As tech providers such as Microsoft enhance their capabilities and products, they will impact business processes and technology skills, and influence other tech providers to reshape their product and service offerings. Microsoft recently organised briefing sessions in Sydney and Singapore, to present their future roadmap, with a focus on their AI capabilities.

Ecosystm Advisors Achim Granzen, Peter Carr, and Tim Sheedy provide insights on Microsoft’s recent announcements and messaging.

Click here to download Ecosystm VendorSphere: Microsoft’s AI Vision – Initiatives & Impact
Ecosystm Question: What are your thoughts on Microsoft Copilot?
Tim Sheedy. The future of GenAI will not be about single LLMs getting bigger and better – it will be about the use of multiple large and small language models working together to solve specific challenges. It is wasteful to use a large and complex LLM to solve a problem that is simpler. Getting these models to work together will be key to solving industry and use case specific business and customer challenges in the future. Microsoft is already doing this with Microsoft 365 Copilot.
Achim Granzen. Microsoft’s Copilot – a shrink-wrapped GenAI tool based on OpenAI – has become a mainstream product. Microsoft has made it available to their enterprise clients in multiple ways: for personal productivity in Microsoft 365, for enterprise applications in Dynamics 365, for developers in Github and Copilot Studio, and to partners to integrate Copilot into their applications suites (E.g. Amdocs’ Customer Engagement Platform).
Ecosystm Question: How, in your opinion, is the Microsoft Copilot a game changer?
Microsoft’s Customer Copyright Commitment, initially launched as Copilot Copyright Commitment, is the true game changer.
Achim Granzen. It safeguards Copilot users from potential copyright infringement lawsuits related to data used for algorithm training or output results. In November 2023, Microsoft expanded its scope to cover commercial usage of their OpenAI interface as well.
This move not only protects commercial clients using Microsoft’s GenAI products but also extends to any GenAI solutions built by their clients. This initiative significantly reduces a key risk associated with GenAI adoption, outlined in the product terms and conditions.
However, compliance with a set of Required Mitigations and Codes of Conduct is necessary for clients to benefit from this commitment, aligning with responsible AI guidelines and best practices.
Ecosystm Question: Where will organisations need most help on their AI journeys?
Peter Carr. Unfortunately, there is no playbook for AI.
- The path to integrating AI into business strategies and operations lacks a one-size-fits-all guide. Organisations will have to navigate uncharted territories for the time being. This means experimenting with AI applications and learning from successes and failures. This exploratory approach is crucial for leveraging AI’s potential while adapting to unique organisational challenges and opportunities. So, companies that are better at agile innovation will do better in the short term.
- The effectiveness of AI is deeply tied to the availability and quality of connected data. AI systems require extensive datasets to learn and make informed decisions. Ensuring data is accessible, clean, and integrated is fundamental for AI to accurately analyse trends, predict outcomes, and drive intelligent automation across various applications.
Ecosystm Question: What advice would you give organisations adopting AI?
Tim Sheedy. It is all about opportunities and responsibility.
- There is a strong need for responsible AI – at a global level, at a country level, at an industry level and at an organisational level. Microsoft (and other AI leaders) are helping to create responsible AI systems that are fair, reliable, safe, private, secure, and inclusive. There is still a long way to go, but these capabilities do not completely indemnify users of AI. They still have a responsibility to set guardrails in their own businesses about the use and opportunities for AI.
- AI and hybrid work are often discussed as different trends in the market, with different solution sets. But in reality, they are deeply linked. AI can help enhance and improve hybrid work in businesses – and is a great opportunity to demonstrate the value of AI and tools such as Copilot.
Ecosystm Question: What should Microsoft focus on?
Tim Sheedy. Microsoft faces a challenge in educating the market about adopting AI, especially Copilot. They need to educate business, IT, and AI users on embracing AI effectively. Additionally, they must educate existing partners and find new AI partners to drive change in their client base. Success in the race for knowledge workers requires not only being first but also helping users maximise solutions. Customers have limited visibility of Copilot’s capabilities, today. Improving customer upskilling and enhancing tools to prompt users to leverage capabilities will contribute to Microsoft’s (or their competitors’) success in dominating the AI tool market.
Peter Carr. Grassroots businesses form the economic foundation of the Asia Pacific economies. Typically, these businesses do not engage with global SIs (GSIs), which drive Microsoft’s new service offerings. This leads to an adoption gap in the sector that could benefit most from operational efficiencies. To bridge this gap, Microsoft must empower non-GSI partners and managed service providers (MSPs) at the local and regional levels. They won’t achieve their goal of democratising AI, unless they do. Microsoft has the potential to advance AI technology while ensuring fair and widespread adoption.

Wondering how India’s tech leaders are navigating the dynamic world of artificial intelligence (AI)? The latest findings from the Big5 CIO Priorities India ’24 Study offer a glimpse into the strategies employed by these industry giants.
According to the study, there’s a noticeable surge in investments in AI, highlighting a strategic shift towards embracing cutting-edge technologies. From streamlining operations to enhancing customer experiences, AI is being harnessed across various sectors to drive innovation and efficiency.
Tech teams across enterprises are not just dabbling but actively embracing AI, integrating it into their core operations. This proactive approach underscores a recognition of AI’s transformative potential and its role in shaping the future of business.


Where is cloud adoption headed in India? Dive into the insights from the Big5 CIO Priorities India ’24 Study to uncover trends in hybrid and public cloud adoption, and other crucial aspects of organisations’ cloud strategies.
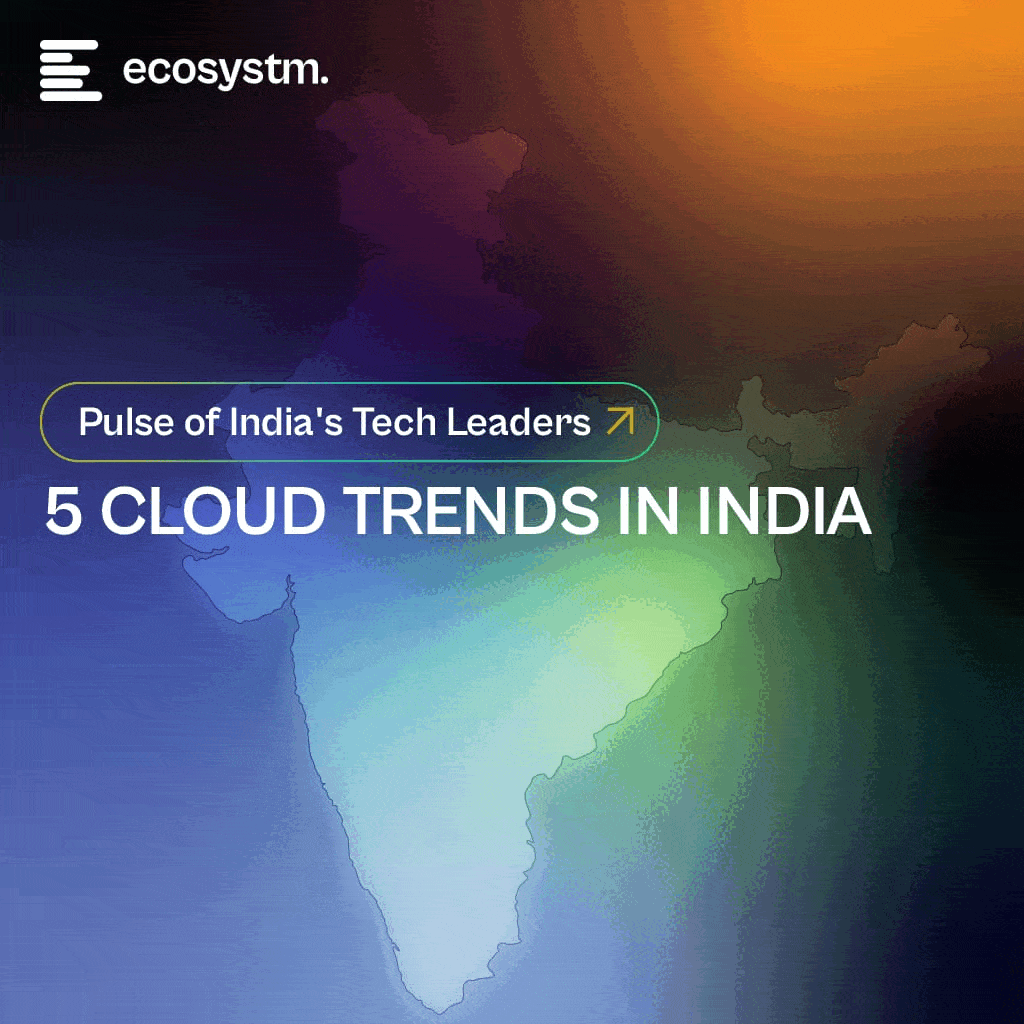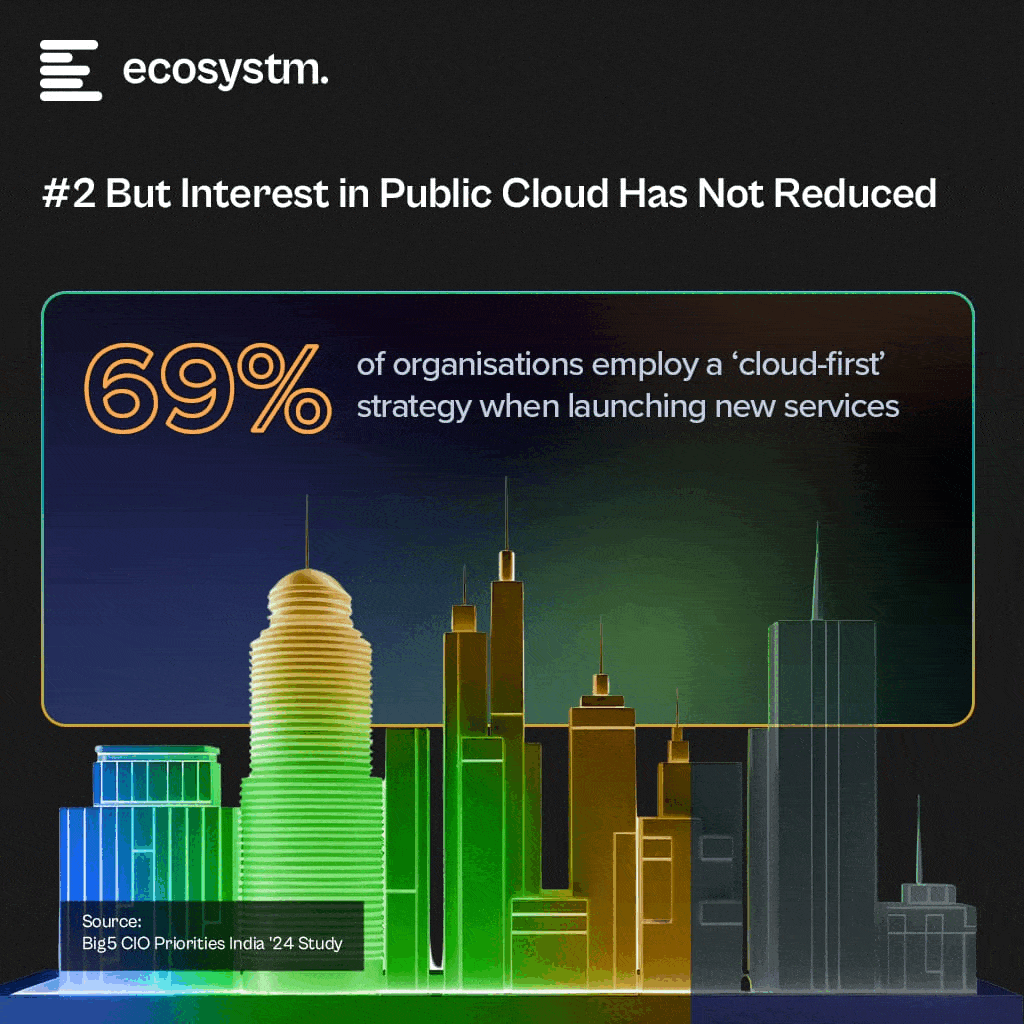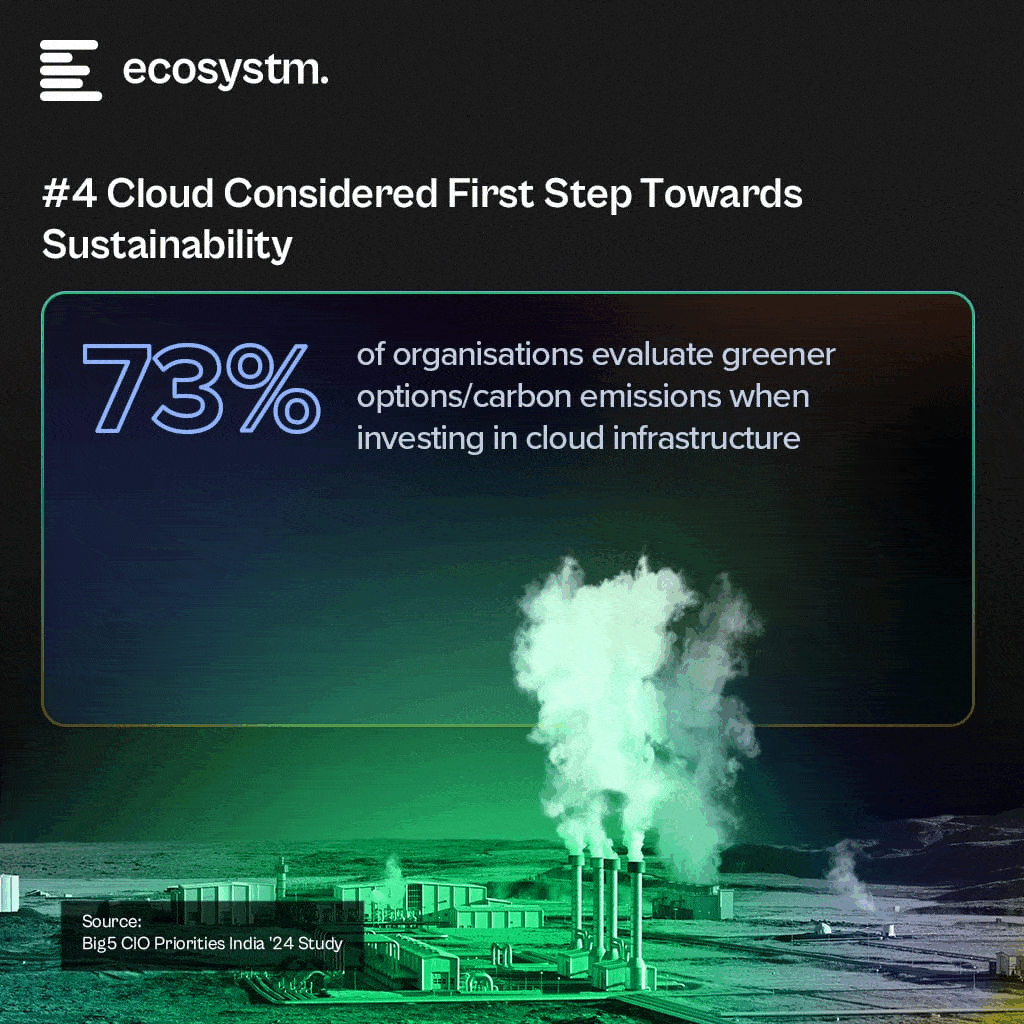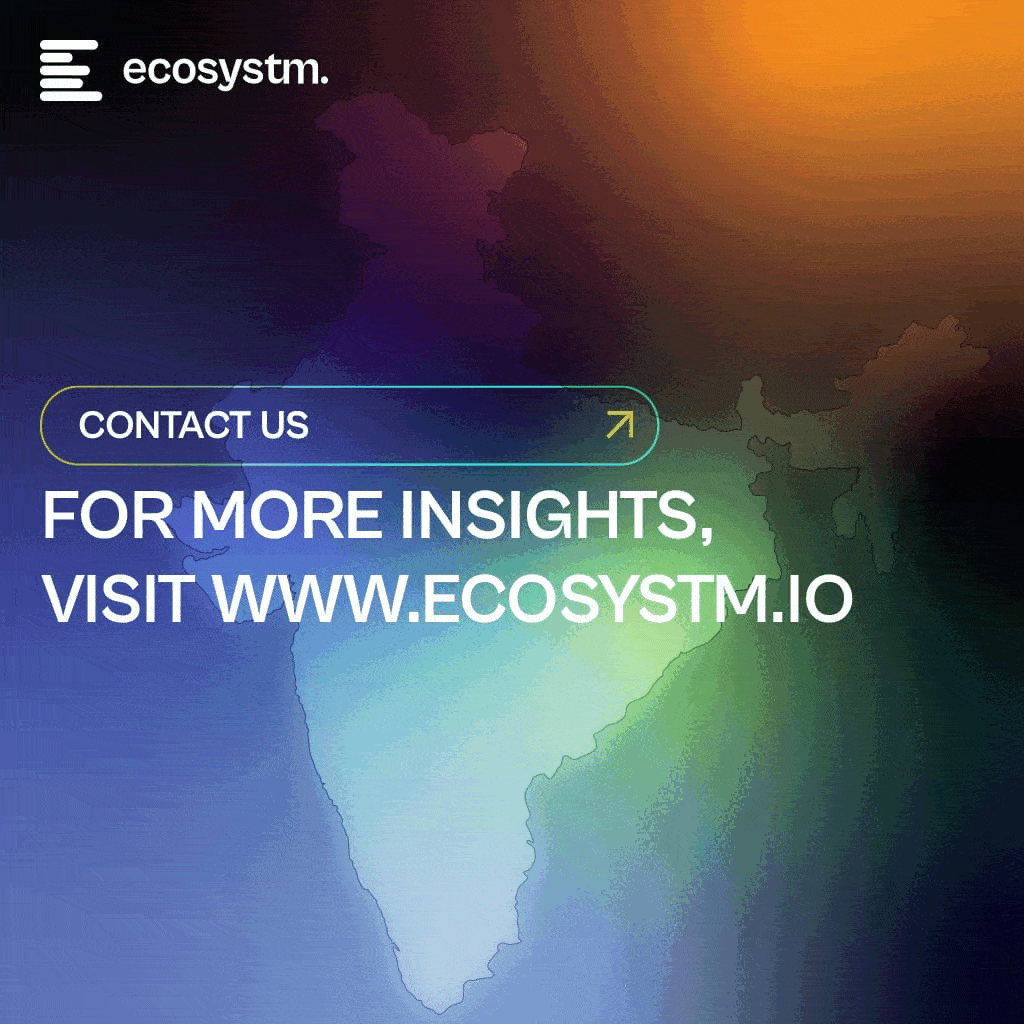
According to the study, a significant 80% of organisations have embraced a hybrid, multi-cloud strategy, showcasing a strategic blend of private and public cloud services. Despite this, there remains a robust interest in public cloud solutions, highlighting the appeal of their scalability and flexibility.
Additionally, the study reveals that 69% of organisations prefer a cloud-first approach when introducing new services. This shift signifies the growing recognition of cloud computing as a foundational pillar for innovation and growth among Indian businesses.
As India’s digital landscape continues to evolve, understanding these cloud adoption trends becomes paramount for organisations looking to stay competitive and resilient in an increasingly digital-first world.

2024 has started cautiously for organisations, with many choosing to continue with tech projects that have already initiated, while waiting for clearer market conditions before starting newer transformation projects. This means that tech providers must continue to refine their market messaging and enhance their service/product offerings to strengthen their market presence in the latter part of the year. Ecosystm analysts present five key considerations for tech providers as they navigate evolving market and customer trends, this year.
Navigating Market Dynamics

Continuing Economic Uncertainties. Organisations will focus on ongoing projects and consider expanding initiatives in the latter part of the year. This means that tech providers should maintain visibility and trust with existing clients. They also need to help their customers meet multiple KPIs.
Popularity of Generative AI. For organisations, this will be the time to go beyond the novelty factor and assess practical business outcomes, allied costs, and change management. Tech providers need to include ROI discussions for short-term and mid-term perspectives as organisations move beyond pilots.
Infrastructure Market Disruption. Tech leaders will keep an eye out for advancements and disruptions in the market (likely to originate from the semiconductor sector). The disruptions might require tech vendors to re-assess the infrastructure partner ecosystem.
Need for New Tech Skills. Tech leaders will evaluate Generative AI’s impact on AIOps and IT Architecture; invest in upskilling for talent retention. Tech providers must prioritise creating user-friendly experiences to make technology accessible to business users. Training and partner enablement will also need a higher focus.
Increased Focus on Governance. Tech leaders will consult tech vendors on how to implement safeguards for data usage, sharing, and cybersecurity. This opens up opportunities in offering governance-related services.
5 Key Considerations for Tech Vendors
#1 Get Ready for the Year of the AI Startup

While many AI companies have been around for years, this will be the year that many of them make a significant play into enterprises in Asia Pacific. This comes at a time when many organisations are attempting to reduce tech debt and simplify their tech architecture.
For these AI startups to succeed, they will need to create watertight business cases, and do a lot of the hard work in pre-integrating their solutions with the larger platforms to reduce the time to value and simplify the systems integration work.
To respond to these emerging threats, existing tech providers will need to not only accelerate their own use of AI in their platforms, but also ramp up the education and promotion of these capabilities.
#2 Lead With Data, Not AI Capabilities

Organisations recognise the need for AI to enhance their workforce, improve customer experience, and automate processes. However, the initial challenge lies in improving data quality, as trust in early AI models hinges on high-quality training data for long-term success.
Tech vendors that can help with data source discovery, metadata analysis, and seamless data pipeline creation will emerge as trusted AI partners. Transformation tools that automate deduplication and quality assurance tasks empower data scientists to focus on high-value work. Automation models like Segment Anything enhance unstructured data labeling, particularly for images. Finally synthetic data will gain importance as quality sources become scarce.
Tech vendors will be tempted to capitalise on the Generative AI hype but for sake of positive early experiences, they should begin with data quality.
#3 Prepare Thoroughly for AI-driven Business Demand

Besides pureplay AI opportunities, AI will drive a renewed and increased interest in data and data management. Tech and service providers can capitalise on this by understanding the larger picture around their clients’ data maturity and governance. Initial conversations around AI can be door openers to bigger, transformational engagements.
Tech vendors should avoid the pitfall of downplaying AI risks. Instead, they should make all efforts to own and drive the conversation with their clients. They need to be forthcoming about their in-house responsible AI guidelines and understand what is happening in AI legislation world-wide (hint: a lot!)
Tech providers must establish strong client partnerships for AI initiatives to succeed. They must address risk and benefit equally to reap the benefits of larger AI-driven transformation engagements.
#4 Converge Network & Security Capabilities

Networking and security vendors will need to develop converged offerings as these two technologies increasingly overlap in the hybrid working era. Organisations are now entering a new phase of maturity as they evolve their remote working policies and invest in tools to regain control. They will require simplified management, increased visibility, and to provide a consistent user experience, wherever employees are located.
There has already been a widespread adoption of SD-WAN and now organisations are starting to explore next generation SSE technologies. Procuring these capabilities from a single provider will help to remove complexity from networks as the number of endpoints continue to grow.
Tech providers should take a land and expand approach, getting a foothold with SASE modules that offer rapid ROI. They should focus on SWG and ZTNA deals with an eye to expanding in CASB and FWaaS, as customers gain experience.
#5 Double Down on Your Partner Ecosystem

The IT services market, particularly in Asia Pacific, is poised for significant growth. Factors, including the imperative to cut IT operational costs, the growing complexity of cloud migrations and transformations, change management for Generative AI capabilities, and rising security and data governance needs, will drive increased spending on IT services.
Tech services providers – consultants, SIs, managed services providers, and VARs – will help drive organisations’ tech spend and strategy. This is a good time to review partners, evaluating whether they can take the business forward, or whether there is a need to expand or change the partner mix.
Partner reviews should start with an evaluation of processes and incentives to ensure they foster desired behaviour from customers and partners. Tech vendors should develop a 21st century partner program to improve chances of success.

Chris White, VP Marketing and Communities at Ecosystm, engages in an insightful conversation with Achim Granzen, Principal Advisor at Ecosystm, as they discuss the potential developments in the AI landscape for 2024 and beyond.
Achim highlights the regulatory landscape, ethical use, and business adoption of AI as well as the real-world applications of Generative AI.
Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 14:07 — 4.8MB)
Subscribe Spotify | Amazon Music | JioSaavn | Podchaser | RSS | More
The Big5 CIO Priorities India ’24 Study reveals the pulse of India’s top technology leaders, offering insights into the country’s technology roadmap.
The study reveals that while a substantial 86% of organisations plan to augment their investments in cybersecurity in 2024, a comparatively modest 30% will prioritise SecOps and security analytics.


2024 will be another crucial year for tech leaders – through the continuing economic uncertainties, they will have to embrace transformative technologies and keep an eye on market disruptors such as infrastructure providers and AI startups. Ecosystm analysts outline the key considerations for leaders shaping their organisations’ tech landscape in 2024.
Navigating Market Dynamics

Continuing Economic Uncertainties. Organisations will focus on ongoing projects and consider expanding initiatives in the latter part of the year.
Popularity of Generative AI. This will be the time to go beyond the novelty factor and assess practical business outcomes, allied costs, and change management.
Infrastructure Market Disruption. Keeping an eye out for advancements and disruptions in the market (likely to originate from the semiconductor sector) will define vendor conversations.
Need for New Tech Skills. Generative AI will influence multiple tech roles, including AIOps and IT Architecture. Retaining talent will depend on upskilling and reskilling.
Increased Focus on Governance. Tech vendors are guide tech leaders on how to implement safeguards for data usage, sharing, and cybersecurity.
5 Key Considerations for Tech Leaders
#1 Accelerate and Adapt: Streamline IT with a DevOps Culture
Over the next 12-18 months, advancements in AI, machine learning, automation, and cloud-native technologies will be vital in leveraging scalability and efficiency. Modernisation is imperative to boost responsiveness, efficiency, and competitiveness in today’s dynamic business landscape.
The continued pace of disruption demands that organisations modernise their applications portfolios with agility and purpose. Legacy systems constrained by technical debt drag down velocity, impairing the ability to deliver new innovative offerings and experiences customers have grown to expect.
Prioritising modernisation initiatives that align with key value drivers is critical. Technology leaders should empower development teams to move beyond outdated constraints and swiftly deploy enhanced applications, microservices, and platforms.

#2 Empowering Tomorrow: Spring Clean Your Tech Legacy for New Leaders
Modernising legacy systems is a strategic and inter-generational shift that goes beyond simple technical upgrades. It requires transformation through the process of decomposing and replatforming systems – developed by previous generations – into contemporary services and signifies a fundamental realignment of your business with the evolving digital landscape of the 21st century.
The essence of this modernisation effort is multifaceted. It not only facilitates the integration of advanced technologies but also significantly enhances business agility and drives innovation. It is an approach that prepares your organisation for impending skill gaps, particularly as the older workforce begins to retire over the next decade. Additionally, it provides a valuable opportunity to thoroughly document, reevaluate, and improve business processes. This ensures that operations are not only efficient but also aligned with current market demands, contemporary regulatory standards, and the changing expectations of customers.

#3 Employee Retention: Consider the Strategic Role of Skills Acquisition
The agile, resilient organisation needs to be able to respond at pace to any threat or opportunity it faces. Some of this ability to respond will be related to technology platforms and architectures, but it will be the skills of employees that will dictate the pace of reform. While employee attrition rates will continue to decline in 2024 – but it will be driven by skills acquisition, not location of work.
Organisations who offer ongoing staff training – recognising that their business needs new skills to become a 21st century organisation – are the ones who will see increasing rates of employee retention and happier employees. They will also be the ones who offer better customer experiences, driven by motivated employees who are committed to their personal success, knowing that the organisation values their performance and achievements.

#4 Next-Gen IT Operations: Explore Gen AI for Incident Avoidance and Predictive Analysis
The integration of Generative AI in IT Operations signifies a transformative shift from the automation of basic tasks, to advanced functions like incident avoidance and predictive analysis. Initially automating routine tasks, Generative AI has evolved to proactively avoiding incidents by analysing historical data and current metrics. This shift from proactive to reactive management will be crucial for maintaining uninterrupted business operations and enhancing application reliability.
Predictive analysis provides insight into system performance and user interaction patterns, empowering IT teams to optimise applications pre-emptively, enhancing efficiency and user experience. This also helps organisations meet sustainability goals through accurate capacity planning and resource allocation, also ensuring effective scaling of business applications to meet demands.

#5 Expanding Possibilities: Incorporate AI Startups into Your Portfolio
While many of the AI startups have been around for over five years, this will be the year they come into your consciousness and emerge as legitimate solutions providers to your organisation. And it comes at a difficult time for you!
Most tech leaders are looking to reduce technical debt – looking to consolidate their suppliers and simplify their tech architecture. Considering AI startups will mean a shift back to more rather than fewer tech suppliers; a different sourcing strategy; more focus on integration and ongoing management of the solutions; and a more complex tech architecture.
To meet business requirements will mean that business cases will need to be watertight – often the value will need to be delivered before a contract has been signed.


Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Juniper Networks for USD 40 per share, totaling an equity value of about USD 14 Billion. This strategic move is aimed to enhance HPE’s portfolio by focusing on higher-growth solutions and reinforcing their high-margin networking business. HPE expects to double their networking business, positioning the combined entity as a leader in networking solutions. With the growing demand for secure, unified technology driven by AI and hybrid cloud trends, HPE aims to offer comprehensive, disruptive solutions that connect, protect, and analyse data from edge to cloud.
This would also be the organisation’s largest deal since becoming an independent company in 2015. The acquisition is expected to be completed by late 2024 or early 2025.
Ecosystm analysts Darian Bird and Richard Wilkins provide their insights on the HPE acquisition and its implications for the tech market.

Converging Networking and Security
One of the big drawcards for HPE is Juniper’s Mist AI. The networking vendors have been racing to catch up – both in capabilities and in marketing. The acquisition though will give HPE a leadership position in network visibility and manageability. With GreenLake and soon Mist AI, HPE will have a solid AIOps story across the entire infrastructure.
HPE has been working steadily towards becoming a player in the converged networking-security space. They integrated Silver Peak well to make a name for themselves in SD-WAN and last year acquiring Axis Security gave them the Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Secure Web Gateway (SWG), and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) modules in the Secure Service Edge (SSE) stack. Bringing all of this to the market with Juniper’s networking prowess positions HPE as a formidable player, especially as the Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) market gains momentum.
As the market shifts towards converged SASE, there will only be more interest in the SD-WAN and SSE vendors. In just over one year, Cato Networks and Netskope have raised funds, Check Point acquired Perimeter 81, and Versa Networks has made noises about an IPO. The networking and security players are all figuring out how they can deliver a single-vendor SASE.
Although HPE’s strategic initiatives signal a robust market position, potential challenges arise from the overlap between Aruba and Juniper. However, the distinct focus on the edge and data center, respectively, may help alleviate these concerns. The acquisition also marks HPE’s foray into the telecom space, leveraging its earlier acquisition of Athonet and establishing a significant presence among service providers. This expansion enhances HPE’s overall market influence, posing a challenge to the long-standing dominance of Cisco.

The strategic acquisition of Juniper Networks by HPE can make a transformative leap in AIOps and Software-Defined Networking (SDN). There is a potential for this to establish a new benchmark in IT management.
AI in IT Operations Transformation
The integration of Mist’s AI-driven wireless solutions and HPE’s SDN is a paradigm shift in IT operations management and will help organisations transition from a reactive to a predictive and proactive model. Mist’s predictive analytics, coupled with HPE’s SDN capabilities, empower networks to dynamically adjust to user demands and environmental changes, ensuring optimal performance and user experience. Marvis, Mist’s Virtual Network Assistant (VNA), adds conversational troubleshooting capabilities, enhancing HPE’s network solutions. The integration envisions an IT ecosystem where Juniper’s AI augments HPE’s InfoSight, providing deeper insights into network behaviour, preemptive security measures, and more autonomous IT operations.
Transforming Cloud and Edge Computing
The incorporation of Juniper’s AI into HPE’s cloud and edge computing solutions promises a significant improvement in data processing and management. AI-driven load balancing and resource allocation mechanisms will significantly enhance multi-cloud environment efficiency, ensuring robust and seamless cloud services, particularly vital in IoT applications where real-time data processing is critical. This integration not only optimises cloud operations but also has the potential to align with HPE’s commitment to sustainability, showcasing how AI advancements can contribute to energy conservation.
In summary, HPE’s acquisition of Juniper Networks, and specifically the integration of the Mist AI platform, is a pivotal step towards an AI-driven, efficient, and predictive IT infrastructure. This can redefine the standards in AIOps and SDN, creating a future where IT systems are not only reactive but also intuitively adaptive to the evolving demands of the digital landscape.

Singapore’s FinTech landscape is on an upward trajectory, with USD 4.1 billion in investments in 2022 and 1,500 FinTechs currently calling Singapore home. Within three years, the goal is USD 10 billion investments and 3,000 FinTechs.
At Elevandi Insights in November last year, Ecosystm CEO Ullrich Loeffler had the pleasure of moderating a roundtable hosted by HSBC that brought together regulators, banks, investors, incubators, FinTechs, and digital economy players to discuss the strategies that can grow and strengthen Singapore’s FinTech ecosystem.
We are pleased to make available to you a Summary Report outlining the key findings; and an action plan that participants felt will accomplish the objective of doubling the number of FinTech startups in the next three years.
This report includes:
• The success factors of an Innovation Ecosystem
• Opportunities for enhancement
• Maximising support from financial institutions
• An action plan for banks to shape FinTech success stories
Our thanks to the roundtable participants for contributing to this discussion, and to HSBC for driving this crucial industry initiative.
Download Summary Report – The Role of the Innovation Ecosystem: Putting Singapore at the Centre of the Global Digital Economy