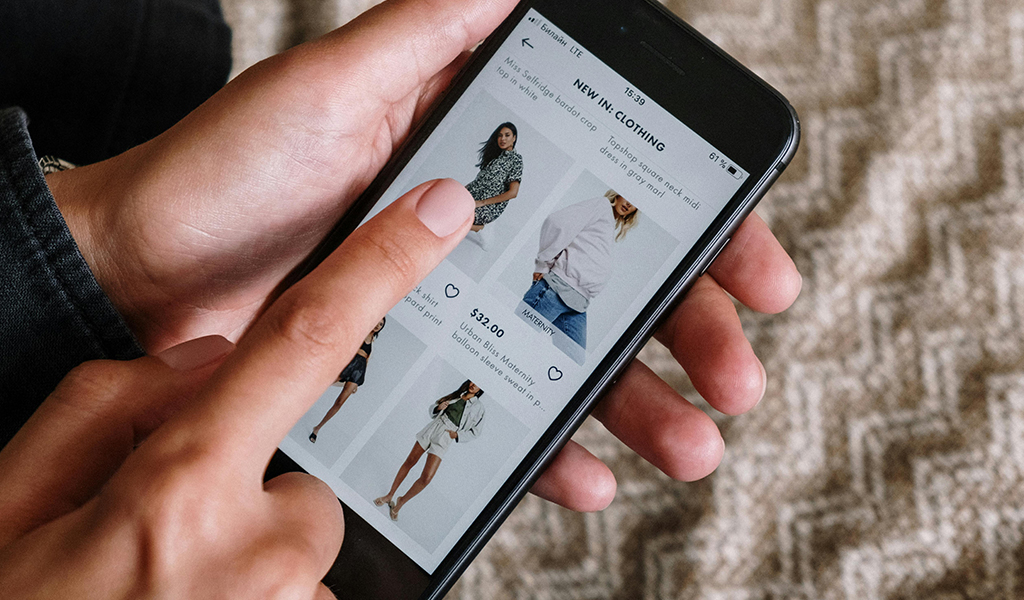
Tech-Powered Retail: The Heart of the Immediate Economy
History is filled with examples of societal innovation, but the Immediate Economy is transforming retail in exciting ways. In the 21st century, technology is both the catalyst and the consequence of the retail industry transformation. It began by capturing and fragmenting the average consumer’s attention, and now it’s reshaping consumer-brand relationships.
Today’s consumers crave personalised shopping. Whole Foods, with its AI-driven Dash Carts, is redefining convenience. Nike and Farfetch, through immersive AR and 3D tech, is making shopping an interactive adventure. Meanwhile, startups like Styl are leveraging AI to bring personalized fashion choices directly to consumers’ smartphones. The world is shrinking, not just in miles, but in the milliseconds it takes to satisfy a desire. From the aisles of Whole Foods to the virtual showrooms of Farfetch, The Immediate Economy offers an immersive world, where time and space bend to technology’s will, and instant gratification is no longer a perk; it’s an expectation. The Immediate Economy is here, and it’s changing how we interact with the world around us. Welcome to the future of retail, and everything else.



























